简单排序
- 简单排序
- 习题1 选择排序
- 习题2 冒泡排序
- 习题3 插入排序
- 习题4 不要用任何比较判断,返回两个数中较大的数
- 习题5 归并排序 递归实现 非递归实现
- 习题6 随机快速排序 递归实现 非递归实现
- 习题7 在一个数组中,一个数左边比它小的数的总和,叫数的小和,所有数的小和累加起来,叫数组小和。求数组小和。
- 习题8 在一个数组中,任何一个前面的数a,和任何一个后面的数b,如果(a,b)是降序的,就称为逆序对,返回数组中所有的逆序对
- 习题9 在一个数组中,对于每个数num,求有多少个后面的数 * 2 依然<num,求总个数
- 习题10 给定一个数组arr,两个整数lower和upper,返回arr中有多少个子数组的累加和在[lower,upper]范围上
- 习题11 快排1.0 给定一个数组arr,数组最右边的数的值为num,请把小于等于num放在数组的左边,大于num的数放在数组的右边,以及排序
- 习题12 快速排序2.0 给定一个数组arr,数组最右边的数的值为num,请把小于num的数放左边,等于num的数放中间,大于num的数放在数组的右边,以及排序
- 习题13 快速排序3.0(随机快排+荷兰国旗技巧优化)
- 习题14 双向链表的随机快速排序
简单排序
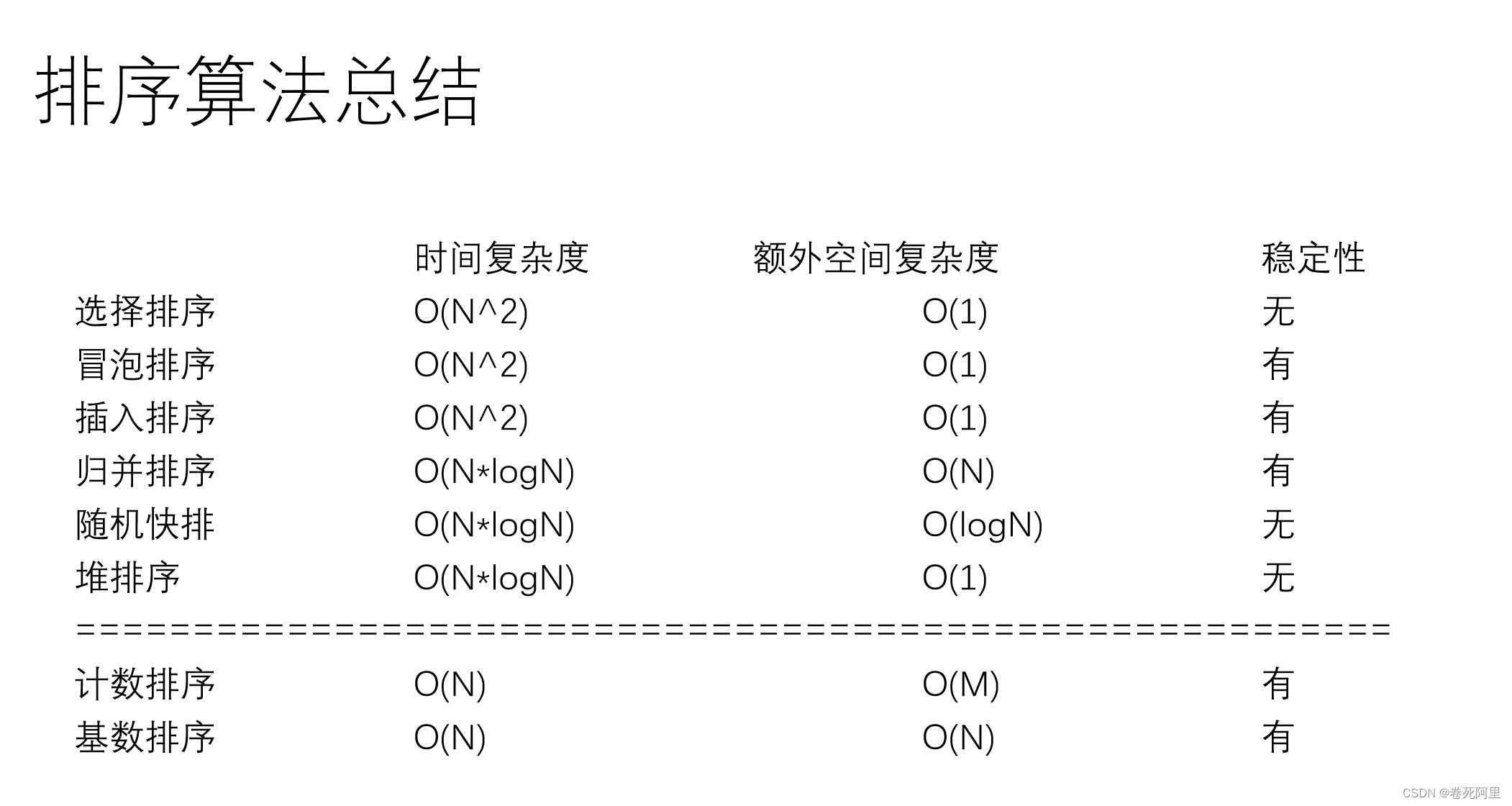
1)不基于比较的排序,对样本数据有严格要求,不易改写
2)基于比较的排序,只要规定好两个样本怎么比大小就可以直接复用
3)基于比较的排序,时间复杂度的极限是O(NlogN)
4)时间复杂度O(NlogN)、额外空间复杂度低于O(N)、且稳定的基于比较的排序是不存在的。
5)为了绝对的速度选快排、为了省空间选堆排、为了稳定性选归并
习题1 选择排序
public static void f1(int[] array) {
if (array == null || array.length < 2) {
return;
}
int size = array.length;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
int minIndex = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < size; j++) {
minIndex = array[j] < array[minIndex] ? j : minIndex;
}
swap(array, i, minIndex);
}
}
public static void swap(int[] array, int i, int j) {
int tmp = array[j];
array[j] = array[i];
array[i] = tmp;
}
习题2 冒泡排序
public static void f1(int[] array){
if(array == null || array.length<2){
return;
}
int N = array.length;
for(int i = 0 ; i < N; N--){
for(int j = i+1; j<N; j++){
if(array[j]< array[j-1]){
swap(array, j, j-1);
}
}
}
}
private static void swap(int[] array, int i , int j){
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = temp;
}
习题3 插入排序
private static void f1(int[] array) {
if (array == null || array.length < 2) {
return;
}
int N = array.length;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = i; j > 0 && array[j] < array[j - 1]; j--) {
swap(array, j, j - 1);
}
}
}
private static void swap(int[] array, int i, int j) {
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = temp;
}
习题4 不要用任何比较判断,返回两个数中较大的数
public static int flip(int n) {
return n ^ 1;
}
public static int sign(int n) {
return flip((n >> 31) & 1);
}
public static int getMax1(int a, int b) {
int c = a - b;
int scA = sign(c);
int scB = flip(scA);
return a * scA + b * scB;
}
public static int getMax2(int a, int b) {
int c = a - b;
int sa = sign(a);
int sb = sign(b);
int sc = sign(c);
int difSab = sa ^ sb;
int sameSab = flip(difSab);
int returnA = difSab * sa + sameSab * sc;
int returnB = flip(returnA);
return a * returnA + b * returnB;
}
习题5 归并排序 递归实现 非递归实现
// 递归方法实现
public static void mergeSort1(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 2) {
return;
}
process(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
}
// arr[L...R]范围上,请让这个范围上的数,有序!
public static void process(int[] arr, int L, int R) {
if (L == R) {
return;
}
// int mid = (L + R) / 2
int mid = L + ((R - L) >> 1);
process(arr, L, mid);
process(arr, mid + 1, R);
merge(arr, L, mid, R);
}
public static void merge(int[] arr, int L, int M, int R) {
int[] help = new int[R - L + 1];
int i = 0;
int p1 = L;
int p2 = M + 1;
while (p1 <= M && p2 <= R) {
help[i++] = arr[p1] <= arr[p2] ? arr[p1++] : arr[p2++];
}
// 要么p1越界,要么p2越界
// 不可能出现:共同越界
while (p1 <= M) {
help[i++] = arr[p1++];
}
while (p2 <= R) {
help[i++] = arr[p2++];
}
for (i = 0; i < help.length; i++) {
arr[L + i] = help[i];
}
}
public static void mergeSort2(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 2) {
return;
}
int step = 1;
int N = arr.length;
while (step < N) {
int L = 0;
while (L < N) {
int M = 0;
if (N - L >= step) {
M = L + step - 1;
} else {
M = N - 1;
}
if (M == N - 1) {
break;
}
int R = 0;
if (N - 1 - M >= step) {
R = M + step;
} else {
R = N - 1;
}
merge(arr, L, M, R);
if (R == N - 1) {
break;
} else {
L = R + 1;
}
}
if (step > N / 2) {
break;
}
step *= 2;
}
}
习题6 随机快速排序 递归实现 非递归实现
public static void splitNum1(int[] arr) {
int lessEqualR = -1;
int index = 0;
int N = arr.length;
while (index < N) {
if (arr[index] <= arr[N - 1]) {
swap(arr, ++lessEqualR, index++);
} else {
index++;
}
}
}
public static void splitNum2(int[] arr) {
int N = arr.length;
int lessR = -1;
int moreL = N - 1;
int index = 0;
// arr[N-1]
while (index < moreL) {
if (arr[index] < arr[N - 1]) {
swap(arr, ++lessR, index++);
} else if (arr[index] > arr[N - 1]) {
swap(arr, --moreL, index);
} else {
index++;
}
}
swap(arr, moreL, N - 1);
}
public static void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j) {
int tmp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = tmp;
}
// arr[L...R]范围上,拿arr[R]做划分值,
// L....R < = >
public static int[] partition(int[] arr, int L, int R) {
int lessR = L - 1;
int moreL = R;
int index = L;
while (index < moreL) {
if (arr[index] < arr[R]) {
swap(arr, ++lessR, index++);
} else if (arr[index] > arr[R]) {
swap(arr, --moreL, index);
} else {
index++;
}
}
swap(arr, moreL, R);
return new int[] { lessR + 1, moreL };
}
public static void quickSort1(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 2) {
return;
}
process(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
}
public static void process(int[] arr, int L, int R) {
if (L >= R) {
return;
}
int[] equalE = partition(arr, L, R);
process(arr, L, equalE[0] - 1);
process(arr, equalE[1] + 1, R);
}
public static class Job {
public int L;
public int R;
public Job(int left, int right) {
L = left;
R = right;
}
}
public static void quickSort2(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 2) {
return;
}
Stack<Job> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(new Job(0, arr.length - 1));
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
Job cur = stack.pop();
int[] equals = partition(arr, cur.L, cur.R);
if (equals[0] > cur.L) { // 有< 区域
stack.push(new Job(cur.L, equals[0] - 1));
}
if (equals[1] < cur.R) { // 有 > 区域
stack.push(new Job(equals[1] + 1, cur.R));
}
}
}
public static int[] netherlandsFlag(int[] arr, int L, int R) {
if (L > R) {
return new int[] { -1, -1 };
}
if (L == R) {
return new int[] { L, R };
}
int less = L - 1;
int more = R;
int index = L;
while (index < more) {
if (arr[index] == arr[R]) {
index++;
} else if (arr[index] < arr[R]) {
swap(arr, index++, ++less);
} else {
swap(arr, index, --more);
}
}
swap(arr, more, R); // <[R] =[R] >[R]
return new int[] { less + 1, more };
}
public static void quickSort3(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 2) {
return;
}
process3(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
}
public static void process3(int[] arr, int L, int R) {
if (L >= R) {
return;
}
swap(arr, L + (int) (Math.random() * (R - L + 1)), R);
int[] equalArea = netherlandsFlag(arr, L, R);
process3(arr, L, equalArea[0] - 1);
process3(arr, equalArea[1] + 1, R);
}
习题7 在一个数组中,一个数左边比它小的数的总和,叫数的小和,所有数的小和累加起来,叫数组小和。求数组小和。
public static int smallSum(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 2) {
return 0;
}
return process(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
}
// arr[L..R]既要排好序,也要求小和返回
// 所有merge时,产生的小和,累加
// 左 排序 merge
// 右 排序 merge
// merge
public static int process(int[] arr, int l, int r) {
if (l == r) {
return 0;
}
// l < r
int mid = l + ((r - l) >> 1);
return
process(arr, l, mid)
+
process(arr, mid + 1, r)
+
merge(arr, l, mid, r);
}
public static int merge(int[] arr, int L, int m, int r) {
int[] help = new int[r - L + 1];
int i = 0;
int p1 = L;
int p2 = m + 1;
int res = 0;
while (p1 <= m && p2 <= r) {
res += arr[p1] < arr[p2] ? (r - p2 + 1) * arr[p1] : 0;
help[i++] = arr[p1] < arr[p2] ? arr[p1++] : arr[p2++];
}
while (p1 <= m) {
help[i++] = arr[p1++];
}
while (p2 <= r) {
help[i++] = arr[p2++];
}
for (i = 0; i < help.length; i++) {
arr[L + i] = help[i];
}
return res;
}
习题8 在一个数组中,任何一个前面的数a,和任何一个后面的数b,如果(a,b)是降序的,就称为逆序对,返回数组中所有的逆序对
public static int reverPairNumber(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 2) {
return 0;
}
return process(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
}
// arr[L..R]既要排好序,也要求逆序对数量返回
// 所有merge时,产生的逆序对数量,累加,返回
// 左 排序 merge并产生逆序对数量
// 右 排序 merge并产生逆序对数量
public static int process(int[] arr, int l, int r) {
if (l == r) {
return 0;
}
// l < r
int mid = l + ((r - l) >> 1);
return process(arr, l, mid) + process(arr, mid + 1, r) + merge(arr, l, mid, r);
}
public static int merge(int[] arr, int L, int m, int r) {
int[] help = new int[r - L + 1];
int i = help.length - 1;
int p1 = m;
int p2 = r;
int res = 0;
while (p1 >= L && p2 > m) {
res += arr[p1] > arr[p2] ? (p2 - m) : 0;
help[i--] = arr[p1] > arr[p2] ? arr[p1--] : arr[p2--];
}
while (p1 >= L) {
help[i--] = arr[p1--];
}
while (p2 > m) {
help[i--] = arr[p2--];
}
for (i = 0; i < help.length; i++) {
arr[L + i] = help[i];
}
return res;
}
习题9 在一个数组中,对于每个数num,求有多少个后面的数 * 2 依然<num,求总个数
public static int reversePairs(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 2) {
return 0;
}
return process(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
}
public static int process(int[] arr, int l, int r) {
if (l == r) {
return 0;
}
// l < r
int mid = l + ((r - l) >> 1);
return process(arr, l, mid) + process(arr, mid + 1, r) + merge(arr, l, mid, r);
}
public static int merge(int[] arr, int L, int m, int r) {
// [L....M] [M+1....R]
int ans = 0;
// 目前囊括进来的数,是从[M+1, windowR)
int windowR = m + 1;
for (int i = L; i <= m; i++) {
while (windowR <= r && (long) arr[i] > (long) arr[windowR] * 2) {
windowR++;
}
ans += windowR - m - 1;
}
int[] help = new int[r - L + 1];
int i = 0;
int p1 = L;
int p2 = m + 1;
while (p1 <= m && p2 <= r) {
help[i++] = arr[p1] <= arr[p2] ? arr[p1++] : arr[p2++];
}
while (p1 <= m) {
help[i++] = arr[p1++];
}
while (p2 <= r) {
help[i++] = arr[p2++];
}
for (i = 0; i < help.length; i++) {
arr[L + i] = help[i];
}
return ans;
}
习题10 给定一个数组arr,两个整数lower和upper,返回arr中有多少个子数组的累加和在[lower,upper]范围上
public static int countRangeSum(int[] nums, int lower, int upper) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
long[] sum = new long[nums.length];
sum[0] = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
sum[i] = sum[i - 1] + nums[i];
}
return process(sum, 0, sum.length - 1, lower, upper);
}
public static int process(long[] sum, int L, int R, int lower, int upper) {
if (L == R) {
return sum[L] >= lower && sum[L] <= upper ? 1 : 0;
}
int M = L + ((R - L) >> 1);
return process(sum, L, M, lower, upper) + process(sum, M + 1, R, lower, upper)
+ merge(sum, L, M, R, lower, upper);
}
public static int merge(long[] arr, int L, int M, int R, int lower, int upper) {
int ans = 0;
int windowL = L;
int windowR = L;
// [windowL, windowR)
for (int i = M + 1; i <= R; i++) {
long min = arr[i] - upper;
long max = arr[i] - lower;
while (windowR <= M && arr[windowR] <= max) {
windowR++;
}
while (windowL <= M && arr[windowL] < min) {
windowL++;
}
ans += windowR - windowL;
}
long[] help = new long[R - L + 1];
int i = 0;
int p1 = L;
int p2 = M + 1;
while (p1 <= M && p2 <= R) {
help[i++] = arr[p1] <= arr[p2] ? arr[p1++] : arr[p2++];
}
while (p1 <= M) {
help[i++] = arr[p1++];
}
while (p2 <= R) {
help[i++] = arr[p2++];
}
for (i = 0; i < help.length; i++) {
arr[L + i] = help[i];
}
return ans;
}
习题11 快排1.0 给定一个数组arr,数组最右边的数的值为num,请把小于等于num放在数组的左边,大于num的数放在数组的右边,以及排序
public static void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j) {
int tmp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = tmp;
}
// arr[L..R]上,以arr[R]位置的数做划分值
// <= X > X
// <= X X
public static int partition(int[] arr, int L, int R) {
if (L > R) {
return -1;
}
if (L == R) {
return L;
}
int lessEqual = L - 1;
int index = L;
while (index < R) {
if (arr[index] <= arr[R]) {
swap(arr, index, ++lessEqual);
}
index++;
}
swap(arr, ++lessEqual, R);
return lessEqual;
}
public static void quickSort1(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 2) {
return;
}
process1(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
}
public static void process1(int[] arr, int L, int R) {
if (L >= R) {
return;
}
// L..R partition arr[R] [ <=arr[R] arr[R] >arr[R] ]
int M = partition(arr, L, R);
process1(arr, L, M - 1);
process1(arr, M + 1, R);
}
public static void quickSort3(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 2) {
return;
}
process3(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
}
public static void process3(int[] arr, int L, int R) {
if (L >= R) {
return;
}
swap(arr, L + (int) (Math.random() * (R - L + 1)), R);
int[] equalArea = netherlandsFlag(arr, L, R);
process3(arr, L, equalArea[0] - 1);
process3(arr, equalArea[1] + 1, R);
}
习题12 快速排序2.0 给定一个数组arr,数组最右边的数的值为num,请把小于num的数放左边,等于num的数放中间,大于num的数放在数组的右边,以及排序
public static void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j) {
int tmp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = tmp;
}
// arr[L...R] 玩荷兰国旗问题的划分,以arr[R]做划分值
// <arr[R] ==arr[R] > arr[R]
public static int[] netherlandsFlag(int[] arr, int L, int R) {
if (L > R) { // L...R L>R
return new int[] { -1, -1 };
}
if (L == R) {
return new int[] { L, R };
}
int less = L - 1; // < 区 右边界
int more = R; // > 区 左边界
int index = L;
while (index < more) { // 当前位置,不能和 >区的左边界撞上
if (arr[index] == arr[R]) {
index++;
} else if (arr[index] < arr[R]) {
// swap(arr, less + 1, index);
// less++;
// index++;
swap(arr, index++, ++less);
} else { // >
swap(arr, index, --more);
}
}
swap(arr, more, R); // <[R] =[R] >[R]
return new int[] { less + 1, more };
}
public static void quickSort2(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 2) {
return;
}
process2(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
}
// arr[L...R] 排有序,快排2.0方式
public static void process2(int[] arr, int L, int R) {
if (L >= R) {
return;
}
// [ equalArea[0] , equalArea[0]]
int[] equalArea = netherlandsFlag(arr, L, R);
process2(arr, L, equalArea[0] - 1);
process2(arr, equalArea[1] + 1, R);
}
习题13 快速排序3.0(随机快排+荷兰国旗技巧优化)
// 荷兰国旗问题
public static int[] netherlandsFlag(int[] arr, int L, int R) {
if (L > R) {
return new int[] { -1, -1 };
}
if (L == R) {
return new int[] { L, R };
}
int less = L - 1;
int more = R;
int index = L;
while (index < more) {
if (arr[index] == arr[R]) {
index++;
} else if (arr[index] < arr[R]) {
swap(arr, index++, ++less);
} else {
swap(arr, index, --more);
}
}
swap(arr, more, R);
return new int[] { less + 1, more };
}
public static void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j) {
int tmp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = tmp;
}
// 快排递归版本
public static void quickSort1(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 2) {
return;
}
process(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
}
public static void process(int[] arr, int L, int R) {
if (L >= R) {
return;
}
swap(arr, L + (int) (Math.random() * (R - L + 1)), R);
int[] equalArea = netherlandsFlag(arr, L, R);
process(arr, L, equalArea[0] - 1);
process(arr, equalArea[1] + 1, R);
}
// 快排非递归版本需要的辅助类
// 要处理的是什么范围上的排序
public static class Op {
public int l;
public int r;
public Op(int left, int right) {
l = left;
r = right;
}
}
// 快排3.0 非递归版本 用栈来执行
public static void quickSort2(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 2) {
return;
}
int N = arr.length;
swap(arr, (int) (Math.random() * N), N - 1);
int[] equalArea = netherlandsFlag(arr, 0, N - 1);
int el = equalArea[0];
int er = equalArea[1];
Stack<Op> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(new Op(0, el - 1));
stack.push(new Op(er + 1, N - 1));
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
Op op = stack.pop(); // op.l ... op.r
if (op.l < op.r) {
swap(arr, op.l + (int) (Math.random() * (op.r - op.l + 1)), op.r);
equalArea = netherlandsFlag(arr, op.l, op.r);
el = equalArea[0];
er = equalArea[1];
stack.push(new Op(op.l, el - 1));
stack.push(new Op(er + 1, op.r));
}
}
}
// 快排3.0 非递归版本 用队列来执行
public static void quickSort3(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 2) {
return;
}
int N = arr.length;
swap(arr, (int) (Math.random() * N), N - 1);
int[] equalArea = netherlandsFlag(arr, 0, N - 1);
int el = equalArea[0];
int er = equalArea[1];
Queue<Op> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(new Op(0, el - 1));
queue.offer(new Op(er + 1, N - 1));
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Op op = queue.poll();
if (op.l < op.r) {
swap(arr, op.l + (int) (Math.random() * (op.r - op.l + 1)), op.r);
equalArea = netherlandsFlag(arr, op.l, op.r);
el = equalArea[0];
er = equalArea[1];
queue.offer(new Op(op.l, el - 1));
queue.offer(new Op(er + 1, op.r));
}
}
}
习题14 双向链表的随机快速排序
public static class Node {
public int value;
public Node last;
public Node next;
public Node(int v) {
value = v;
}
}
public static Node quickSort(Node h) {
if (h == null) {
return null;
}
int N = 0;
Node c = h;
Node e = null;
while (c != null) {
N++;
e = c;
c = c.next;
}
return process(h, e, N).h;
}
public static class HeadTail {
public Node h;
public Node t;
public HeadTail(Node head, Node tail) {
h = head;
t = tail;
}
}
// L...R是一个双向链表的头和尾,
// L的last指针指向null,R的next指针指向null
// 也就是说L的左边没有,R的右边也没节点
// 就是一个正常的双向链表,一共有N个节点
// 将这一段用随机快排的方式排好序
// 返回排好序之后的双向链表的头和尾(HeadTail)
public static HeadTail process(Node L, Node R, int N) {
if (L == null) {
return null;
}
if (L == R) {
return new HeadTail(L, R);
}
// L..R上不只一个节点
// 随机得到一个随机下标
int randomIndex = (int) (Math.random() * N);
// 根据随机下标得到随机节点
Node randomNode = L;
while (randomIndex-- != 0) {
randomNode = randomNode.next;
}
// 把随机节点从原来的环境里分离出来
// 比如 a(L) -> b -> c -> d(R), 如果randomNode = c,那么调整之后
// a(L) -> b -> d(R), c会被挖出来,randomNode = c
if (randomNode == L || randomNode == R) {
if (randomNode == L) {
L = randomNode.next;
L.last = null;
} else {
randomNode.last.next = null;
}
} else { // randomNode一定是中间的节点
randomNode.last.next = randomNode.next;
randomNode.next.last = randomNode.last;
}
randomNode.last = null;
randomNode.next = null;
Info info = partition(L, randomNode);
// <randomNode的部分去排序
HeadTail lht = process(info.lh, info.lt, info.ls);
// >randomNode的部分去排序
HeadTail rht = process(info.rh, info.rt, info.rs);
// 左部分排好序、右部分排好序
// 把它们串在一起
if (lht != null) {
lht.t.next = info.eh;
info.eh.last = lht.t;
}
if (rht != null) {
info.et.next = rht.h;
rht.h.last = info.et;
}
// 返回排好序之后总的头和总的尾
Node h = lht != null ? lht.h : info.eh;
Node t = rht != null ? rht.t : info.et;
return new HeadTail(h, t);
}
public static class Info {
public Node lh;
public Node lt;
public int ls;
public Node rh;
public Node rt;
public int rs;
public Node eh;
public Node et;
public Info(Node lH, Node lT, int lS, Node rH, Node rT, int rS, Node eH, Node eT) {
lh = lH;
lt = lT;
ls = lS;
rh = rH;
rt = rT;
rs = rS;
eh = eH;
et = eT;
}
}
// (L....一直到空),是一个双向链表
// pivot是一个不在(L....一直到空)的独立节点,它作为划分值
// 根据荷兰国旗问题的划分方式,把(L....一直到空)划分成:
// <pivot 、 =pivot 、 >pivot 三个部分,然后把pivot融进=pivot的部分
// 比如 4(L)->6->7->1->5->0->9->null pivot=5(这个5和链表中的5,是不同的节点)
// 调整完成后:
// 4->1->0 小于的部分
// 5->5 等于的部分
// 6->7->9 大于的部分
// 三个部分是断开的
// 然后返回Info:
// 小于部分的头、尾、节点个数 : lh,lt,ls
// 大于部分的头、尾、节点个数 : rh,rt,rs
// 等于部分的头、尾 : eh,et
public static Info partition(Node L, Node pivot) {
Node lh = null;
Node lt = null;
int ls = 0;
Node rh = null;
Node rt = null;
int rs = 0;
Node eh = pivot;
Node et = pivot;
Node tmp = null;
while (L != null) {
tmp = L.next;
L.next = null;
L.last = null;
if (L.value < pivot.value) {
ls++;
if (lh == null) {
lh = L;
lt = L;
} else {
lt.next = L;
L.last = lt;
lt = L;
}
} else if (L.value > pivot.value) {
rs++;
if (rh == null) {
rh = L;
rt = L;
} else {
rt.next = L;
L.last = rt;
rt = L;
}
} else {
et.next = L;
L.last = et;
et = L;
}
L = tmp;
}
return new Info(lh, lt, ls, rh, rt, rs, eh, et);
}





















 135
135











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








