简洁:由于 C++ 语言没有自动内存回收机制,程序员每次 new 出来的内存都要手动 delete。很容易造成内存泄漏或者多次delete崩溃。基于此问题,智能指针应运而生。
本文先来剖析标准库STL的智能指针auto_ptr.
用法如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
class TestBody
{
public:
TestBody(int param = 0):m_num(param)
{
m_info = "INFO";
cout<<"construct TestBody"<<endl;
}
~TestBody()
{
cout<<"destory TestBody"<<endl;
}
void SetInfo(string info)
{
m_info = info;
}
void PrintInfo()
{
cout<<"info:"<<m_info<<endl;
}
private:
int m_num;
string m_info;
};
void TestAutoPtr1()
{
auto_ptr<TestBody> smartPoint1(new TestBody(1));
if(smartPoint1.get())
{
smartPoint1->PrintInfo();
smartPoint1->SetInfo("TestAutoPtr1");
smartPoint1->PrintInfo();
}
}
int main(void)
{
TestAutoPtr1();
return 0;
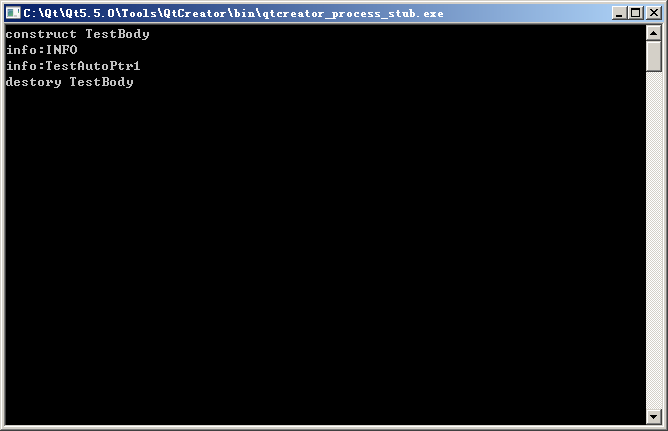
}结果如图:
下面例子:
void TestAutoPtr2()
{
auto_ptr<TestBody> smartPoint1(new TestBody(1));
if(smartPoint1.get())
{
smartPoint1->PrintInfo();
auto_ptr<TestBody> smartPoint2 = smartPoint1;
smartPoint2->PrintInfo();
smartPoint1->PrintInfo();//直接崩溃
}
}跟进源码看,是赋值操作法的问题:auto_ptr smartPoint2 = smartPoint1;。smartPoint2 剥夺了 smartPoint1的控制权;
template<typename _Tp1>auto_ptr&
operator=(auto_ptr<_Tp1>& __a) throw()
{
reset(__a.release());
return *this;
}
void reset(element_type* __p = 0) throw()
{
if (__p != _M_ptr)
{
delete _M_ptr;
_M_ptr = __p;
}
}
element_type* release() throw()
{
element_type* __tmp = _M_ptr;
_M_ptr = 0;
return __tmp;
}





















 244
244

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








