Stacking
Arrays can be stacked horizontally, depth wise, or vertically. We can use, for that purpose, thevstack(),dstack(), hstack(), column_stack(),row_stack(), andconcatenate() functions.
Time for action--stacking arrays
First, set up some arrays:
In: a = arange(9).reshape(3,3)
In: a
Out:
array([[0, 1, 2],
[3, 4, 5],
[6, 7, 8]])
In: b = 2 * a
In: b
Out:
array([[0, 2, 4],
[6, 8 ,10],
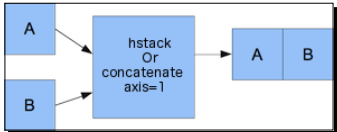
[12, 14, 16]])1. Horizontal stacking: Starting with horizontal stacking, form a tuple of the ndarray objects and give it to the hstack() function as follows:
In: hstack((a,b))
Out:
array([[0, 1, 2, 0, 2, 4],
[3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10],
[6, 7, 8, 12, 14, 16]])In: concatenate((a,b),axis=1)
Out:
array([[0, 1, 2, 0, 2, 4],
[3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10],
[6, 7, 8, 12, 14, 16]])
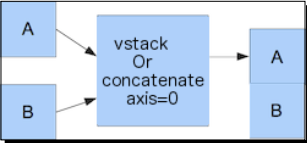
2. Vertical stacking: WIth vertical stacking, again, a tuple is formed. This time, it is given to thevstack() function as follows:
In: vstack((a,b))
Out:
array([[0, 1, 2],
[3, 4, 5],
[6, 7, 8],
[0, 2, 4],
[6, 8, 10],
[12, 14, 16]])In: concatenate((a,b), axis=0)
Out:
array([[0, 1, 2],
[3, 4, 5],
[6, 7, 8],
[0, 2, 4],
[6, 8, 10],
[12, 14, 16]])
The following diagram shows vertical stacking with concatenate() function:
3. Depth stacking: Additionally, depth-wise stacking using dstack() and a tuple stacks a list of arrays along the third axis(deoth). For instance, stack two-dimension arrays of image data on top of each other:
In: dstack((a,b))
Out:
array([[[0, 0],
[1, 2],
[2, 4]],
[[3, 6],
[4, 8],
[5, 10]],
[[6, 12],
[7, 14],
[8, 16]]])4. Column stacking: Stacking the one-dimensional arrays with the column_stack() function column-wise as follows:
In: oned = arange(2)
In: oned
Out: array([0,1])
In: twice_oned = 2 * oned
In: twice_oned
Out: array([0,2])
In: column_stack((oned, twice_oned))
Out:
array([[0,0],
[1,2]])In: column_stack((a,b))
Out:
array([[0, 1, 2, 0, 2, 4],
[3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10],
[6, 7, 8, 12, 14, 16]])
In: column_stack((a,b)) == hstack((a,b))
Out:
array([[True, True, True, True, True, True],
[True, True, True, True, True, True],
[True, True, True, True, True, True]], dtype=bool)The == operator is used in Python to compare for equality. When applied to Numpy arrays, the operator performs element-wise comparisons.
5. Row stacking:Numpy, of course, also has a function that does row-wise stacking.
It is called row_stack(), and for one-dimensional arrays, it just stacks the arrays in rows into atwo-dimensional array:
In: row_stack((oned, twice_oned))
Out:
array([[0,1],
[0,2]])In: row_stack((a,b))
Out:
array([[0, 1, 2],
[3, 4, 5],
[6, 7, 8],
[0, 2, 4],
[6, 8, 10],
[12, 14, 16]])
In: row_stack((a,b)) == vstack((a,b))
Out:
array([[True, True, True],
[True, True, True],
[True, True, True],
[True, True, True],
[True, True, True],
[True, True, True]], dtype=bool)





















 698
698











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








