Prim相比于Kruskal的优势?
递归构造CBT(by FBT+CBT in recursion)
- 数组树,用递归,不要浪费时间构建完整的树

idea+comment
- 我选择直接从这N个树构造CBT
- way0. 递归,保证每次加入一个节点都形成CBT,难度巨大
- way1. 每次先找根,然后分成左右两个子树,用递归即可,但还要联系左右子树的区间
- way2. 补全成满二叉树,自第二上归并构造,这个容易点,接着层序遍历,忽略补上的数,但不喝题意
- 综上,只能用way1,好痛苦呀,
- 好消息是,way1的一部分可以用到way2,好像实际上,way1可以借助于way2迭代; 但无论怎么说,这个题目挺复杂的
- tuple<type1,…,type3> result=make_tuple<type1,…,type3>,return result;
- tie<type1,…,type3>=result;
- 完成:cal_loc_root_lr(),build_full_binary_tree(),build_CBT(),main()
- check-1: 完全平衡,最大N 错误
comment1: some trifle calculation in cal_loc_root_lr
code+result
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<cmath>
#include<tuple> //fullfilled by struct
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Node{
public:
Node *lc;
Node *rc;
int val;
};
//check-1
tuple<int,int> cal_loc_root_lr(vector<int> &ele,int begin,int end){
//进入条件为end-begin>=0,len>=1,不用考虑len=0
int len=end-begin+1;
int h=log(len)/log(2)+1;
int lr; //lr=0表示最底层左边非空,lr=1表示最底层右边非空
int loc_root;
tuple<int,int> result;
//需要区分~h=1~ len=1的情形
if(h==1){
lr=0;
loc_root=begin;
}
else{
if(len<=begin+3*pow(2,h-2)-2){
lr=0;
loc_root=end-pow(2,h-2)+1;
}
else {
lr=1;
loc_root=begin+pow(2,h-1)-1;
}
}
result=make_tuple(lr,loc_root);
return result;
}
//check-1
Node* build_full_binary_tree(vector<int> &ele,int begin,int end){
if(end-begin<0)
return NULL;
int mid=(begin+end)/2;
Node *root=new Node;
root->val=ele[mid];
if(end-begin>0){
root->lc=build_full_binary_tree(ele,begin,mid-1);
root->rc=build_full_binary_tree(ele,mid+1,end);
}
else{
root->lc=NULL;
root->rc=NULL;
}
return root;
}
//check-1
Node* build_CBT(vector<int> &ele,int begin,int end){
//终止条件
if(end-begin<0)
return NULL;
//迭代过程(end-begin>=0)
int lr,loc_root;
tie(lr,loc_root)=cal_loc_root_lr(ele,begin,end);
// cout<<"begin="<<begin<<",end="<<end<<",loc_root"<<loc_root<<endl;
Node *root=new Node;
root->val=ele[loc_root];
if(lr==0){
root->lc=build_CBT(ele,begin,loc_root-1);
root->rc=build_full_binary_tree(ele,loc_root+1,end);
}
else{
root->lc=build_full_binary_tree(ele,begin,loc_root-1);
root->rc=build_CBT(ele,loc_root+1,end);
}
return root;
}
//check-1
int main(){
int N; cin>>N;
vector<int> ele(N);
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
cin>>ele[i];
sort(ele.begin(),ele.end());
Node *root=build_CBT(ele,0,ele.size()-1);
//perform level-order traverse
queue<Node*> nqueue;
nqueue.push(root);
int sign=0;
while(!nqueue.empty()){
Node *tem=nqueue.front();
if(sign==0){
cout<<tem->val;
sign=1;
}
else cout<<" "<<tem->val;
if(tem->lc!=NULL) nqueue.push(tem->lc);
if(tem->rc!=NULL) nqueue.push(tem->rc);
nqueue.pop();
}
return 0;
}

Exp++
class Node{ xxx };is utilized to replace struct, assigning of which isNode * root=new Node[size]- function in C++ can return multiple values as follows:
//返回值
tuple<type1,...,type3> result=make_tuple<x1(type1),...,x3(type3)>,return result;
//接收值
tie<x1(type1),...,x2(type3)>=result;
- Depending on multiple sub-function with certain effect indicated by note to standardize main program,improving readability meanwhile for debugging.
- 迭代过程中的计算要细心
File Transfer——伪装成青铜的王者

- 难点:1. 类定义(不会,还是用结构体); 2. 输入处理,
//judge connectivity of graph
//analogy in realistic problem
//GNode can be expressed as both class and graph matrix, the former is adopted
//exp1: the first step is combing relations between target functions
//que1: 如何对一个含有vector成员的类(的对象)进行初始化
//que2: 可以用cin判断读入的是否为空吗?—— getline(cin,),如何读取
#include<iostream>
#include<vector> //standardization of array
#include<stack> //for DFS of graph nodes
using namespace std;
struct GEdge{
int index;
GEdge * next;
};
struct GNode{
int val;
GEdge* firstedge;
};
//含vector成员类对象的初始化
struct Graph{
int Nv;
GNode* GNodeList;
}; //无向图
//链表尾插入节点待处理
bool c1_to_c2(Graph* G,int c1,int c2){
if(c1==c2) return false;
GEdge* ec1=G->GNodeList[c1].firstedge;
while(ec1->next!=NULL){
if(ec1->index==c2) return false; //已建立连接,对称,故直接返回
else ec1=ec1->next;
}
//采用头插法
GEdge* new_ec2=new GEdge;
new_ec2->index=c2;
new_ec2->next=ec1;
G->GNodeList[c1].firstedge=new_ec2;
return true;
}
void connect(Graph* G,int c1,int c2){
if(c1_to_c2(G,c1,c2)==false){ //c1指向c2
return ;
}
c1_to_c2(G,c2,c1); //c2指向c1
return ;
}
//DFS from GNode c1
void DFS(Graph* G,vector<int> &visit,int c1){ //引用变量才能修改,vector好像是指针,不用左引用&
stack<GNode> nstack;
nstack.push(G->GNodeList[c1]);
while(!nstack.empty()){
GEdge* tem=nstack.top().firstedge;
int sign=0;
while(tem!=NULL){
if(visit[tem->index]==0){
visit[tem->index]=1;
nstack.push(G->GNodeList[tem->index]);
sign=1;
}
else tem=tem->next;
}
if(sign==0) nstack.pop();
}
return ;
}
//perform DFS from c1
//另一种栈式遍历,不用visit数组背诵,好像还是要visit数组
void Check(Graph* G,int c1,int c2){
vector<int> visit(G->Nv,0);
if(c1==c2){
cout<<"no"<<endl;
return ;
}
stack<GNode> nstack;
visit[c1]=1;
nstack.push(G->GNodeList[c1]);
while(!nstack.empty()){
GEdge* tem=nstack.top().firstedge;
while(tem!=NULL){
if(tem->index==c2){
cout<<"yes"<<endl;
return ;
}
if(visit[tem->index]==0){
visit[tem->index]=1;
nstack.push(G->GNodeList[tem->index]);
}
tem=tem->next;
}
}
cout<<"no"<<endl;
return ;
}
//DFS from each unvisited GNode
void Isolation(Graph* G){
vector<int> visit(G->Nv,0);
int cnt=0;
for(int i=0;i<G->Nv;i++){
if(visit[i]==0){
DFS(G,visit,i);
cnt++;
}
}
cout<<"There are "<<cnt<<" components."<<endl;
}
//按行处理
int main(){
int N; cin>>N;
Graph* G=new Graph;
G->Nv=N;
G->GNodeList=new GNode[N];
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
G->GNodeList[i].val=i;
G->GNodeList[i].firstedge=NULL;
}
string str;
char symbol; int c1,c2;
int cnt=0;
//无语的字符串读取
while(getline(cin,str)){
cnt++;
cout<<str<<endl;
if(str.empty()){
break;
}
symbol=str[0];
if(symbol=='S')
Isolation(G);
else {
sscanf(str.c_str(),"%c %d %d",&symbol,&c1,&c2);
if(symbol=='C')
Check(G,c1,c2);
else c1_to_c2(G,c1,c2);
}
}
cout<<"there are "<<cnt<<" lines all together"<<endl;
return 0;
}
输入处理
每次这种按行读取都要爆炸
特点
- 按行读取,要用getline(cin,str);
- 不同行的处理方式不同,因此不能scanf(“%d %c”,&x1,&c1);
cin>>N;只会按N的类型读取一个对应的变量,直到空格或换行前,但不会读取这个空格(“\ “)或换行符(”\n”)
cin读取数据是从第一个非空白字符开始到下一个空白字符结束;
如果我在第一次输入时,利用空格隔开两个字符串,那么cin在第一次取的时候,只会读取前一个字符串,到空格结束,此时缓冲区还保留着前面输入的第二个字符串,那么第二次cin就会直接从缓冲区取残留数据,而不会请求输入。
cin、cin.get()、cin.getline()、getline()的区别
- 读取"\n":a)
char str1[50]; gets(str1); b)string str1; getline(cin,str1);
a)在.c可以用,在.cpp不能用,C++11标准已移除;

- scanf()从光标位置读取,因此光标在换行符处
getline(cin,litter)掉换行符;cin>>自动从下一个非空格非"\n"读取,故不用getline(cin,str1)读掉换行符; - scanf()并不是读到换行符停止,而是遇到空白字符(空格、制表符、换行符等),在仅仅读取一行时有效;
读取一整行再处理,要跟一个getline(cin,rubbish);读掉"\n";或者getline(cin,str1);+sscanf(str1.c_str(),"%d %s",&x1,str1)
- 字符处理部分如下:
int N; cin>>N;
string str;
char symbol; int c1,c2;
int cnt=0;
//无语的字符串读取
while(getline(cin,str)){
cnt++;
cout<<str<<endl;
if(str.empty()){
break;
}
symbol=str[0];
if(symbol=='S')
Isolation(G);
else {
sscanf(str.c_str(),"%c %d %d",&symbol,&c1,&c2);
if(symbol=='C') Check(G,c1,c2);
else c1_to_c2(G,c1,c2);
}
}
cout<<"there are "<<cnt<<" lines all together"<<endl;
结果
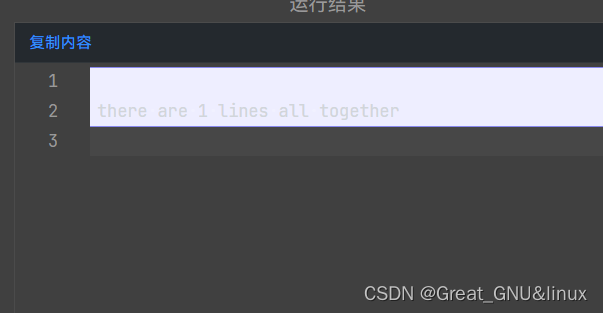
说明只读了个空行,然后跳出;
推测: cin>>N读了5赋值给N后,还有"\n"未读取,getline()跟着读取后赋值给str,遂break;
果然是这样——在cin>>N后,跟着一个getline(cin,str);读掉空行后结果如下:
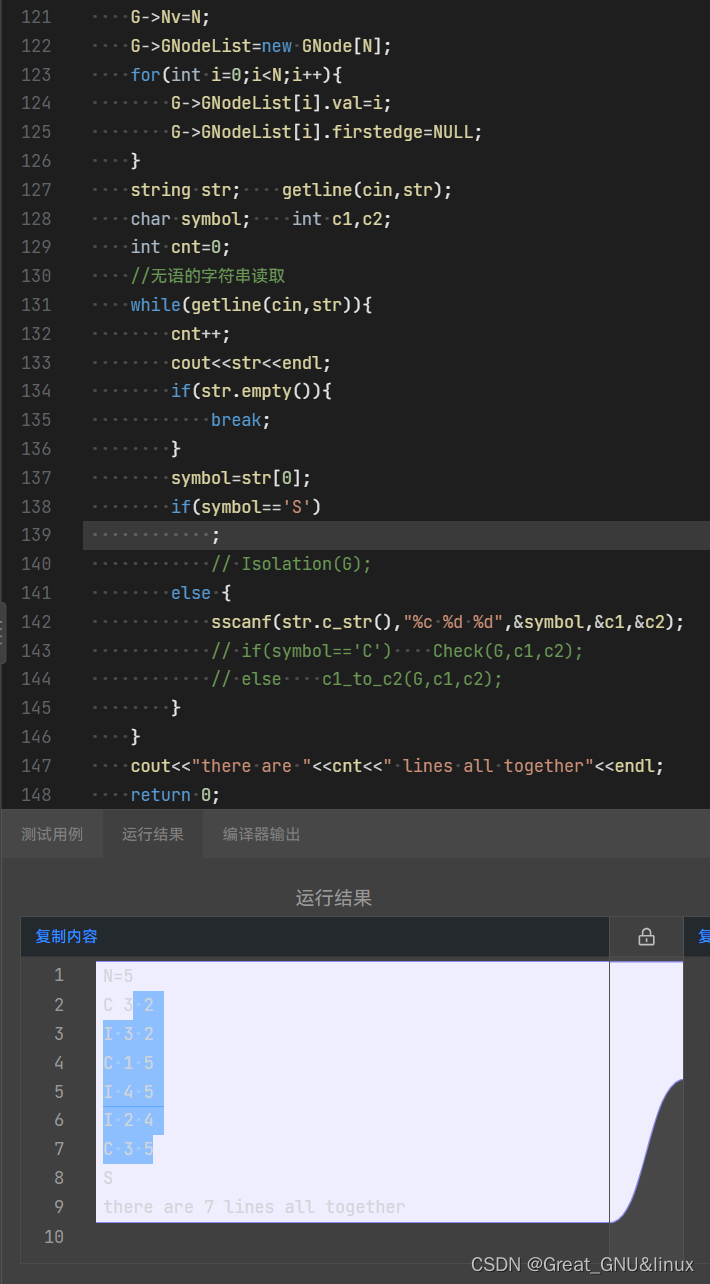
段错误
控制变量法(分别Note掉line 140,143,144),用简单的例子测试,发现connect函数有问题(而且connect打成c1_to_c2了~~)
分析如下:
- 序号为i的node在GNode中的位置为i-1
- 修改1:N+1个节点,查联通分量从1开始; 修改2:i在GNodelist[i]中坐标为i-1,但index和val仍为i;
- 采用修改1:
更新(头插法不用遍历)如下:
//judge connectivity of graph
//analogy in realistic problem
//GNode can be expressed as both class and graph matrix, the former is adopted
//exp1: the first step is combing relations between target functions
//que1: 如何对一个含有vector成员的类(的对象)进行初始化
//que2: 可以用cin判断读入的是否为空吗?—— getline(cin,),如何读取
//err1: 超时>>while无限循环>>迭代后未更新变量
//err2: 段错误>>访问了不能访问的指针(变量)
//check2:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector> //standardization of array
#include<stack> //for DFS of graph nodes
using namespace std;
struct GEdge{
int index;
GEdge * next;
};
struct GNode{
int val;
GEdge* firstedge;
};
//含vector成员类对象的初始化
struct Graph{
int Nv;
GNode* GNodeList;
}; //无向图
//链表尾插入节点待处理, check:1
void c1_to_c2(Graph* G,int c1,int c2){
if(c1==c2) return ;
GEdge* ec1=G->GNodeList[c1].firstedge;
//用头插法不用遍历到邻接链表尾
// while(ec1!=NULL){
// if(ec1->index==c2) return false; //已建立连接,对称,故直接返回
// else ec1=ec1->next;
// }
//采用头插法
GEdge* new_ec2=new GEdge;
new_ec2->index=c2;
new_ec2->next=ec1;
G->GNodeList[c1].firstedge=new_ec2;
return ;
}
void connect(Graph* G,int c1,int c2){
c1_to_c2(G,c1,c2); //c1指向c2
c1_to_c2(G,c2,c1); //c2指向c1
return ;
}
//perform DFS from c1
//另一种栈式遍历,不用visit数组背诵,好像还是要visit数组
void Check(Graph* G,int c1,int c2){
vector<int> visit(G->Nv+1,0);
if(c1==c2){
cout<<"yes"<<endl;
return ;
}
stack<GNode> nstack;
visit[c1]=1;
nstack.push(G->GNodeList[c1]);
while(!nstack.empty()){
GEdge* tem=nstack.top().firstedge;
nstack.pop();
while(tem!=NULL){
if(tem->index==c2){
cout<<"yes"<<endl;
return ;
}
if(visit[tem->index]==0){
visit[tem->index]=1;
nstack.push(G->GNodeList[tem->index]);
}
tem=tem->next;
}
}
cout<<"no"<<endl;
return ;
}
//DFS from GNode c1; check:1
void DFS(Graph* G,vector<int> &visit,int c1){ //引用变量才能修改,vector好像是指针,不用左引用&
stack<GNode> nstack;
nstack.push(G->GNodeList[c1]);
while(!nstack.empty()){
GEdge* tem=nstack.top().firstedge;
int sign=0;
while(tem!=NULL){
if(visit[tem->index]==0){
visit[tem->index]=1;
nstack.push(G->GNodeList[tem->index]);
sign=1;
break;
}
else tem=tem->next;
}
if(sign==0) nstack.pop();
}
return ;
}
//DFS from each unvisited GNode
void Isolation(Graph* G){
vector<int> visit(G->Nv+1,0);
int cnt=0;
for(int i=1;i<=G->Nv;i++){
if(visit[i]==0){
DFS(G,visit,i);
cnt++;
}
}
if(cnt==1) cout<<"The network is connected.";
else cout<<"There are "<<cnt<<" components."<<endl;
return ;
}
//按行处理
int main(){
int N; cin>>N;
// cout<<"N="<<N<<endl;
Graph* G=new Graph;
G->Nv=N;
G->GNodeList=new GNode[N+1];
//序号为i的node在GNode中的位置为i-1
//修改1:N+1个节点,查联通分量从1开始; 修改2:i在GNodelist[i]中坐标为i-1,但index和val仍为i;
//采用修改1:
for(int i=1;i<=N;i++){
G->GNodeList[i].val=i;
G->GNodeList[i].firstedge=NULL;
}
string str; getline(cin,str);
char symbol; int c1,c2;
int cnt=0;
//无语的字符串读取
while(getline(cin,str)){
cnt++;
// cout<<str<<endl;
if(str.empty()){
break;
}
symbol=str[0];
if(symbol=='S')
Isolation(G);
else {
sscanf(str.c_str(),"%c %d %d",&symbol,&c1,&c2);
if(symbol=='C') Check(G,c1,c2);
else connect(G,c1,c2);
}
}
// cout<<"there are "<<cnt<<" lines all together"<<endl;
return 0;
}
结果如下:

Exp++
- 这么简单的题目,浪费好多时间
Push
cin>>variable从第一个非空白符读到下一个"\ “/”\n",getline(cin,str)会读完以"\n"结尾的一整行,共用<iostream>头文件- 字符串->其他类型用stox(in ),其他类型转char *用sprintf(),"="转为string
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string tem="1245";
int b=stoi(tem)-10;
char str1[10];
sprintf(str1,"%d",b+20);
string s1=str1;
string flos="12.3";
float h=stof(flos);
cout<<b<<endl;
cout<<str1;
cout<<s1<<endl;
cout<<h<<endl;
}
- 节点的链接链表的插入宜采用头插法(不用遍历到Tail+不用单独处理头指针是否为NULL)
- 段错误>>数组越界>>数组序号==真实序号-1,超时>>while无限循环>>迭代条件未更新
- 试用类表示节点,并初始化(+其中的vector数组)
- 针对测试点6,并查集能被用到这个题目,整道题目都在梦游~~,试用Union-Find set解答此题目
Pop
- 两种方式的栈式先序遍历(for looking for 连通分量in 无向图)
- 如何找有向图的强连通分量——栈式(用array实现)DFS,找到在栈中的节点为一个连通分量,标记清空,如此迭代
Union-Find Set
- 1)判断图中节点的连通性
- 2)获得无向图的连通分量
- 采用路径压缩(非根节点均指向根节点)可加速查找和连接,O(1)
- 特点:仅father[连通分支的根节点]=-1,其余指向其父节点/根节点(path compress)
int component;
vector<int> father;
int Find_Root_Comp(int x){
if(father[x]==-1)
return x;
else{
int F=Find_Root_Comp(father[x]);
father[x]=F;
return F;
}
}
void Union(int x,int y){
int fatherx=Find_Root_Comp(x);
int fathery=Find_Root_Comp(y);
if(fatherx!=fathery){
father[fatherx]=fathery;
component--;
}
return ;
}
bool Check(int x,int y){
int fatherx=Find_Root_Comp(x);
int fathery=Find_Root_Comp(y);
if(fatherx==fathery){
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
priority_queue计算Huffman编码总长度
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int>> f_queue; //升序队列
priority_queue <int,vector<int>,less<int> >q; //降序队列,定义: priority_queue<Type, Container, Functional>
int Huff_code_sum(vector<int> f_set){
//计算最小长度和只需要f_set
//way1:构造huffman树,定义节点,按算法为每个节点赋一个string成员,构造编码
//way2:书上采用priority_queue计算huffman编码总长
//but,priority_queue的头元素=top(),queue的头元素=front()
sort(f_set.begin(),f_set.end());
for(auto i:f_set)
f_queue.push(i);
int sum=0;
while(f_queue.size()>1){
int x=f_queue.top();
f_queue.pop();
int y=f_queue.top();
f_queue.pop();
sum+=x+y;
f_queue.push(x+y);
}
return sum;
}
如何寻找源和汇的最短路径
- 普通的栈式DFS不保证找到根到每个节点的最短路径,只能找到图中从根节点能遍历到的所有节点。 (√)
+optimal_path+min_len可以找到最短路径。 (√) - 普通的Dijkstra和Floyd可以输出最短路径长,难以输出节点;
- 递归DFS也可以,DFS均可用剪枝减小时间复杂度;
- BFS可以容易地输出最短路径长,但是不能找到最短路径
- 为什么BFS不适合用递归实现?——父节点的不同子节点的递归函数不交叉,不能在同一层输出;
或者说,什么样的结构适合用递归实现——子问题的解可以容易地拼接成原问题的解;=DP
最短路长用BFS

7.11

//用图数据结构表示,
//用BFS,队列实现的时候,给未遍历的每个节点赋一个位置数组
//也可以DFS寻找最短S和D的最短路径
//试一下可以用邻接矩阵形式的图结构,这样不必定义图节点,
//递归标记最短路径,
//~~1)多条最短路径仍需处理;~~
//2)非递归形式=回溯剪枝?
//note: 简单的例子能提供更高效的信息
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
int N,D;
vector<pair<int,int>> coord;
int min_len=1000;
vector<int> optimal_path;
bool check(int x,int y){
if(x==0) return (pow(coord[y].first,2)+pow(coord[y].second,2)<=pow(D+7.5,2))?true:false;
return (pow(coord[x].first-coord[y].first,2)+pow(coord[x].second-coord[y].second,2)<=pow(D,2))?true:false;
}
//检查非根节点是否可以到岸
bool test_plausible(int x){
if(x==0) return (abs(coord[x].first-50)<=D+7.5||abs(coord[x].first+50)<=D+7.5||\
abs(coord[x].second-50)<=D+7.5||abs(coord[x].second+50)<=D+7.5)?true:false;
return (abs(coord[x].first-50)<=D||abs(coord[x].first+50)<=D||\
abs(coord[x].second-50)<=D||abs(coord[x].second+50)<=D)?true:false;
}
//递归寻找最短路径,赋值给optimal_path
void shortest_path(int root,vector<int> &path,int depth,vector<int> &visit){
//depth表示从根节点到root的路径的节点数目数
//path初始化为(N+1,-1); depth不能用引用改变,否则for循环中depth不等
for(int i=0;i<=N;i++){
if(i!=root&&check(root,i)&&visit[i]==0){ //i与root相连且未访问
visit[i]=1;
path[depth]=i; //长度为depth+1,在后面第42行写错俩
if(test_plausible(i)){
//若有多条最短路径,需要单独处理,path[1]第一跳更小
if(depth+1<min_len||((depth+1==min_len)&&\
((pow(coord[path[1]].first,2)+pow(coord[path[1]].second,2))\
<=(pow(coord[optimal_path[1]].first,2)+pow(coord[optimal_path[1]].second,2))))){
optimal_path=path;
min_len=depth+1;
// cout<<"a new path="<<endl;
// for(int i=1;i<min_len;i++)
// cout<<coord[optimal_path[i]].first<<" "<<coord[optimal_path[i]].second<<endl;
}
//这里可以剪枝——不用从i下探=执行shortest_path函数
visit[i]=0; //恢复现场;
}
else shortest_path(i,path,depth+1,visit);
}
}
visit[root]=0; //恢复现场
return ;
}
int main(){
//tackle with input
cin>>N>>D;
coord.assign(N+1,make_pair(0,0));
for(int i=1;i<=N;i++)
cin>>coord[i].first>>coord[i].second;
// //define plausible array
// vector<bool> plausible(N+1,0);
// if(D>=42.5) plausible[0]=true;
// else plausible[0]=false;
// for(int i=1;i<=N;i++)
// plausible[i]=test_plausible(i);
//perform dfs to search for shortest path
vector<int> path(N+1,-1); int depth=0; //熟知,size+array可以表示一个栈
vector<int> visit(N+1,0);
visit[0]=1; //将根节点加入队列
path[depth]=0;
if(test_plausible(0)){
optimal_path=path;
min_len=1;
}
else{
shortest_path(0,path,depth+1,visit); //保持形式一致性
}
if(min_len==1000){
cout<<0<<endl;
return 0;
}
cout<<min_len<<endl;
for(int i=1;i<min_len;i++){ //根节点不用输出
if(path[i]!=-1)
cout<<coord[optimal_path[i]].first<<" "<<coord[optimal_path[i]].second<<endl;
else
break;
}
return 0;
}
Exp++
- 图结构未必要定义图节点——1)图的邻接表;2)手动判断连接关系(check(x,y));
同样,栈=array+size(to search for top) - 最短路径可用递归+剪枝——用DFS的栈式遍历(+visit);用array path+int size保存路径上的节点;optimal_path+min_len保存路径上的点
伪代码
stack.push(root)
while(!stack.empty()){
tem=stack.top()
sign=0;
for(auto i: tem.neighbour()){
if(visit[i]==0){
visit[i]=1;
path[depth++]=i;
if(it is destination)
compare and save optimal_path& min_len;
else{
stack.push(i);
sign=1;
break;
}}}
if(sign==0){ //恢复现场
visit[i]=0;
depth–;
stack.pop();
}}
- 调试trick++:1)简单的例子能提供更高效的反馈;2)把自己的输出和标准输出拼接作为新的输入
默写key path(自带Torpo sort)

reading
- if 成环,输出Impossible——可用拓扑排序,成环<=>不存在拓扑排序
- else ,output AOE=最长关键路径
- 执行书上的算法,输出关键路径长,和关键路径,2在1的过程中进行
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
void AOE(vector<int> S,vector<int> E,vector<int> L,int N){
vector<int> in_degree(N);
vector<int> earliest_time(N,-1);
int earliest_comletion_time=0;
for(int i=0;i<S.size();i++)
in_degree[E[i]]++;
queue<int> zero_point;
int out_num=0;
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
if(in_degree[i]==0){
earliest_time[i]=0;
zero_point.push(i);
out_num++;
}
}
while(!zero_point.empty()){
int tem=zero_point.front();
for(int i=0;i<S.size();i++){ //S.size()==M,遍历边
if(S[i]==tem){
//更新tem出发的终点的完成时间
if(earliest_time[E[i]]==-1||earliest_time[E[i]]<earliest_time[tem]+L[i])
earliest_time[E[i]]=earliest_time[tem]+L[i];
//更新tem出发的终点的度数,
in_degree[E[i]]--;
//若度数为0,更新全局最早完成时间,并入点
if(in_degree[E[i]]==0){
if(earliest_comletion_time<earliest_time[E[i]])
earliest_comletion_time=earliest_time[E[i]];
zero_point.push(E[i]);
out_num++;
}
}
}
zero_point.pop();
}
if(out_num<N)
cout<<"Impossible"<<endl;
else
cout<<earliest_comletion_time<<endl;
return ;
}
int main(){
int N,M; cin>>N>>M;
vector<int> S(M),E(M),L(M);
for(int i=0;i<M;i++)
cin>>S[i]>>E[i]>>L[i];
AOE(S,E,L,N);
return 0;
}
Exp++
-
如何输出关键路径?——最短路径可以比较获得,
Solution 1. 先从前往后找出每个点的最早完成时间, 2. 再反向torpo sort定出每个点的最晚完成时间, 3. e[i]=l[i]的点在关键路径上,自后往前,每次找前一个e[i]=l[i]的点,连成关键路径,O(N^2)
7-21 Counting Leaves
- 胶水,回顾了queue栈式遍历,用于记录深度by map;count leaf_num for each layer;

//note:如何避免自定义变量重名?
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<map>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string str;
int N; cin>>N;
while(N!=0){
int M; cin>>M; getline(cin,str);
map<int,int> depth_of_node; //store depth for node
map<int,vector<int>> child_of_node; //store children_id for each node
//read child_of_node
for(int i=0;i<M;i++){
int fath; cin>>fath;
int child_num; cin>>child_num;
vector<int> child(child_num);
for(int i=0;i<child_num;i++)
cin>>child[i];
getline(cin,str);
child_of_node.insert(make_pair(fath,child));
}
//calculate depth_of_node by queue
int max_depth=1;
depth_of_node.insert(make_pair(1,1));
queue<int> trav;
trav.push(1);
while(!trav.empty()){
int tem=trav.front();
trav.pop(); //维护迭代条件
for(auto i:child_of_node[tem]){
max_depth=((depth_of_node[tem]+1)>max_depth)?(depth_of_node[tem]+1):max_depth;
depth_of_node.insert(make_pair(i,depth_of_node[tem]+1)); //计算深度:depth[child]=depth[tem]+1;
trav.push(i); //层序遍历迭代
}
}
vector<int> leaf_num(max_depth+1,0); //store leafnum for each layer; 假设根节点深度为1
//count for each layer;
for(auto i:depth_of_node){
int node_id=i.first; //node's id
int node_depth=i.second;
if(child_of_node[node_id].size()==0) //为叶节点
leaf_num[node_depth]++;
}
int sign=0;
for(int i=1;i<leaf_num.size();i++){
if(sign==0) sign=1;
else cout<<" ";
cout<<leaf_num[i];
}
cout<<endl;
cin>>N;
}
}
打卡:

B+树
最大流(抄的模板)
- 初始化可行轨道,如f(e)=0,

- 回溯(bfs记录父节点)找可增载轨道,更新f(e),

- 直到没有可增载轨道,输出此时的最大流Val(f)

Code Reading
传统的最大流算法如下:
- BFS用parent数组记录,同时可以找到一条从converge到source的路径,即找可增载轨道
- 找可增载轨道后,从尾到前遍历,记录最大可增值量,之后更新路径上的最大流值,与val(f)
这个相当于传统的改进
- 初始默认f(e)=0,故找到可行的轨道后,可增载量=这条轨道上的最大流即为最小的管道,
- 这个相当于每次找到可增载轨道后,从所有轨道上删除可增载部分,并加入到val(f)中,下一次迭代又相当于f(e’)=0,故可行
但可增载量的计算和可增载轨道的寻找,并不能理解
//最大流问题
// C++ program for implementation of Ford Fulkerson algorithm
#include <iostream>
#include <limits.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
#include <map>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
/* Returns true if there is a path from source 's' to sink 't' in
residual graph. Also fills parent[] to store the path */
bool bfs(vector<vector<int>> rGraph,int V, int s, int t, int parent[])
{
// Create a visited array and mark all vertices as not visited
bool visited[V];
memset(visited, 0, sizeof(visited));
// Create a queue, enqueue source vertex and mark source vertex as visited
queue<int> q;
q.push(s);
visited[s] = true;
parent[s] = -1;
// Standard BFS Loop
int u;
while (!q.empty())
{
// edge: u -> v
u = q.front(); // head point u
q.pop();
for (int v = 0; v < V; ++v) // tail point v
{
if (!visited[v] && rGraph[u][v] > 0) // find one linked vertex
{
q.push(v);
parent[v] = u; // find pre point
visited[v] = true;
}
}
}
// If we reached sink in BFS starting from source, then return true, else false
return visited[t] == true;
}
// Returns the maximum flow from s to t in the given graph
int fordFulkerson(vector<vector<int>> graph,int V, int s, int t)
{
int u, v;
// int rGraph[V][V];
vector<vector<int>> rGraph(graph.size(),vector<int>(graph.size(),0));
for (u = 0; u < V; ++u)
{
for (v = 0; v < V; ++v)
{
rGraph[u][v] = graph[u][v];
}
}
int parent[V];
int max_flow = 0;
// Augment the flow while tere is path from source to sink
while (bfs(rGraph, V, s, t, parent))
{
// edge: u -> v
int path_flow = INT_MAX;
for (v = t; v != s; v = parent[v])
{
// find the minimum flow
u = parent[v];
path_flow = min(path_flow, rGraph[u][v]);
}
// update residual capacities of the edges and reverse edges along the path
for (v = t; v != s; v = parent[v])
{
u = parent[v];
rGraph[u][v] -= path_flow;
rGraph[v][u] += path_flow; // assuming v->u weight is add path_flow
}
// Add path flow to overall flow
max_flow += path_flow;
}
return max_flow;
}
int main()
{
int N; string str;
string source,destination; cin>>source>>destination>>N; getline(cin,str);
map<pair<string,string>,int> oform;
map<string,int> dict; dict.insert(make_pair(source,0));
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
string si,di; int cap;
cin>>si>>di>>cap; getline(cin,str);
if(dict.find(si)==dict.end())
dict.insert(make_pair(si,dict.size()));
if(dict.find(di)==dict.end())
dict.insert(make_pair(di,dict.size()));
oform.insert(make_pair(make_pair(si,di),cap));
}
dict.insert(make_pair(destination,dict.size()));
int V=dict.size();
vector<vector<int>> graph(V,vector<int>(V,0));
for(auto i:oform)
graph[dict[i.first.first]][dict[i.first.second]]=i.second;
// cout << "the maximum flow from v0 to v5 is:" << endl;
cout<<fordFulkerson(graph,V, 0, dict.size()-1);
return 0;
}
source=converge,不行

Exp++
- BFS用parent数组记录,同时可以找到一条从converge到source的路径,即找可增载轨道
- 图的遍历要不邻接表,要不邻接矩阵,搜索求路径backtrack,求节点BDFS,最近点Dijkstra/Floyd,优先次序key path torpo sort,仅仅判断连通性+求最小生成树(Kruskal)用并查集,再了不起最大流

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








