先截取裁判程序里的一个函数来解释思路,而后即是答案,题目在最后;
void DisplayPath(AMGraph G , int begin ,int temp ){
if(Path[begin][temp] != -1){
DisplayPath(G , begin ,Path[begin][temp]);
cout << G.vexs[Path[begin][temp]] << "->";
}
}这道题基于弗洛伊德算法,却和陈越老师教材上的程序有一定区别,因为这道题要考虑这道题在裁判程序里的输出函数Display函数,这个函数是在递归输出i->j的路径,且观察上面截取的这个程序,该程序递归从temp向begin找,一直到遇到Path是-1说明begin等于temp时结束查找回到递归上一层开始输出上一个结点对应的值(由此得知目标没有输出,所以裁判程序的main函数在调用该函数后加了输出目标的一句)(而且可以知道层数高的vexs先输出,所以在递归过程中先到的是考进destnation的点),所以Path[beagin][destnation]里存的应该是在begin向destination的路径中靠经destination的点,至此第一个改变:Path[i][j]=Path[k][j];
第二个改变即:if(D[i][j]<MaxInt&&i!=j) Path[i][j]=i; else Path[i][j]=-1; 即在对Path初始化时,若i可以到j就令Path[i][j] = i ; 不能到或者 i = j 时就赋值为-1;这样满足了裁判的输出程序(1,若i->j连通且不需要经过其它节点就最短则Display函数会输出i; 2,Path[baegin][temp]里存的是从begin到temp的路径中靠近temp的那个点)
这个裁判程序里的DisPlay也很有趣,值得好好体会以下(书上未改变的原代码无法显示具体路径经过了哪些点,而在改动过的下面第一段代码搭配Display函数并在最后输出destnation后可以得到最短的具体路径);
答案代码:
void ShortestPath_Floyed(AMGraph G){
int i,j,k;
for(i=0;i<G.vexnum;i++){
for(j=0;j<G.vexnum;j++){
D[i][j]=G.arcs[i][j];
if(D[i][j]<MaxInt&&i!=j){//这句判断很重要,i!=j,因为不能让i->j
Path[i][j]=i;
}
else Path[i][j]=-1;
}
}
for(k=0;k<G.vexnum;k++){//中转结点
for(i=0;i<G.vexnum;i++){
for(j=0;j<G.vexnum;j++){
if(D[i][j]>D[i][k]+D[k][j]){
D[i][j]=D[i][k]+D[k][j];
//根据裁判程序里的Display函数,判断输出依靠递归,从j向前反推
//所以Path[i][j]里存i->j最短路里靠经j的那个点
//所以 Path[i][j]=k错误
//所以改出这句话的重点是对Display函数的观察思考;
Path[i][j]=Path[k][j];//记录路径
}
}
}
}
// fakeDisplayPath(G , begin ,Path[0][5]);
return;
}
题目:
试实现弗洛伊德最短路径算法。
函数接口定义:
void ShortestPath_Floyed(AMGraph G);
其中 G 是基于邻接矩阵存储表示的有向图。
裁判测试程序样例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MaxInt 32767
#define MVNum 100
typedef char VerTexType;
typedef int ArcType;
int Path[MVNum][MVNum];
int D[MVNum][MVNum];
typedef struct{
VerTexType vexs[MVNum];
ArcType arcs[MVNum][MVNum];
int vexnum,arcnum;
}AMGraph;
void CreateUDN(AMGraph &G);//实现细节隐藏
void ShortestPath_Floyed(AMGraph G);
void DisplayPath(AMGraph G , int begin ,int temp ){
if(Path[begin][temp] != -1){
DisplayPath(G , begin ,Path[begin][temp]);
cout << G.vexs[Path[begin][temp]] << "->";
}
}
int main(){
AMGraph G;
char start , destination;
int num_start , num_destination;
CreateUDN(G);
ShortestPath_Floyed(G);
cin >> start >> destination;
num_start = LocateVex(G , start);
num_destination = LocateVex(G , destination);
DisplayPath(G , num_start , num_destination);
cout << G.vexs[num_destination]<<endl;
cout << D[num_start][num_destination];
return 0;
}
/* 请在这里填写答案 */输入样例:
第1行输入结点数vexnum和边数arcnum。第2行输入vexnum个字符表示结点的值,接下来依次输入arcnum行,每行输入3个值,前两个字符表示结点,后一个数表示两个结点之间边的权值。最后一行输入源点及终点。
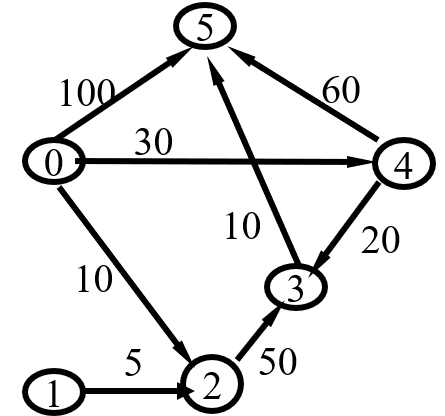
6 8
012345
0 5 100
0 2 10
0 4 30
1 2 5
2 3 50
3 5 10
4 3 20
4 5 60
0 5
输出样例:
第一行输出源点到终点的最短路径,第二行输出源点到终点的最短路径距离。
0->4->3->5
60





















 3825
3825

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








