The following tables compare general and technical information for a number of relational database management systems. Please see the individual products' articles for further information. This article is not all-inclusive or necessarily up-to-date. Unless otherwise specified in footnotes, comparisons are based on the stable versions without any add-ons, extensions or external programs.
Contents[hide] |
[edit] General information
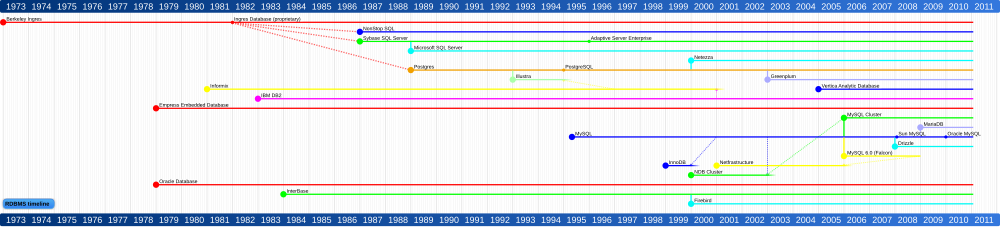
[edit] Timeline
Timeline of the development of major RDBMS software:
[edit] Operating system support
The operating systems the RDBMSes can run on.
 | Windows | Mac OS X | Linux | BSD | UNIX | AmigaOS | Symbian | z/OS1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4th Dimension | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| ADABAS | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| Adaptive Server Enterprise | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No |
| Advantage Database Server | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | No |
| Altibase | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | No |
| Apache Derby2 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| CUBRID | Yes | Partial10 | Yes | No | No | No | No | No |
| Drizzle | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No |
| DB25 | Yes | Yes (Express C) | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| Empress Embedded Database | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No |
| Firebird | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Maybe |
| HSQLDB2 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| H22 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| FileMaker | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Informix Dynamic Server | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| Ingres | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Partial |
| InterBase | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes (Solaris) | No | No | No |
| Linter SQL RDBMS6 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes6 | No | No | No |
| LucidDB | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | No | No |
| MaxDB | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | Maybe |
| Microsoft Access (JET) | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Microsoft Visual Foxpro | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Microsoft SQL Server | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Microsoft SQL Server Compact (Embedded Database) | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| MonetDB | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | No |
| MySQL8 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Navibase | Partial | Yes | Partial | Partial | No | No | No | No |
| Omnis Studio | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | No | No |
| OpenBase SQL | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No |
| Oracle4 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| Oracle Rdb3 | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | |
| OpenEdge | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | No |
| OpenLink Virtuoso | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| Pervasive PSQL | Yes | Yes (OEM only) | Yes | No | No | No | No | No |
| Polyhedra7 | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | No |
| PostgreSQL | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No |
| R:Base | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| RDM Embedded | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No |
| RDM Server | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No |
| ScimoreDB | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| SmallSQL2 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| SQL Anywhere | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | No |
| SQLBase | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | No |
| SQLite | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Maybe |
| Superbase | Yes | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | No |
| Teradata | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | No |
| UniData | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | No |
| UniVerse | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | No |
Note (1): Open source databases listed as UNIX-compatible will likely compile and run under z/OS’s built-in UNIX System Services (USS) subsystem. Most databases listed as Linux-compatible can run alongside z/OS on the same server using Linux on zSeries.
Note (2): The database availability depends on Java Virtual Machine not on the operating system
Note (3): Oracle Rdb was originally developed by DEC, and runs on OpenVMS
Note (4): Oracle database 11g also runs on OpenVMS, HP/UX and AIX. Mac OS X is limited to 10gR2. 10g also supported BS2000/OSD and z/OS (31-bit), but that support has been discontinued in 11g. Earlier versions than 10g were available on a wide variety of platforms.
Note (5): DB2 is also available for i5/OS, z/VM, z/VSE. Previous versions were also available for OS/2.
Note (6): Linter SQL RDBMS also runs on OpenVMS, Solaris, QNX, OS9000 and OS9.
Note (7): Polyhedra also runs on AIX, OSE, Solaris, LynxOS and VxWorks. Previous versions also ran on Ultrix, VMS and pSOS. Source code kits allow customers to port to other platforms.
Note (8): MySQL also runs on Solaris, Opensolaris, and can be made from source on other platforms as well.
Note (9): Binaries are not yet available for Mac OS X and BSD.
Note (10): CUBRID provides a client interface of its RDBMS for Mac OS X called the CUBRID Manager, which can be used for remote CUBRID connection.
[edit] Fundamental features
Information about what fundamental RDBMS features are implemented natively.
MySQL InnoDB is ACID compliant
 | ACID | Referential integrity | Transactions | Unicode | Interface |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4th Dimension | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | GUI & SQL |
| ADABAS | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | proprietary direct call & SQL (via 3rd party) |
| Adaptive Server Enterprise | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | SQL |
| Advantage Database Server | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes3 | API & SQL |
| Altibase | Yes | Yes | Yes | ? | SQL |
| Apache Derby | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | SQL |
| CUBRID | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | GUI & SQL |
| Drizzle | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | SQL |
| DB2 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | GUI & SQL |
| Empress Embedded Database | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | API & SQL |
| Firebird | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | SQL |
| HSQLDB | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | SQL |
| H2 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | SQL |
| Informix Dynamic Server | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | SQL |
| Ingres | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | SQL & QUEL |
| InterBase | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | SQL |
| Linter SQL RDBMS | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | GUI & SQL |
| LucidDB | Yes | No | No | Yes | SQL |
| MaxDB | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | SQL |
| Microsoft Access (JET) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | GUI & SQL |
| Microsoft Visual FoxPro | No | Yes | Yes | No | GUI & SQL |
| Microsoft SQL Server | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | GUI & SQL |
| Microsoft SQL Server Compact (Embedded Database) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | GUI & SQL |
| MonetDB | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ? |
| MySQL | Yes2 | Yes2 | Yes2 except for DDL [27] | Yes | SQL |
| Navibase | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | API & GUI & SQL |
| OpenBase SQL | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | GUI & SQL |
| Oracle | Yes | Yes | Yes except for DDL [27] | Yes | API & GUI & SQL |
| Oracle Rdb | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | SQL |
| OpenLink Virtuoso | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | API & GUI & SQL |
| Polyhedra DBMS | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | SQL |
| PostgreSQL | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | GUI & SQL |
| RDM Embedded | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | SQL & API |
| RDM Server | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | SQL & API |
| ScimoreDB | Yes | Yes | Yes | Partial | SQL |
| SQL Anywhere | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | SQL |
| SQLBase | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | API & GUI & SQL |
| SQLite | Yes | Yes | Yes | Optional[28] | SQL |
| Teradata | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | SQL |
| UniData | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Multiple |
| UniVerse | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Multiple |
| ACID | Referential integrity | Transactions | Unicode | Interface |
Note (1): Currently only supports read uncommited transaction isolation. Version 1.9 adds serializable isolation and version 2.0 will be fully ACID compliant.
Note (2): For ACID compliance with MySQL, the InnoDB storage engine must be chosen.[29][30]
Note (3): Support for Unicode is new in version 10.0.
[edit] Limits
Information about data size limits.
 | Max DB size | Max table size | Max row size | Max columns per row | Max Blob/Clob size | Max CHAR size | Max NUMBER size | Min DATE value | Max DATE value | Max column name size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4th Dimension | limited | ? | ? | 65135 | 200 GB (2 GiB Unicode) | 200 GB (2 GiB Unicode) | 64 bits | ? | ? | ? |
| Advantage Database Server | Unlimited | 16 EiB | 65530 B | 65135 / (10+ AvgFieldNameLength) | 4 GiB | ? | 64 bits | ? | ? | 128 |
| Apache Derby | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | 1012 (5000 in views) | 2 147 483 647 chars | 254 (VARCHAR: 32672) | ? | 0001-01-01 | 9999-12-31 | 128 |
| CUBRID | 2 EB | 2 EB | Unlimited | 6400 | Unlimited | 1 GB | 64 bits | 0001-01-01 | 9999-12-31 | 254 |
| Drizzle | Unlimited | 64 TB | 8 kB | 1000 | 4 GB (longtext, longblob) | 64 kB (text) | 64 bits | 0001 | 9999 | 64 |
| DB2 | 512 TiB | 512 TB | 32 677 B | 1012 | 2 GB | 32 KiB) | 64 bits | 0001 | 9999 | 128 |
| Empress Embedded Database | Unlimited | 263-1 bytes | 2 GB | 32767 | 2 GB | 2 GB | 64 bits | 0000-01-01 | 9999-12-31 | 32 |
| Firebird | Unlimited1 | ~32 TB | 65 536 B | Depends on data types used. | 2 GB | 32 767 B | 64 bits | 100 | 32768 | 31 |
| HSQLDB | 64 TB | Unlimited8 | Unlimited8 | Unlimited8 | 64 TB7 | Unlimited8 | Unlimited8 | 0001-01-01 | 9999-12-31 | 128 |
| H2 | 64 TB | Unlimited8 | Unlimited8 | Unlimited8 | 64 TB7 | Unlimited8 | 64 bits | -99999999 | 99999999 | Unlimited8 |
| Informix Dynamic Server | ~128 PB | ~128 PB | 32 765 bytes (exclusive of large objects) | 32765 | 4 TB | 32765 | 1032 | 01/01/000110 | 12/31/9999 | 128 bytes |
| Ingres | Unlimited | Unlimited | 256 kB | 1024 | 2 GB | 32 000 B | 64 bits | 0001 | 9999 | 32 |
| InterBase | Unlimited1 | ~32 TB | 65 536 B | Depends on data types used. | 2 GB | 32 767 B | 64 bits | 100 | 32768 | 31 |
| Linter SQL RDBMS | Unlimited | 230 rows | 64 kB (w/o BLOBs), 4 GB (BLOB) | 250 | 4 GB | 4 kB | 64 bits | 0001-01-01 | 2099-12-31 | 128 |
| Microsoft Access (JET) | 2 GB | 2 GB | 16 MB | 255 | 64 kB (memo field), 1 GB ("OLE Object" field) | 255 B (text field) | 32 bits | 0100 | 9999 | 64 |
| Microsoft Visual Foxpro | Unlimited | 2 GB | 65 500 B | 255 | 2 GB | 16 MB | 32 bits | 0001 | 9999 | ? |
| Microsoft SQL Server | 524 258 TB (32 767 files * 16 TB max file size) | 524 258 TB | Unlimited | 30000 | 2 GB | 2 GB6 | 126 bits2 | 0001 | 9999 | 128 |
| Microsoft SQL Server Compact (Embedded Database) | 4 GB | 4 GB | 8060 bytes | 1024 | 500 MB | 4000 | 126 bits 2 | 0001 | 9999 | 128 |
| MySQL 5 | Unlimited | MyISAM storage limits: 256 TB; Innodb storage limits: 64 TB | 64 kB3 | 40964 | 4 GB (longtext, longblob) | 64 kB (text) | 64 bits | 1000 | 9999 | 64 |
| Oracle | Unlimited (4 GB * block size per tablespace) | 4 GB * block size (with BIGFILE tablespace) | 8 kB | 1000 | Unlimited | 4000 B | 126 bits | -4712 | 9999 | 30 |
| Polyhedra | Limited by available RAM, address space | 232 rows | Unlimited | 65536 | 4 GB (subject to RAM) | 4 GB (subject to RAM) | 32 bits | 0001-01-01 | 8000-12-31 | 255 |
| PostgreSQL | Unlimited | 32 TB | 1.6 TB | 250-1600 depending on type | 1 GB (text, bytea) - stored inline or 2 GB (stored in pg_largeobject) | 1 GB | Unlimited | -4713 | 5874897 | 63 |
| ScimoreDB | Unlimited | 16 EB | 8050 B | 255 | 16 TB | 8000 B | 64 bits | ? | ? | ? |
| SQL Anywhere | 104 TB (13 files, each file up to 8 TB (32k pages)) | Limited by file size | Limited by file size | 45000 | 2 GB | 2 GB | 64 bits | 0001-01-01 | 9999-12-31 | ? |
| SQLite | 32 TB (230 pages * 32 kB max page size) | ? | ? | 32767 | 1 GB | 1 GB | 64 bits | No DATE type9 | No DATE type9 | ? |
| Teradata | Unlimited | Unlimited | 64 kB wo/lobs (64 GB w/lobs) | 2048 | 2 GB | 10 000 | 64 bits | ? | 9999-12-31 Select 80991231 (date); | 30 |
| UniVerse | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited |
| Max DB size | Max table size | Max row size | Max columns per row | Max Blob/Clob size | Max CHAR size | Max NUMBER size | Min DATE value | Max DATE value | Max column name size |
Note (1): Firebird 2.x maximum database size is effectively unlimited with the largest known database size >980 GB.[31] Firebird 1.5.x maximum database size: 32 TB.
Note (2): limit is 1038using DECIMAL datatype[32]
Note (3): InnoDB is limited to 8,000 bytes (excluding VARBINARY, VARCHAR, BLOB, or TEXT columns)[33]
Note (4): InnoDB is limited to 1,000 columns[33]
Note (6): Using VARCHAR (MAX) in SQL 2005 and later
Note (7): When using a page size of 32 kB, and when BLOB/CLOB data is stored in the database file.
Note (8): Java array size limit of 2,147,483,648 (231) objects per array applies. This limit applies to number of characters in names, rows per table, columns per table, and characters per CHAR/VARCHAR.
Note (9): Despite the lack of a date datatype, SQLite does include date and time functions,[34] which work for timestamps between 0000-01-01 00:00:00 and 5352-11-01 10:52:47.
Note (10): Informix DATETIME type has adjustable range from YEAR only through 1/10000th second. DATETIME date range is 0001-01-01 00:00:00.00000 through 9999-12-31 23:59:59.99999.
[edit] Tables and views
Information about what tables and views (other than basic ones) are supported natively.
 | Temporary table | Materialized view |
|---|---|---|
| 4th Dimension | Yes | Planned for inclusion in next major release |
| ADABAS | ? | ? |
| Adaptive Server Enterprise | Yes1 | No |
| Advantage Database Server | Yes | No (only common views) |
| Altibase | Yes | Yes |
| Apache Derby | Yes | No |
| CUBRID | No | No |
| Drizzle | Yes | No4 |
| DB2 | Yes | Yes |
| Empress Embedded Database | Yes | Yes |
| Firebird | Yes | No (only common views) |
| HSQLDB | Yes | No |
| H2 | Yes | No |
| Informix Dynamic Server | Yes | No2 |
| Ingres | Yes | Planned for inclusion in next major release |
| InterBase | Yes | No |
| Linter SQL RDBMS | Yes | No |
| LucidDB | No | No |
| MaxDB | Yes | No |
| Microsoft Access (JET) | No | No |
| Microsoft Visual Foxpro | Yes | Yes |
| Microsoft SQL Server | Yes | Yes3 |
| Microsoft SQL Server Compact (Embedded Database) | Yes | No |
| MonetDB | Yes | No |
| MySQL | Yes | No4 |
| OpenBase SQL | Yes | Yes |
| Oracle | Yes | Yes |
| Oracle Rdb | Yes | Yes |
| OpenLink Virtuoso | Yes | Yes |
| Polyhedra DBMS | No | No (only common views) |
| PostgreSQL | Yes | No5 |
| SQL Anywhere | Yes | Yes |
| ScimoreDB | No | No |
| SQLite | Yes | No |
| Teradata | Yes | Yes |
| UniData | Yes | No |
| UniVerse | Yes | No |
Note (1): Server provides tempdb, which can be used for public and private (for the session) temp tables.[35]
Note (2): Materialized views are not supported in Informix; the term is used in IBM’s documentation to refer to a temporary table created to run the view’s query when it is too complex, but one cannot for example define the way it is refreshed or build an index on it. The term is defined in the Informix Performance Guide.[36]
Note (3): Query optimizer support only in Developer and Enterprise Editions. In other versions, a direct reference to materialized view and a query hint are required.[37]
Note (4): Materialized views can be emulated using stored procedures and triggers.[38]
Note (5): Materialized views can be emulated with stored procedures and triggers using PL/pgSQL, PL/Perl, PL/Python, or other procedural languages.[39]
[edit] Indexes
Information about what indexes (other than basic B-/B+ tree indexes) are supported natively.
 | R-/R+ tree | Hash | Expression | Partial | Reverse | Bitmap | GiST | GIN | Full-text | Spatial | FOT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4th Dimension | ? | Cluster | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | |
| ADABAS | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | |
| Adaptive Server Enterprise | No | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | ? | |
| Advantage Database Server | No | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | ? | |
| Apache Derby | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No[40] | ? | |
| CUBRID | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | No | No | ? | ? | |
| Drizzle | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | ? | |
| DB2 | No | ? | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes[41] | ? | |
| Empress Embedded Database | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | No | ? | |
| Firebird | No | No | Yes | No | Yes 1 | No | No | No | No[42] | ? | |
| HSQLDB | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | ? | |
| H2 | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | Yes[43] | ? | |
| Informix Dynamic Server | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Ingres | Yes | Yes | Ingres v10 | No | No | Ingres v10 | No | No | No | ? | |
| InterBase | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | ? | |
| Linter SQL RDBMS10 | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | Yes[44] | ? | |
| LucidDB | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | No | No | ? | |
| MaxDB | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | ? | |
| Microsoft Access (JET) | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No[45] | ? | |
| Microsoft Visual Foxpro | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes2 | Yes | No | No | No | ? | |
| Microsoft SQL Server | ? | Non/Cluster & fill factor | Yes3 | Yes4 | No3 | No | No | No | Yes[46] | Yes[47] | |
| Microsoft SQL Server Compact (Embedded Database) | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No[48] | ? | |
| MonetDB | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | ? | ? | |
| MySQL | MyISAM tables only | MEMORY, Cluster (NDB), InnoDB,5 tables only | No[49] | No | No | No | No | No | MyISAM tables only[50] | ? | |
| Oracle | Yes 11 | Cluster Tables | Yes | Yes 6 | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes[51] | Yes[52] | |
| Oracle Rdb | No | Yes | ? | No | No | ? | No | No | ? | ? | |
| OpenLink Virtuoso | Yes | Cluster | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | ? | |
| Polyhedra DBMS | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | ? | ? | |
| PostgreSQL | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes7 | Yes8 | Yes | Yes | Yes[53] | Postgis[54] | |
| ScimoreDB | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | Yes[55] | ? | |
| SQL Anywhere | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | ? | |
| SQLite | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | No | No | No | Yes[56] | SpatiaLite[57] | |
| Teradata | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | ?[58] | ? | |
| UniVerse | Yes | Yes | Yes3 | Yes3 | Yes3 | No | No | No | ? | ? | |
| R-/R+ tree | Hash | Expression | Partial | Reverse | Bitmap | GiST | GIN | Full-text | Spatial |
Note (1): The users need to use a function from freeAdhocUDF library or similar.[59]
Note (2): Can be implemented for most data types using expression-based indexes.
Note (3): Can be emulated by indexing a computed column[60] (doesn't easily update) or by using an "Indexed View"[61] (proper name not just any view works[62])
Note (4): Can be implemented by using an indexed view.[63]
Note (5): InnoDB automatically generates adaptive hash index[64] entries as needed.
Note (6): Can be implemented using Function-based Indexes in Oracle 8i and higher, but the function needs to be used in the sql for the index to be used.
Note (7): A PostgreSQL functional index can be used to reverse the order of a field.
Note (8): PostgreSQL will likely support on-disk bitmap indexes in a future version. Version 8.2 supports a related technique known as "in-memory bitmap scans".
Note (10): B+ tree and full-text only for now.
Note (11): R-Tree indexing available in base edition with Locator but some functionality requires Personal Edition or Enterprise Edition with Spatial option
[edit] Database capabilities
 | Union | Intersect | Except | Inner joins | Outer joins | Inner selects | Merge joins | Blobs and Clobs | Common Table Expressions | Windowing Functions | Parallel Query |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4th Dimension | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | ? | ? | ? |
| ADABAS | Yes | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? |
| Adaptive Server Enterprise | Yes | ? | ? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ? | ? | Yes |
| Advantage Database Server | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ? | No | ? |
| Altibase | Yes | ? | ? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ? | ? | ? |
| Apache Derby | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ? | ? | Yes | No | No | ? |
| CUBRID | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | ? |
| Drizzle | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | No[65] |
| DB2 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes[66] |
| Empress Embedded Database | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ? | ? | ? |
| Firebird | Yes | ? | ? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ? |
| HSQLDB | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| H2 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | experimental[67] | No[68] | ? |
| Informix Dynamic Server | Yes | ? | Yes, via MINUS | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ? | Yes[69] |
| Ingres | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | ? |
| InterBase | Yes | ? | ? | Yes | Yes | ? | ? | Yes | ? | ? | ? |
| Linter SQL RDBMS | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | ? |
| LucidDB | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | ? | ? | ? |
| MaxDB | Yes | ? | ? | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | ? | ? | ? |
| Microsoft Access (JET) | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | ? |
| Microsoft Visual Foxpro | Yes | ? | ? | Yes | Yes | Yes | ? | Yes | ? | ? | ? |
| Microsoft SQL Server | Yes | Yes (2005 and beyond) | Yes (2005 and beyond) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes[70] |
| Microsoft SQL Server Compact (Embedded Database) | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | ? | No | Yes | No | No | ? |
| MonetDB | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? |
| MySQL | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No[71] | No | No[72] |
| OpenBase SQL | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ? | ? | ? |
| Oracle | Yes | Yes | Yes, via MINUS | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes 1 | Yes | Yes[73] |
| Oracle Rdb | Yes | ? | ? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ? | ? | ? |
| OpenLink Virtuoso | Yes | ? | ? | Yes | Yes | Yes | ? | Yes | ? | ? | ? |
| Polyhedra DBMS | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | ? | ? | Yes | ? | ? | ? |
| PostgreSQL | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No[74] |
| ScimoreDB | Yes | ? | ? | Yes | LEFT only | Yes | Yes | Yes | ? | ? | ? |
| SmallSQL | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? |
| SQL Anywhere | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ? |
| SQLite | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | LEFT only | Yes | ? | Yes | No | No | ? |
| Teradata | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| UniVerse | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | ? |
| Union | Intersect | Except | Inner joins | Outer joins | Inner selects | Merge joins | Blobs and Clobs | Common Table Expressions | Windowing Functions | Parallel Query |
Note (1): Recursive CTEs introduced in 11gR2 supersedes similar construct called CONNECT BY
[edit] Data types
 | Type system | Integer | Floating point | Decimal | String | Binary | Date/Time | Boolean | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CUBRID[75] | Static | SMALLINT (16-bit), INTEGER (32-bit), BIGINT (64-bit) | FLOAT, REAL(32-bit), DOUBLE(64-bit) | DECIMAL, NUMERIC | CHAR, VARCHAR, NCHAR, NVARCHAR, CLOB | BLOB | DATE, DATETIME, TIME, TIMESTAMP | BIT | MONETARY, BIT VARYING, SET, MULTISET, SEQUENCE |
| Drizzle[76] | Static | INT (32-bit), BIGINT (64-bit) | DOUBLE (aka REAL) (64-bit) | DECIMAL | BINARY, VARCHAR, VARBINARY, TEXT, | BLOB | DATETIME, DATE, TIMESTAMP | ENUM, SERIAL | |
| Empress Embedded Database | Static | TINYINT, SQL_TINYINT or INTEGER8 SMALLINT, SQL_SMALLINT or INTEGER16 INTEGER, INT, SQL_INTEGER or INTEGER32 BIGINT, SQL_BIGINT or INTEGER64 | REAL, SQL_REAL or FLOAT32 DOUBLE PRECISION, SQL_DOUBLE or FLOAT64 FLOAT or SQL_FLOAT EFLOAT | DECIMAL, DEC, NUMERIC, SQL_DECIMAL or SQL_NUMERIC DOLLAR | CHARACTER, ECHARACTER, CHARACTER VARYING, NATIONAL CHARACTER, NATIONAL CHARACTER VARYING and NLSCHARACTER CHARACTER LARGE OBJECT, TEXT, NATIONAL CHARACTER LARGE OBJECT, and NLSTEXT | BINARY LARGE OBJECT or BLOB BULK | DATE, EDATE, TIME, ETIME, EPOCH_TIME, TIMESTAMP, MICROTIMESTAMP | BOOLEAN | SEQUENCE 32 SEQUENCE |
| HSQLDB[77] | Static | TINYINT (8-bit), SMALLINT (16-bit), INTEGER (32-bit), BIGINT (64-bit) | DOUBLE (64-bit) | DECIMAL, NUMERIC | CHAR, VARCHAR, LONGVARCHAR, CLOB | BINARY, VARBINARY, LONGVARBINARY, BLOB | DATE, TIME, TIMESTAMP, INTERVAL | BOOLEAN | OTHER (object), BIT, BIT VARYING, ARRAY |
| Informix Dynamic Server[78] | Static | SMALLINT (16-bit), INT (32-bit), INT8 (64-bit proprietary), BIGINT (64-bit) | SMALLFLOAT (32-bit), FLOAT (64-bit) | DECIMAL (32 digits float/fixed), MONEY | CHAR, VARCHAR, NCHAR, NVARCHAR, LVARCHAR, CLOB, TEXT | TEXT, BYTE, BLOB, CLOB | DATE, DATETIME, INTERVAL | BOOLEAN | SET, LIST, MULTISET, ROW, TIMESERIES, SPATIAL, USER DEFINED TYPES |
| Ingres[79] | Static | TINYINT (8-bit), SMALLINT (16-bit), INTEGER (32-bit), BIGINT (64-bit) | FLOAT4 (32-bit), FLOAT (64-bit) | DECIMAL | C, CHAR, VARCHAR, LONG VARCHAR, NCHAR, NVARCHAR, LONG NVARCHAR, TEXT | BYTE, VARBYTE, LONG VARBYTE (BLOB) | DATE, ANSIDATE, INGRESDATE, TIME, TIMESTAMP, INTERVAL | N/A | MONEY, OBJECT_KEY, TABLE_KEY, USER-DEFINED DATA TYPES (via OME) |
| Microsoft SQL Server[80] | Static | TINYINT, SMALLINT, INT, BIGINT | FLOAT, REAL | NUMERIC, DECIMAL, SMALLMONEY, MONEY | CHAR, VARCHAR, TEXT, NCHAR, NVARCHAR, NTEXT | BINARY, VARBINARY, IMAGE, FILESTREAM | DATE, DATETIMEOFFSET, DATETIME2, SMALLDATETIME, DATETIME, TIME | BIT | CURSOR, TIMESTAMP, HIERARCHYID, UNIQUEIDENTIFIER, SQL_VARIANT, XML, TABLE |
| Microsoft SQL Server Compact (Embedded Database)[81] | Static | TINYINT, SMALLINT, INT, BIGINT | FLOAT, REAL | NUMERIC, DECIMAL, MONEY | NCHAR, NVARCHAR, NTEXT | BINARY, VARBINARY, IMAGE | DATETIME | BIT | TIMESTAMP, ROWVERSION, UNIQUEIDENTIFIER, IDENTITY, ROWGUIDCOL |
| MySQL[82] | Static | TINYINT (8-bit), SMALLINT (16-bit), MEDIUMINT (24-bit), INT (32-bit), BIGINT (64-bit) | FLOAT (32-bit), DOUBLE (aka REAL) (64-bit) | DECIMAL | CHAR, BINARY, VARCHAR, VARBINARY, TEXT, TINYTEXT, MEDIUMTEXT, LONGTEXT | TINYBLOB, BLOB, MEDIUMBLOB, LONGBLOB | DATETIME, DATE, TIMESTAMP, YEAR | BOOLEAN (aka BOOL) = synonym for TINYINT | ENUM, SET, GIS data types (Geometry, Point, Curve, LineString, Surface, Polygon, GeometryCollection, MultiPoint, MultiCurve, MultiLineString, MultiSurface, MultiPolygon) |
| Oracle[83] | Static + Dynamic (through ANYDATA) | NUMBER | BINARY_FLOAT, BINARY_DOUBLE | NUMBER | CHAR, VARCHAR2, CLOB, NCLOB, NVARCHAR2, NCHAR | BLOB, RAW, LONGRAW, BFILE | DATE, TIMESTAMP (with/without TIMEZONE), INTERVAL | N/A | SPATIAL, IMAGE, AUDIO, VIDEO, DICOM, XMLType |
| Polyhedra | Static | INTEGER8 (8-bit), INTEGER(16-bit), INTEGER (32-bit) | FLOAT32 (32-bit), FLOAT (aka REAL; 64-bit) | N/A | VARCHAR, LARGE VARCHAR (aka CHARACTER LARGE OBJECT) | LARGE BINARY (aka BINARY LARGE OBJECT) | DATETIME | BOOLEAN | N/A |
| PostgreSQL[84] | Static | SMALLINT (16-bit), INTEGER (32-bit), BIGINT (64-bit) | REAL (32-bit), DOUBLE PRECISION (64-bit) | DECIMAL, NUMERIC | CHAR, VARCHAR, TEXT | BYTEA | DATE, TIME (with/without TIMEZONE), TIMESTAMP (with/without TIMEZONE), INTERVAL | BOOLEAN | ENUM, POINT, LINE, LSEG, BOX, PATH, POLYGON, CIRCLE, CIDR, INET, MACADDR, BIT, UUID, XML, arrays |
| SQLite[85] | Dynamic | INTEGER (64-bit) | REAL (aka FLOAT, DOUBLE) (64-bit) | N/A | TEXT (aka CHAR, CLOB) | BLOB | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| UniData | Dynamic | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| UniVerse | Dynamic | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Type system | Integer | Floating point | Decimal | String | Binary | Date/Time | Boolean | Other |
[edit] Other objects
Information about what other objects are supported natively.
 | Data Domain | Cursor | Trigger | Function 1 | Procedure 1 | External routine 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4th Dimension | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| ADABAS | ? | Yes | ? | Yes? | Yes? | ? |
| Adaptive Server Enterprise | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Advantage Database Server | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Apache Derby | No | Yes | Yes | Yes 2 | Yes 2 | Yes 2 |
| CUBRID | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes 2 | Yes |
| Drizzle | Yes | Yes | Yes 4 | Yes 4 | Yes 4 | Yes 4 |
| Empress Embedded Database | Yes via RANGE CHECK | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| DB2 | Yes via CHECK CONSTRAINT | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Firebird | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| HSQLDB | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| H2 | Yes | No | Yes 2 | Yes 2 | Yes 2 | Yes |
| Informix Dynamic Server | Yes via CHECK | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Ingres | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| InterBase | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Linter SQL RDBMS | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| LucidDB | No | Yes | No | Yes 2 | Yes 2 | Yes 2 |
| MaxDB | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ? |
| Microsoft Access (JET) | Yes | No | No | No | Yes, But single DML/DDL Operation | Yes |
| Microsoft Visual Foxpro | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Microsoft SQL Server | Yes (2000 and beyond) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Microsoft SQL Server Compact (Embedded Database) | No | Yes | No | No | No | No |
| MonetDB | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| MySQL | No 3 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| OpenBase SQL | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Oracle | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Oracle Rdb | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| OpenLink Virtuoso | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Polyhedra DBMS | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| PostgreSQL | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| ScimoreDB | No | No | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| SQL Anywhere | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| SQLite | No | No | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| Teradata | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| UniData | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| UniVerse | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Data Domain | Cursor | Trigger | Function 1 | Procedure 1 | External routine 1 |
Note (1): Both function and procedure refer to internal routines written in SQL and/or procedural language like PL/SQL. External routine refers to the one written in the host languages, such as C, Java, Cobol, etc. "Stored procedure" is a commonly used term for these routine types. However, its definition varies between different database vendors.
Note (2): In Derby, H2, LucidDB, and CUBRID, users code functions and procedures in Java.
Note (3): ENUM datatype exist. CHECK clause is parsed, but not enforced in runtime.
Note (4): In Drizzle the user codes functions and procedures in C++.
[edit] Partitioning
Information about what partitioning methods are supported natively.
 | Range | Hash | Composite (Range+Hash) | List | Native Replication API |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4th Dimension | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? |
| ADABAS | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? |
| Adaptive Server Enterprise | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | ? |
| Advantage Database Server | No | No | No | No | Yes |
| Apache Derby | No | No | No | No | ? |
| CUBRID | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | ? |
| IBM DB2 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ? |
| Empress Embedded Database | No | No | No | No | Yes |
| Firebird | No | No | No | No | No |
| HSQLDB | No | No | No | No | No |
| H2 | No | No | No | No | No |
| Informix Dynamic Server | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Ingres | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| InterBase | No | No | No | No | Yes |
| Linter SQL RDBMS | No | No | No | No | No |
| MaxDB | No | No | No | No | ? |
| Microsoft Access (JET) | No | No | No | No | Yes |
| Microsoft Visual Foxpro | No | No | No | No | No |
| Microsoft SQL Server | Yes | No | No | No | ? |
| Microsoft SQL Server Compact (Embedded Database) | No | No | No | No | Yes |
| MonetDB | Yes (M5) | Yes (M5) | Yes (M5) | No | ? |
| MySQL | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ? |
| OpenBase SQL | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? |
| Oracle | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ? |
| Oracle Rdb | Yes | Yes | ? | ? | ? |
| OpenLink Virtuoso | Yes | No | No | No | ? |
| Polyhedra DBMS | No | No | No | No | No |
| PostgreSQL | Yes1 | Yes1 | Yes1 | Yes1 | ? |
| ScimoreDB | No | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| SQL Anywhere | No | No | No | No | ? |
| SQLite | No | No | No | No | ? |
| Teradata | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ? |
| UniVerse | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Range | Hash | Composite (Range+Hash) | List | Native Replication API |
Note (1): PostgreSQL 8.1 provides partitioning support through check constraints. Range, List and Hash methods can be emulated with PL/pgSQL or other procedural languages.[86]
[edit] Access control
Information about access control functionalities (work in progress).
 | Native network encryption1 | Brute-force protection | Enterprise directory compatibility | Password complexity rules2 | Patch access3 | Run unprivileged4 | Audit | Resource limit | Separation of duties (RBAC)5 | Security Certification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adaptive Server Enterprise | Yes (optional; to pay) | Yes | Yes (optional ?) | Yes | Partial (need to register; depend on which product)[87] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes (EAL4+ 1) |
| Advantage Database Server | Yes | No | No | No | ? | Yes | No | No | Yes | ? |
| DB2 | Yes | ? | Yes (LDAP, Kerberos…) | Yes | ? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes (EAL4+6) |
| Empress Embedded Database | ? | ? | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Firebird | No | Yes[88] | Yes (Windows trusted authenification) | No | Partial (no security page)[89] | Yes | No | No | No7 | ? |
| HSQLDB | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | No |
| H2 | Yes | Yes | ? | No | ? | Yes | ? | Yes | Yes | No |
| Informix Dynamic Server | Yes | ? | Yes10 | ?10 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ? |
| Linter SQL RDBMS | Yes (with SSL) | Yes | No | Yes (length only) | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| MySQL | Yes (SSL with 4.0) | No | Yes (with 5.5) | No | Partial (no security page)[90] | Yes | ? | ? | ?8 | No |
| OpenBase SQL | Yes | ? | Yes (Open Directory, LDAP) | No | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? |
| Microsoft SQL Server | Yes | ? | Yes (Microsoft Active Directory) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes (From 2008) | Yes | Yes | Yes (EAL1+1) |
| Microsoft SQL Server Compact (Embedded Database) | No (not relevant, only file permissions) | No (not relevant) | No (not relevant) | No (not relevant) | Yes | Yes (file access) | Yes | Yes | No | ? |
| Oracle | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes (EAL4+1) |
| PostgreSQL | Yes | No | Yes (LDAP, Kerberos…9) | Yes (as of 9.0 with passwordcheck module) | Yes[91] | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes (EAL11) |
| SQL Anywhere | Yes | ? | Yes (Kerberos) | Yes | ? | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes (EAL3+1 as Adaptive Server Anywhere) |
| SQLite | No (not relevant, only file permissions) | No (not relevant) | No (not relevant) | No (not relevant) | Partial (no security page)[92] | Yes (file access) | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Native network encryption1 | Brute-force protection | Enterprise directory compatibility | Password complexity rules2 | Patch access3 | Run unprivileged4 | Audit | Resource limit | Separation of duties (RBAC)5 | Security Certification |
Note (1): Network traffic could be transmitted in a secure way (not clear-text, en general SSL encryption). Precise if option is default, included option or an extra modules to buy.
Note (2): Options are present to set a minimum size for password, respect complexity like presence of numbers or special characters.
Note (3): How do you get security updates? Is it free access, do you need a login or to pay? Is there easy access through a Web/FTP portal or RSS feed or only through offline access (mail CD-ROM, phone).
Note (4): Does database process run as root/administrator or unprivileged user? What is default configuration?
Note (5): Is there a separate user to manage special operation like backup (only dump/restore permissions), security officer (audit), administrator (add user/create database), etc.? Is it default or optional?
Note (6): Common Criteria certified product list[93]
Note (7): FirebirdSQL seems to only have SYSDBA user and DB owner. There are no separate roles for backup operator and security administrator.
Note (8): User can define a dedicated backup user but nothing particular in default install[94]
Note (9): Authentication methods[95]
Note (10): Informix Dynamic Server supports PAM and other configurable authentication. By default uses OS authentication.
[edit] Databases vs schemas (terminology)
|
| This section may contain original research. Please improve it by verifying the claims made and adding references. Statements consisting only of original research may be removed. More details may be available on the talk page. (June 2010) |
The SQL specification makes clear what an "SQL schema" is; however, different databases implement it incorrectly. To compound this confusion the functionality can, when incorrectly implemented, overlap with that of the parent-database. An SQL schema is simply a namespace within a database, things within this namespace are addressed using the member operator dot ".". This seems to be a universal amongst all of the implementations.
A true fully (database, schema, and table) qualified query is exemplified as such: SELECT * FROM database.schema.table
Now, the issue, both a schema and a database can be used to isolate one table, "foo" from another like named table "foo". The following is pseudo code:
SELECT * FROM db1.foovs.SELECT * FROM db2.foo(no explicit schema between db and table)SELECT * FROM [db1.]default.foovs.SELECT * FROM [db1.]alternate.foo(no explicit db prefix)
The problem that arises is that former MySQL users will create multiple databases for one project. In this context, MySQL databases are analogous in function to Postgres-schemas, insomuch as Postgres lacks off-the-shelf cross-database functionality that MySQL has. Conversely, PostgreSQL has applied more of the specification implementing cross-table, cross-schema, and then left room for future cross-database functionality.
MySQL aliases schema with database behind the scenes, such that CREATE SCHEMA and CREATE DATABASE are analogs. It can therefore be said that MySQL has implemented cross-table functionality, skipped schema functionality entirely, and provided similar functionality into their implementation of a database. In summary, Postgres fully supports schemas but lacks some functionality MySQL has with databases, while MySQL does not even attempt to support true schemas.
Oracle has its own spin where creating a user is synonymous with creating a schema. Thus a database administrator can create a user called PROJECT and then create a table PROJECT.TABLE. Users can exist without schema objects, but an object is always associated with an owner (though that owner may not have privileges to connect to the database). With the Oracle 'shared-everything' RAC architecture, the same database can be opened by multiple servers concurrently. This is independent of replication, which can also be used, whereby the data is copied for use by different server. In the Oracle view, the 'database' is a set of files which contains the data while the 'instance' is a set of processes (and memory) through which a database is accessed.
The end result is confusion between the database factions. The Postgres and Oracle communities maintain that one database is all that is needed for one project, per the definition of database. MySQL proponents maintain that schemas have no legitimate purpose when the functionality can be achieved with databases. Postgres adheres to the SQL specification, in a more intuitive fashion (bottom-up), while MySQL’s pragmatic counterargument allows their users to get the job done while creating conceptual confusion.






















 1530
1530

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








