The Rotation Game
| Time Limit: 15000MS | Memory Limit: 150000K | |
| Total Submissions: 4983 | Accepted: 1655 |
Description
The rotation game uses a # shaped board, which can hold 24 pieces of square blocks (see Fig.1). The blocks are marked with symbols 1, 2 and 3, with exactly 8 pieces of each kind.
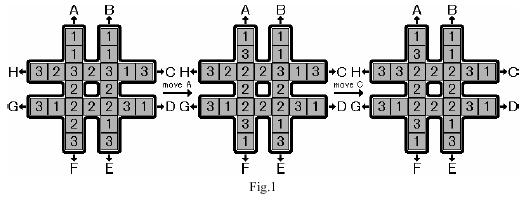
Initially, the blocks are placed on the board randomly. Your task is to move the blocks so that the eight blocks placed in the center square have the same symbol marked. There is only one type of valid move, which is to rotate one of the four lines, each consisting of seven blocks. That is, six blocks in the line are moved towards the head by one block and the head block is moved to the end of the line. The eight possible moves are marked with capital letters A to H. Figure 1 illustrates two consecutive moves, move A and move C from some initial configuration.

Initially, the blocks are placed on the board randomly. Your task is to move the blocks so that the eight blocks placed in the center square have the same symbol marked. There is only one type of valid move, which is to rotate one of the four lines, each consisting of seven blocks. That is, six blocks in the line are moved towards the head by one block and the head block is moved to the end of the line. The eight possible moves are marked with capital letters A to H. Figure 1 illustrates two consecutive moves, move A and move C from some initial configuration.
Input
The input consists of no more than 30 test cases. Each test case has only one line that contains 24 numbers, which are the symbols of the blocks in the initial configuration. The rows of blocks are listed from top to bottom. For each row the blocks are listed from left to right. The numbers are separated by spaces. For example, the first test case in the sample input corresponds to the initial configuration in Fig.1. There are no blank lines between cases. There is a line containing a single `0' after the last test case that ends the input.
Output
For each test case, you must output two lines. The first line contains all the moves needed to reach the final configuration. Each move is a letter, ranging from `A' to `H', and there should not be any spaces between the letters in the line. If no moves are needed, output `No moves needed' instead. In the second line, you must output the symbol of the blocks in the center square after these moves. If there are several possible solutions, you must output the one that uses the least number of moves. If there is still more than one possible solution, you must output the solution that is smallest in dictionary order for the letters of the moves. There is no need to output blank lines between cases.
Sample Input
1 1 1 1 3 2 3 2 3 1 3 2 2 3 1 2 2 2 3 1 2 1 3 3 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 0
Sample Output
AC 2 DDHH 2
题意:两行两列数(只能是1~3),组成一个“井”字型棋盘,每次操作能循环移动其中一行或一列,目标是让棋盘中心的数相同。输出移动方案(步数最小,字典序最小)。
思路:IDA* 搜索
这是本人第一篇博客,它也是有故事的。。因为本人喜欢玩魔方,喜欢写程序,就一直想写解魔方的程序。百度之,用IDA*,高大上,不懂。。。后来加入了ACM,就一直对搜索题情有独钟,经过一段时间,终于AC了第一道用IDA*的题目。
个人感觉,这个IDA*就是一个经过强力剪枝的DFS,能够提前“预判”到没有前途的路径,把它舍弃掉。在这个程序中,get_h()用于预估当前状态与目标态的距离,既不能高估又必须尽可能准确。估价函数起到了非常重要的作用,如果没有一个有效的估价函数,IDA*也就没有了意义。
偷了点懒,没有写判重,不过似乎不影响。废话不说,上代码:
- #include <iostream>
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <cmath>
- #include <algorithm>
- #include <iomanip>
- #include <cstdlib>
- #include <string>
- #include <memory.h>
- #include <vector>
- #include <queue>
- #include <stack>
- #include <ctype.h>
- using namespace std;
- int puzzle [8][8];
- int get_h(){
- int a=0;
- int b=0;
- int c=0;
- for(int i=3;i<6;i++){
- for(int j=3;j<6;j++){
- if(puzzle[i][j]==1)a++;
- if(puzzle[i][j]==2)b++;
- if(puzzle[i][j]==3)c++;
- }
- }
- int ans=max(a,b);
- ans=max(ans,c);
- return 8-ans;
- }
- void input(){
- scanf("%d",&puzzle[1][5]);
- scanf("%d",&puzzle[2][3]);
- scanf("%d",&puzzle[2][5]);
- for(int i=1;i<=7;i++){
- scanf("%d",&puzzle[3][i]);
- }
- scanf("%d",&puzzle[4][3]);
- scanf("%d",&puzzle[4][5]);
- for(int i=1;i<=7;i++){
- scanf("%d",&puzzle[5][i]);
- }
- scanf("%d",&puzzle[6][3]);
- scanf("%d",&puzzle[6][5]);
- scanf("%d",&puzzle[7][3]);
- scanf("%d",&puzzle[7][5]);
- }
- void A(){
- int tmp=puzzle[1][3];
- for(int i=1;i<7;i++){
- puzzle[i][3]=puzzle[i+1][3];
- }
- puzzle[7][3]=tmp;
- }
- void B(){
- int tmp=puzzle[1][5];
- for(int i=1;i<7;i++){
- puzzle[i][5]=puzzle[i+1][5];
- }
- puzzle[7][5]=tmp;
- }
- void C(){
- int tmp=puzzle[3][7];
- for(int i=7;i>1;i--){
- puzzle[3][i]=puzzle[3][i-1];
- }
- puzzle[3][1]=tmp;
- }
- void D(){
- int tmp=puzzle[5][7];
- for(int i=7;i>1;i--){
- puzzle[5][i]=puzzle[5][i-1];
- }
- puzzle[5][1]=tmp;
- }
- void E(){
- int tmp=puzzle[7][5];
- for(int i=7;i>1;i--){
- puzzle[i][5]=puzzle[i-1][5];
- }
- puzzle[1][5]=tmp;
- }
- void F(){
- int tmp=puzzle[7][3];
- for(int i=7;i>1;i--){
- puzzle[i][3]=puzzle[i-1][3];
- }
- puzzle[1][3]=tmp;
- }
- void G(){
- int tmp=puzzle[5][1];
- for(int i=1;i<7;i++){
- puzzle[5][i]=puzzle[5][i+1];
- }
- puzzle[5][7]=tmp;
- }
- void H(){
- int tmp=puzzle[3][1];
- for(int i=1;i<7;i++){
- puzzle[3][i]=puzzle[3][i+1];
- }
- puzzle[3][7]=tmp;
- }
- bool judge(){
- if( !(puzzle[3][3]-puzzle[3][4]) && !(puzzle[3][4]-puzzle[3][5]) && !(puzzle[3][4]-puzzle[3][5]) &&
- !(puzzle[3][5]-puzzle[4][5]) && !(puzzle[4][5]-puzzle[5][5]) && !(puzzle[5][5]-puzzle[5][4]) &&
- !(puzzle[5][4]-puzzle[5][3]) && !(puzzle[5][3]-puzzle[4][3]) ) {
- return true;
- }
- return false;
- }
- char ans[100];
- int depth=0;
- bool DFS(int d){
- if(d+get_h()>depth)return false;
- if(depth==d){
- if(judge()){
- return true;
- }else{
- return false;
- }
- }
- A();
- if(DFS(d+1)){ans[d]='A';return true;}
- F();
- B();
- if(DFS(d+1)){ans[d]='B';return true;}
- E();
- C();
- if(DFS(d+1)){ans[d]='C';return true;}
- H();
- D();
- if(DFS(d+1)){ans[d]='D';return true;}
- G();
- E();
- if(DFS(d+1)){ans[d]='E';return true;}
- B();
- F();
- if(DFS(d+1)){ans[d]='F';return true;}
- A();
- G();
- if(DFS(d+1)){ans[d]='G';return true;}
- D();
- H();
- if(DFS(d+1)){ans[d]='H';return true;}
- C();
- return false;
- }
- int main(){
- memset(puzzle,0,sizeof(puzzle));
- while(scanf("%d",&puzzle[1][3])){
- depth=0;
- memset(ans,0,sizeof(ans));
- if(!puzzle[1][3])break;
- input();
- while(!DFS(0)){
- depth++;
- }
- if(depth==0){
- printf("No moves needed\n");
- }else{
- printf("%s\n",ans);
- }
- printf("%d\n",puzzle[3][3]);
- }
- return 0;
- }
























 159
159

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








