The Difference Between Encoding, Encryption, and Hashing
Encoding is often confused with encryption. They are not the same. But before I go into the differences, I'll first mention the similarities:
- Both transform data into another format.
- Both are reversible (unlike hashing).
And now the differences:
Encoding

Encoding transforms data into another format using a schemethat is publicly available so that it can easily be reversed. It does not require a key as the only thing required to decode it is the algorithm that was used to encode it.
Examples: ASCII, Unicode, URL Encoding, Base64
Encryption

The purpose of encryption is to transform data in order to keep it secret from others, e.g. sending someone a secret letter that only they should be able to read, or securely sending a password over the Internet. Rather than focusing on usability, the goal is to ensure the data cannot be consumed by anyone other than the intended recipient(s).
Encryption transforms data into another format in such a way that only specific individual(s) can reverse the transformation. It uses a key, which is kept secret, in conjunction with the plaintext and the algorithm, in order to perform the encryption operation. As such, the ciphertext, algorithm, and key are all required to return to the plaintext.
Hashing
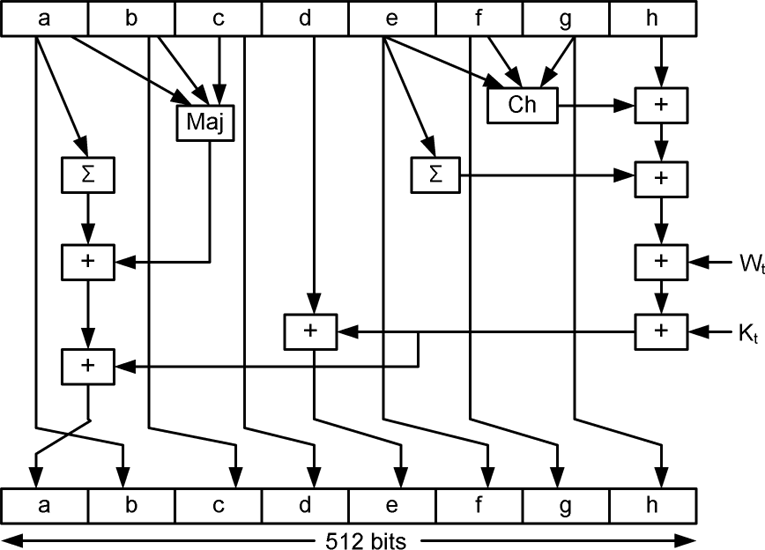
Hashing is often confused with encoding and encryption but it's quite different than either. In security, the purpose of hashing is to take arbitrary input and produce a fixed-length string that has the following attributes:
- The same input will always produce the same output.
- Multiple disparate inputs should not produce the same output.
- It should not be possible to go from the output to the input.
- Any modification of a given input should result in drastic change to the hash.
Hashing is used in conjunction with authentication to produce strong evidence that a given message has not been modified. This is accomplished by taking a given input, hashing it, and then encrypting the sent hash with the recipient's public key.
When the recipient opens the message with their private key they then hash the message themselves and compare it to the hash that was given encrypted by the sender. If they match it is an unmodified message.
Examples: SHA-3, MD5 (Now obsolete), etc.
Summary
- Encoding is for maintaining data usability and can be reversed by employing the same algorithm that encoded the content, i.e. no key is used.
- Encryption is for maintaining data confidentiality and requires the use of a key (kept secret) in order to return to plaintext.
- Hashing is for validating the integrity of content by detecting all modification thereof via obvious changes to the hash output.
Recommended
References
[ Encryption | wikipedia.org ]
[ Encoding | wikipedia.org]
[ Hashing | wikipedia.org]






















 4746
4746

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








