lower_bound() 和 upper_bound() 是 C++ 标准库中的函数,用于在有序序列中查找目标值的插入位置。
lower_bound() 函数:
lower_bound() 函数返回一个迭代器,指向第一个不小于目标值的元素位置。
template<class ForwardIt, class T>
ForwardIt lower_bound(ForwardIt first, ForwardIt last, const T& value);
first和last:表示要搜索的有序序列的范围,[first, last) 是一个左闭右开区间。value:要查找的目标值。
lower_bound() 函数的返回值是一个迭代器,指向序列中第一个不小于目标值的元素的位置。如果序列中不存在不小于目标值的元素,则返回迭代器指向的位置为序列的末尾(即 last)。
upper_bound() 函数:
upper_bound() 函数返回一个迭代器,指向第一个大于目标值的元素位置。
template<class ForwardIt, class T>
ForwardIt upper_bound(ForwardIt first, ForwardIt last, const T& value);
first和last:表示要搜索的有序序列的范围,[first, last) 是一个左闭右开区间。value:要查找的目标值。
upper_bound() 函数的返回值是一个迭代器,指向序列中第一个大于目标值的元素的位置。如果序列中不存在大于目标值的元素,则返回迭代器指向的位置为序列的末尾(即 last)。
C++ 代码示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<int> nums = {1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6, 7};
int target = 4;
// 使用 lower_bound() 函数查找插入位置
auto lb = lower_bound(nums.begin(), nums.end(), target);
cout << "第一个不小于目标值4的元素的位置: " << distance(nums.begin(), lb) << endl;
// 使用 upper_bound() 函数查找插入位置
auto ub = upper_bound(nums.begin(), nums.end(), target);
cout << "第一个大于目标值4的元素的位置: " << distance(nums.begin(), ub) << endl;
return 0;
}
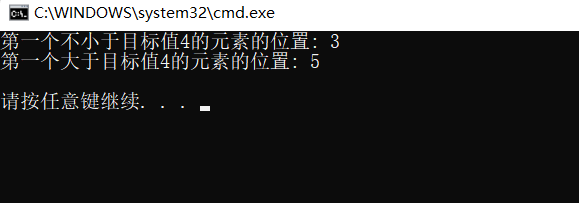
以上代码演示了如何使用 lower_bound() 和 upper_bound() 函数在有序序列中查找目标值的插入位置。给定一个有序序列 nums 和目标值 target,通过 lower_bound() 和 upper_bound() 函数找到第一个不小于目标值的位置和第一个大于目标值的位置。
希望这个解释和代码示例能够帮助你理解 lower_bound() 和 upper_bound() 函数的原理和使用方法。




















 5121
5121











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








