通过start()调用线程
public class Solution extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("i am thread");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution thred = new Solution();
//thred.run();
thred.start();
}
}
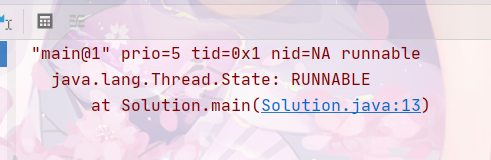
我们通过打断点的方式,借助idea的get thread dump工具进行查看thred.start();调用栈

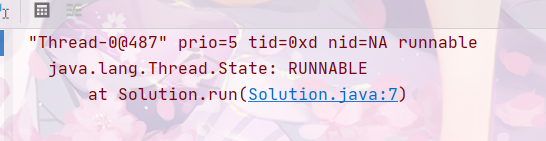
查看thred.run();调用栈


通过比较,我们可以很清楚的看出,run方法仅仅只是方法调用,程序仍然是main线程,start才会开启一个线程。
线程池
线程池的目的是为了复用
newCachedThreadPool、newFixedThreadPool、newSingleThreadExecutor三种线程池进行比较
我们通过下面的代码进行查看
public class Solution{
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService1= Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
ExecutorService executorService2=Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
ExecutorService executorService3=Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
for (int i=1;i<=100;i++){
executorService1.execute(new MyTask(i));
}
}
}
class MyTask implements Runnable{
int i=0;
public MyTask(int i){
this.i=i;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"--"+i);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
运行结果:
newCachedThreadPool:
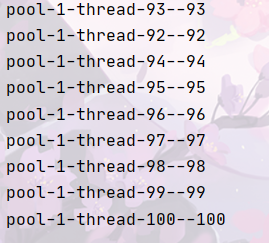
newFixedThreadPool:
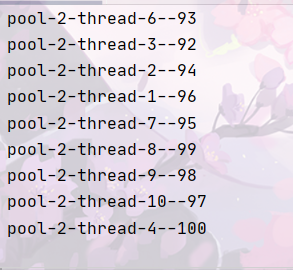
newSingleThreadExecutor:
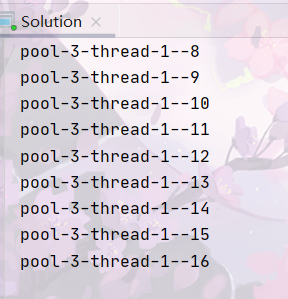
如上代码运行结果时间上newSingleThreadExecutor>newFixedThreadPool>newCachedThreadPool
newCachedThreadPool的运行结果最快。
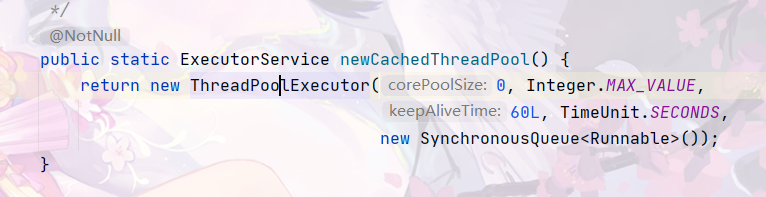
newCachedThreadPool底层代码查看


newFixedThreadPool底层代码查看
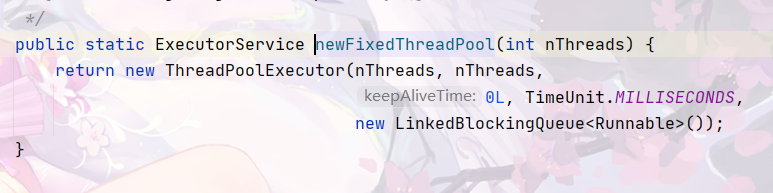
非核心线程数=maximumPoolSize-corePoolSize

newSingleThreadExecutor底层代码查看



问题
1、newCachedThreadPool可能会让CPU达到100%
2、newFixedThreadPool可能导致内存溢出
等待队列中任务过多
3、newSingleThreadExecutor可能导致内存溢出
等待队列中任务过多
自定义线程池
发现三种线程池都会返回ThreadPoolExecutor类,那么我们可以使用自定义线程池
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor=new ThreadPoolExecutor(10,20,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(10));
for (int i=1;i<=100;i++){
threadPoolExecutor.execute(new MyTask(i));
}
但是会发生如下错误

在第31个任务的时候,因为核心线程,非核心线程,等待队列都达到饱和,所以会执行拒绝策略

问题
观察输出结果

21到30的任务比11到20的任务先输出
原因:提交优先级:核心线程->等待队列->非核心线程
执行优先级:核心线程->非核心线程->等待队列
提交优先级和执行优先级
for (int i=1;i<=100;i++){
threadPoolExecutor.execute(new MyTask(i));
}
查看execute()方法:提交优先级源码
public void execute(Runnable command) {
if (command == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
/*
* Proceed in 3 steps:
*
* 1. If fewer than corePoolSize threads are running, try to
* start a new thread with the given command as its first
* task. The call to addWorker atomically checks runState and
* workerCount, and so prevents false alarms that would add
* threads when it shouldn't, by returning false.
*
* 2. If a task can be successfully queued, then we still need
* to double-check whether we should have added a thread
* (because existing ones died since last checking) or that
* the pool shut down since entry into this method. So we
* recheck state and if necessary roll back the enqueuing if
* stopped, or start a new thread if there are none.
*
* 3. If we cannot queue task, then we try to add a new
* thread. If it fails, we know we are shut down or saturated
* and so reject the task.
*/
int c = ctl.get();
if (workerCountOf(c) < corePoolSize) {
if (addWorker(command, true))
return;
c = ctl.get();
}
if (isRunning(c) && workQueue.offer(command)) {
int recheck = ctl.get();
if (! isRunning(recheck) && remove(command))
reject(command);
else if (workerCountOf(recheck) == 0)
addWorker(null, false);
}
else if (!addWorker(command, false))
reject(command);
}
执行优先级:

提交优先级:

查看:执行优先级代码
/**
* Checks if a new worker can be added with respect to current
* pool state and the given bound (either core or maximum). If so,
* the worker count is adjusted accordingly, and, if possible, a
* new worker is created and started, running firstTask as its
* first task. This method returns false if the pool is stopped or
* eligible to shut down. It also returns false if the thread
* factory fails to create a thread when asked. If the thread
* creation fails, either due to the thread factory returning
* null, or due to an exception (typically OutOfMemoryError in
* Thread.start()), we roll back cleanly.
*
* @param firstTask the task the new thread should run first (or
* null if none). Workers are created with an initial first task
* (in method execute()) to bypass queuing when there are fewer
* than corePoolSize threads (in which case we always start one),
* or when the queue is full (in which case we must bypass queue).
* Initially idle threads are usually created via
* prestartCoreThread or to replace other dying workers.
*
* @param core if true use corePoolSize as bound, else
* maximumPoolSize. (A boolean indicator is used here rather than a
* value to ensure reads of fresh values after checking other pool
* state).
* @return true if successful
*/
private boolean addWorker(Runnable firstTask, boolean core) {
retry:
for (;;) {
int c = ctl.get();
int rs = runStateOf(c);
// Check if queue empty only if necessary.
if (rs >= SHUTDOWN &&
! (rs == SHUTDOWN &&
firstTask == null &&
! workQueue.isEmpty()))
return false;
for (;;) {
int wc = workerCountOf(c);
if (wc >= CAPACITY ||
wc >= (core ? corePoolSize : maximumPoolSize))
return false;
if (compareAndIncrementWorkerCount(c))
break retry;
c = ctl.get(); // Re-read ctl
if (runStateOf(c) != rs)
continue retry;
// else CAS failed due to workerCount change; retry inner loop
}
}
boolean workerStarted = false;
boolean workerAdded = false;
Worker w = null;
try {
w = new Worker(firstTask);
final Thread t = w.thread;
if (t != null) {
final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock;
mainLock.lock();
try {
// Recheck while holding lock.
// Back out on ThreadFactory failure or if
// shut down before lock acquired.
int rs = runStateOf(ctl.get());
if (rs < SHUTDOWN ||
(rs == SHUTDOWN && firstTask == null)) {
if (t.isAlive()) // precheck that t is startable
throw new IllegalThreadStateException();
workers.add(w);
int s = workers.size();
if (s > largestPoolSize)
largestPoolSize = s;
workerAdded = true;
}
} finally {
mainLock.unlock();
}
if (workerAdded) {
t.start();
workerStarted = true;
}
}
} finally {
if (! workerStarted)
addWorkerFailed(w);
}
return workerStarted;
}

流程
1、execute
2、addWorker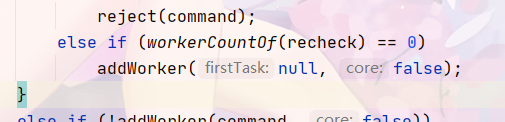
3、workAdded=true,调用t.start
4、run
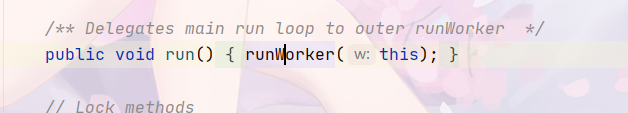
5、runWorker

这里可以就可以看出先执行非核心线程,而不是等待队列
6、如果task为空,执行getTask

执行等待队列






















 1021
1021











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








