Description
Astronomers often examine star maps where stars are represented by points on a plane and each star has Cartesian coordinates. Let the level of a star be an amount of the stars that are not higher and not to the right of the given star. Astronomers want to know the distribution of the levels of the stars.
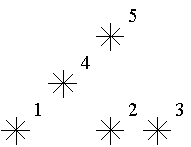
For example, look at the map shown on the figure above. Level of the star number 5 is equal to 3 (it's formed by three stars with a numbers 1, 2 and 4). And the levels of the stars numbered by 2 and 4 are 1. At this map there are only one star of the level 0, two stars of the level 1, one star of the level 2, and one star of the level 3.
You are to write a program that will count the amounts of the stars of each level on a given map.
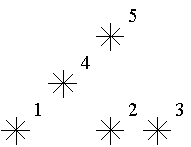
For example, look at the map shown on the figure above. Level of the star number 5 is equal to 3 (it's formed by three stars with a numbers 1, 2 and 4). And the levels of the stars numbered by 2 and 4 are 1. At this map there are only one star of the level 0, two stars of the level 1, one star of the level 2, and one star of the level 3.
You are to write a program that will count the amounts of the stars of each level on a given map.
Input
The first line of the input file contains a number of stars N (1<=N<=15000). The following N lines describe coordinates of stars (two integers X and Y per line separated by a space, 0<=X,Y<=32000). There can be only one star at one point of the plane. Stars are listed in ascending order of Y coordinate. Stars with equal Y coordinates are listed in ascending order of X coordinate.
Output
The output should contain N lines, one number per line. The first line contains amount of stars of the level 0, the second does amount of stars of the level 1 and so on, the last line contains amount of stars of the level N-1.
Sample Input
5 1 1 5 1 7 1 3 3 5 5
Sample Output
1 2 1 1 0
题目大意:输入平面坐标上的点的个数N以及他们的横纵坐标,对于每一个点,从此点向x轴和y轴做垂线,则该点的等级(level)为这两条垂线与x轴和y轴围成的矩形中包含的点的个数,其中边界上的点会被计算在内,但该点不会被计算在内。输入数据按y升序,若y相同则按x升序。输出每个等级(0--N-1)所含的点的个数。
还是采用线段树来维护整个区间。经过严(cha)密(yue)推(zi)理(liao)后可以得出结论:由于数据特殊的输入顺序,决定了该点的输入坐标就是前面的所有已经输入了的坐标中X轴坐标位于0到当前的点的横坐标的点的个数。有了这一点,建树,查找过程就不难实现了,详细解释还是在代码中给出。
输入数据较大,scanf大法好。
#include <iostream> #include <stdio.h> using namespace std; int n,i,a[15002],ans[15002],cnt,tree[3000000]; void build(int root,int l,int r,int x)//建树,树的区间表示该区间(X轴)内点的个数 { int mid; if (l==r) { tree[root]++; return; } mid=(l+r)/2; if (mid>=x) { build(root*2,l,mid,x); } else if (mid<x) { build(root*2+1,mid+1,r,x); } tree[root]=tree[root*2]+tree[root*2+1]; return; } void findn(int root,int l,int r,int x,int y)//l,r分别是当前查找区间的左边界和右边界,x,y分别是目标区间的左边界和右边界 { int mid; if (x<=l&&y>=r)//如果当前区间被目标区间完全包含,则计数。 { cnt=cnt+tree[root]; return; } mid=(l+r)/2; if (mid>=y)//如果中间值比目标右界还靠右,说明要找的区间在当前节点的右儿子 { findn(root*2,l,mid,x,y); } else if (mid<x)//左儿子 { findn(root*2+1,mid+1,r,x,y); } else//左儿子右儿子各有一部分 { findn(root*2,l,mid,x,y); findn(root*2+1,mid+1,r,x,y); } } int main() { int maxn=0,y; scanf("%d",&n); for (i=0;i<=n-1;i++) { scanf("%d%d",&a[i],&y);//y完全没用,但还是要读 if (a[i]>=maxn) { maxn=a[i]; } } for (i=0;i<=n-1;i++) { cnt=0; build(1,0,maxn,a[i]);//从第一个节点开始建树 findn(1,0,maxn,0,a[i]);//从第一个节点开始搜树 ans[cnt-1]++; } for(i=0;i<=n-1;i++) { printf("%d\n",ans[i]); } return 0; }






















 519
519

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








