后面章节将分析 dma buffer 的管理,其中细节需要对音频数据相关概念有一定的了解。因此本章说明下音频数据中的几个重要概念:
- Sample:样本长度,音频数据最基本的单位,常见的有 8 位和 16 位;
- Channel:声道数,分为单声道 mono 和立体声 stereo;
- Frame:帧,构成一个完整的声音单元,Frame = Sample * channel;
- Rate:又称 sample rate,采样率,即每秒的采样次数,针对帧而言;
- Period size:周期,每次硬件中断处理音频数据的帧数,对于音频设备的数据读写,以此为单位;
- Buffer size:数据缓冲区大小,这里指 runtime 的 buffer size,而不是结构图 snd_pcm_hardware 中定义的 buffer_bytes_max;一般来说 buffer_size = period_size * period_count, period_count 相当于处理完一个 buffer 数据所需的硬件中断次数。
下面一张图直观的表示 buffer/period/frame/sample 之间的关系:
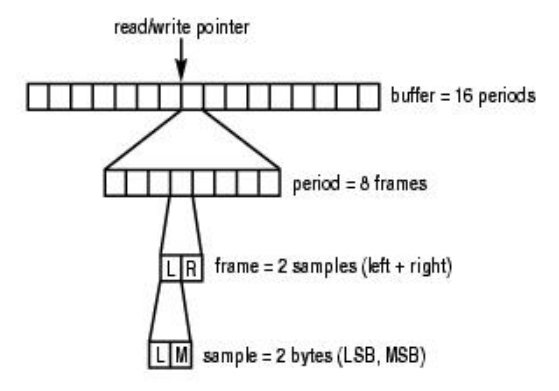
这个 buffer 中有 16 个 period,每当 DMA 搬运完一个 period 的数据就会出生一次中断,因此搬运这个 buffer中的数据将产生 16 次中断。ALSA 为什么这样做?因为数据缓存区可能很大,一次传输可能会导致不可接受的延迟;为了解决这个问题,所以将缓存区拆分成多个周期 period,以周期 period 为单元传输数据。
7.1. Frames & Periods
敏感的读者会察觉到 period 和 buffer size 在 PCM 数据搬运中扮演着非常重要角色。下面引用两段来自 alsa 官网对 Period 的详细解释:
Period
The interval between interrupts from the hardware. This defines the input latency, since the CPU will not have any idea that there is data waiting until the audio interface interrupts it.
The audio interface has a “pointer” that marks the current position for read/write in its h/w buffer. The pointer circles around the buffer as long as the interface is running.
Typically, there are an integral number of periods per traversal of the h/w buffer, but not always. There is at least one card (ymfpci) that generates interrupts at a fixed rate indepedent of the buffer size (which can be changed), resulting in some “odd” effects compared to more traditional designs.
Note: h/w generally defines the interrupt in frames, though not always.
Alsa’s period size setting will affect how much work the CPU does. if you set the period size low, there will be more interrupts and the work that is done every interrupt will be done more often. So, if you don’t care about low latency, set the period size large as possible and you’ll have more CPU cycles for other things. The defaults that ALSA provides are in the middle of the range, typically.
(from an old AlsaDevel thread[1], quoting Paul Davis)
Retrieved from “








 本文介绍了音频数据中的核心概念,如Sample、Channel、Frame和Rate,着重讲解了Period及其作用。Period是硬件中断处理音频数据的帧数,影响CPU的工作量和延迟。通过举例说明了帧和周期的关系,以及如何计算I2S传输一个周期数据所需的时间。此外,讨论了在某些平台中,如何使用hrtimer模拟PCM周期中断来确保数据传输的实时性。
本文介绍了音频数据中的核心概念,如Sample、Channel、Frame和Rate,着重讲解了Period及其作用。Period是硬件中断处理音频数据的帧数,影响CPU的工作量和延迟。通过举例说明了帧和周期的关系,以及如何计算I2S传输一个周期数据所需的时间。此外,讨论了在某些平台中,如何使用hrtimer模拟PCM周期中断来确保数据传输的实时性。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章















 4921
4921

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








