文章目录
一、DFS和BFS
| 数据结构 | 空间 | 备注 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DFS | stack | O ( h ) O(h) O(h)(树的高度相关) | / |
| BFS | queue | O ( 2 h ) O(2^{h}) O(2h)(树的层相关) | 具有最短路径的性质 |
1.1 DFS
回溯、恢复现场
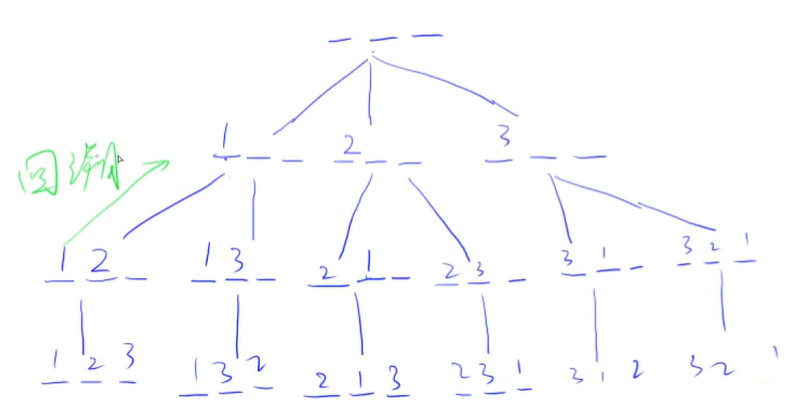
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 10;
int n;
int path[N]; //路径保存(存储方案)
bool st[N]; //检验这个点是否被用过
void dfs(int u)
{
if (u == n) //递归到最后一层
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d ", path[i]);
puts("");
return;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) //未递归到最后一层
{
if (!st[i]) //如果该点未被使用过
{
path[u] = i; //将该点记录
st[i] = true;
dfs(u + 1);
st[i] = false; //恢复现场
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
dfs(0);
return 0;
}
- 第一种搜索顺序:按行枚举
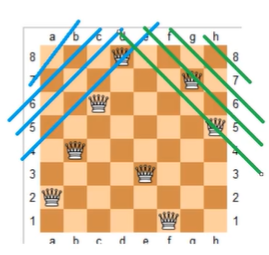
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 20; //对角线需要两倍的n
int n;
char g[N][N]; //存储棋子情况
bool col[N], dg[N], udg[N]; //列、对角线、反对角线情况
void dfs(int u)
{
if (u == n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
puts(g[i]); //输出每行的棋子情况
puts("");
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (!col[i] && !dg[u + i] && !udg[n - u + i])
{
g[u][i] = 'Q';
col[i] = dg[u + i] = udg[n - u + i] = true; //记录为true
dfs(u + 1);
col[i] = dg[u + i] = udg[n - u + i] = false; //恢复现场
g[u][i] = '.';
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
g[i][j] = '.';
dfs(0);
return 0;
}
- 第二种搜索顺序:一个一个格子进行搜索。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 20; //对角线需要两倍的n
int n;
char g[N][N]; //存储棋子情况
bool row[N],col[N], dg[N], udg[N]; //行、列、对角线、反对角线情况
void dfs(int x,int y,int s) //行列坐标及当前皇后的数量
{
if (y == n)
y = 0, x++;
if (x == n)
{
if (s == n) //找到了一种成功的方案
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) puts(g[i]);
puts("");
}
return;
}
//枚举两种情况:不放皇后
dfs(x, y + 1, s);
//放皇后
if (!row[x] && !col[y] && !dg[x + y] && !udg[x - y + n])
{
g[x][y] = 'Q';
row[x] = col[y] = dg[x + y] = udg[x - y + n] = true;
dfs(x, y + 1, s + 1);
row[x] = col[y] = dg[x + y] = udg[x - y + n] = false;
g[x][y] = '.'; //恢复现场
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
g[i][j] = '.';
dfs(0, 0, 0);
return 0;
}
1.2 BFS
当所有边的权重都为1时,才可以使用BFS求解最短路径问题。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 110;
int n, m;
int g[N][N]; //存储地图
int d[N][N]; //存储最短路径
PII q[N * N];
int bfs()
{
int hh = 0, tt = 0; //定义空队列
q[0] = { 0,0 }; //记录开始点坐标
memset(d, -1, sizeof d); //初始化最短距离为-1
d[0][0] = 0;
//向量表示(-1,0),(0,1),(1,0),(0,-1)
int dx[4] = { -1,0,1,0 }, dy[4] = { 0,1,0,-1 };
while (hh <= tt)
{
auto t = q[hh++]; //将队首元素入队
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int x = t.first + dx[i], y = t.second + dy[i];
if (x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < m && g[x][y] == 0 && d[x][y] == -1)
{
//g数组等于0表示该点是路径上的点,d数组为-1表示未被选过
d[x][y] = d[t.first][t.second] + 1;
q[++tt] = { x,y }; //将该点记录
}
}
}
return d[n - 1][m - 1];
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
cin >> g[i][j];
cout << bfs() << endl;
return 0;
}
若需要输出路径,则可以在d[x][y] = d[t.first][t.second] + 1;后添加一句代码用于存储当前元素的前一个元素Prev[x][y] = t;【记录路径】,然后在函数返回前输出路径:
int x = n - 1,y = m - 1;
while(x || y)
{
cout << x << ' ' << y << endl;
auto t = Prev[x][y];
x = t.first, y = t.second;
}
1.3 图的存储方式与遍历
树是无环连通图,是一种特殊的图。图分为有向图和无向图。
- 邻接矩阵
- 邻接表:每个节点开了一个单链表
给定一颗树,树中包含 n 个结点(编号 1∼n)和 n−1 条无向边。
请你找到树的重心,并输出将重心删除后,剩余各个连通块中点数的最大值。
重心定义:重心是指树中的一个结点,如果将这个点删除后,剩余各个连通块中点数的最大值最小,那么这个节点被称为树的重心。
输入格式
第一行包含整数 n,表示树的结点数。
接下来 n−1 行,每行包含两个整数 a 和 b,表示点 a 和点 b 之间存在一条边。
输出格式
输出一个整数 m,表示将重心删除后,剩余各个连通块中点数的最大值。
数据范围
1 ≤ n ≤ 1 0 5 1≤n≤10^5 1≤n≤105
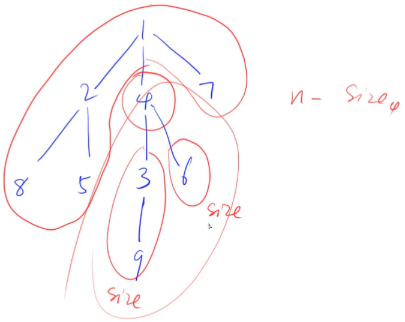
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010, M = N * 2;
int h[N], e[M], ne[M]; //h数组存储每个链表的链表头,e数组存储每个节点的编号,ne存储的是每个节点的next指针
int n, idx;
bool st[N]; //标记是否已经被访问
int ans = N; //记录答案
void add(int a, int b)
{
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx++;
}
//以u为根的子树中点的数量
int dfs(int u)
{
st[u] = true; //标记一下,已经被搜过
int sum = 1, res = 0; //sum记录当前子树的点, res记录当前子树的连通块点数
for (int i = h[u]; i != -1; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if (!st[j])
{
int s = dfs(j); //获得子树连通块点的数量
res = max(res, s); //将s与res取大
sum += s; //将子树的数量加入点数
}
}
res = max(res, n - sum); //n - sum为除了以该点为子树的剩余部分
ans = min(ans, res); //记录结果
return sum; //返回子树数量
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
add(a, b), add(b, a); //无向边,需要添加不同方向的两条边
}
dfs(1); //从任意节点开始深度优先
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int h[N], e[N], ne[N], idx, n, m;
int d[N], q[N]; //d数组记录最远距离,q数组记录队列
void add(int a, int b)
{
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx++;
}
int bfs()
{
int hh = 0, tt = 0;
q[0] = 1; //初始化
memset(d, -1, sizeof d);
d[1] = 0;
while (hh <= tt)
{
int t = q[hh++];
for (int i = h[t]; i != -1; i = ne[i]) //扩展每个点的邻边
{
int j = e[i];
if (d[j] == -1) //第一次被访问
{
d[j] = d[t] + 1;
q[++tt] = j;
}
}
}
return d[n];
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
add(a, b);
}
cout << bfs() << endl;
return 0;
}
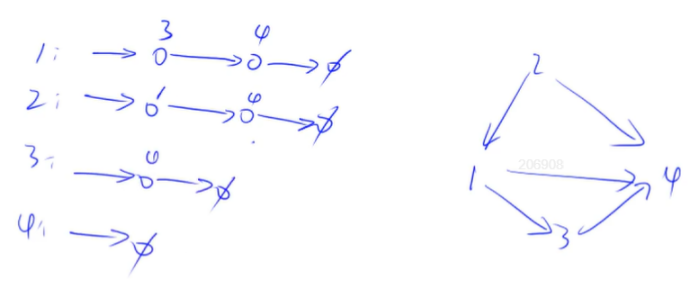
1.4 有向图的拓扑序列
若一个由图中所有点构成的序列 A 满足:对于图中的每条边 (x,y),x 在 A 中都出现在 y 之前,则称 A 是该图的一个拓扑序列。
有向无环图称为拓扑图。
queue <- 所有入度为0的点
while queue不为空
{
t <- 队头
枚举 t 的所有出边 t -> j
删去t -> j, d[j]--;
if d[j] == 0:
queue <- j;
}
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int n, m;
int h[N], e[N], ne[N], idx;
int d[N];
int q[N];
void add(int a, int b)
{
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx ++ ;
}
bool topsort()
{
int hh = 0, tt = -1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
if (!d[i])
q[ ++ tt] = i;
while (hh <= tt)
{
int t = q[hh ++ ];
for (int i = h[t]; i != -1; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if (-- d[j] == 0)
q[ ++ tt] = j;
}
}
return tt == n - 1;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i ++ )
{
int a, b;
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
add(a, b);
d[b] ++ ;
}
if (!topsort()) puts("-1");
else
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) printf("%d ", q[i]);
puts("");
}
return 0;
}
二、最短路径问题
[注意算法的时间复杂度]
单源最短路径
- 所有边权都是正数
- 朴素
Dijkstra算法 O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2) 边稠密图m~n^2 - 堆优化版的
Dijkstra算法 O ( m l o g n ) O(mlogn) O(mlogn) 边稀疏图m~n
- 朴素
- 存在负权边
Bellman-Ford算法O(nm)SPFA算法 一般O(m),最坏O(nm)
多源汇最短路径(起点、终点任选)
Floyd算法 O ( n 3 ) O(n^3) O(n3)
2.1 朴素Dijkstra算法
-
dist[1]=0,dist[i]=+∞,s为当前已确定最短路径的点 -
for i: 0~nt<-不在s中的、距离最近的点s<-t,用t更新其他点的距离,dist[x] > dist[t] + w
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 510;
int n, m;
int g[N][N];
int dist[N];
bool st[N];
int dijkstra()
{
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
dist[1] = 0; //初始化
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int t = -1; //t为-1表示还未选择一个点
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
if (!st[j] && (t == -1 || dist[t] > dist[j]))
t = j; //选取还未被选择的且距离最近的点
}
st[t] = true;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
dist[j] = min(dist[j], dist[t] + g[t][j]);
}
}
if (dist[n] == 0x3f3f3f3f) return -1; //不连通
return dist[n];
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
memset(g, 0x3f, sizeof g);
while (m--)
{
int a, b, c;
scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c);
g[a][b] = min(g[a][b], c);
}
int t = dijkstra();
printf("%d\n", t);
return 0;
}
2.2 堆优化版的Dijkstra算法
堆:
- 手写堆(n个数)
- 优先队列(m个数)
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
int n, m;
int h[N], w[N], e[N], ne[N], idx;
int dist[N];
bool st[N];
void add(int a, int b, int c)
{
e[idx] = b, w[idx] = c, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx ++ ;
}
int dijkstra()
{
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
dist[1] = 0;
priority_queue<PII, vector<PII>, greater<PII>> heap; //小根堆
heap.push({0, 1});
while (heap.size())
{
auto t = heap.top();
heap.pop();
int ver = t.second, distance = t.first;
if (st[ver]) continue; //被更新过,是冗余备份
st[ver] = true;
for (int i = h[ver]; i != -1; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if (dist[j] > dist[ver] + w[i])
{
dist[j] = dist[ver] + w[i];
heap.push({dist[j], j});
}
}
}
if (dist[n] == 0x3f3f3f3f) return -1;
return dist[n];
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
while (m -- )
{
int a, b, c;
scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c);
add(a, b, c);
}
cout << dijkstra() << endl;
return 0;
}
2.3 Bellman-Ford算法
for n次
for 所有边 a,b,w
dist[b] = min(dist[b],dist[a] + w); //松弛操作
有三角不等式:dist[b] <= dist[a] + w。
k次—>经过不超过k条边的最短路径的距离
n次—>存在一条最短路径,上面有n条边,则路径上一定存在负环
算法时间复杂度 O(nm),n表示点数,m表示边数。
注意在模板题中需要对下面的模板稍作修改,加上备份数组,详情见模板题。
int n, m; // n表示点数,m表示边数
int dist[N]; // dist[x]存储1到x的最短路距离
struct Edge // 边,a表示出点,b表示入点,w表示边的权重
{
int a, b, w;
}edges[M];
// 求1到n的最短路距离,如果无法从1走到n,则返回-1。
int bellman_ford()
{
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
dist[1] = 0;
// 如果第n次迭代仍然会松弛三角不等式,就说明存在一条长度是n+1的最短路径,由抽屉原理,路径中至少存在两个相同的点,说明图中存在负权回路。
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
{
for (int j = 0; j < m; j ++ )
{
int a = edges[j].a, b = edges[j].b, w = edges[j].w;
if (dist[b] > dist[a] + w)
dist[b] = dist[a] + w;
}
}
if (dist[n] > 0x3f3f3f3f / 2) return -1;
return dist[n];
}
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 510, M = 10010;
struct Edge
{
int a, b, c;
}edges[M];
int n, m, k;
int dist[N];
int last[N]; //用于备份
void bellman_ford()
{
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist); //初始化
dist[1] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
memcpy(last, dist, sizeof dist); //将当前的值赋值到last数组中来备份
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
auto e = edges[j];
dist[e.b] = min(dist[e.b], last[e.a] + e.c); //取最小值
}
}
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &k);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
int a, b, c;
scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c);
edges[i] = { a, b, c };
}
bellman_ford();
//除以2的原因是0x3f3f3f3f也可能经历一些小的改变
if (dist[n] > 0x3f3f3f3f / 2) puts("impossible");
else printf("%d\n", dist[n]);
return 0;
}
2.4 SPFA算法
考虑到dist[e.b] = min(dist[e.b], last[e.a] + e.c);一式只有当a变化的时候dist[e.b]才会发生改变,故有:
while queue 不空
(1)t <- q.front;
q.pop();
(2)更新t的所有出边: t -w-> b; //待更新的点的集合
queue <- b
2.4.1 SPFA算法求最短路径
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int n, m;
int h[N], w[N], e[N], ne[N], idx;
int dist[N];
bool st[N];
void add(int a, int b, int c)
{
e[idx] = b, w[idx] = c, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx++;
}
int spfa()
{
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
dist[1] = 0;
queue<int> q;
q.push(1);
st[1] = true;
while (q.size())
{
int t = q.front(); //将队首元素取出
q.pop();
st[t] = false; //设为false代表已经出队
for (int i = h[t]; i != -1; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if(dist[j] > dist[t] + w[i])
{
dist[j] = dist[t] + w[i];
if (!st[j])
{
//如果不在队列里,将其入队
q.push(j);
st[j] = true;
}
}
}
}
return dist[n];
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
while (m--)
{
int a, b, c;
scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c);
add(a, b, c);
}
int t = spfa();
if (t == 0x3f3f3f3f) puts("impossible");
else printf("%d\n", t);
return 0;
}
2.4.2 SPFA算法判断负环
有:dist[x] = dist[t] + w[i]; cnt[x] = cnt[t] + 1,若有cnt[x] >= n,则在这个路径上有n+1个点,由抽屉原理可知,存在有两个相同的点,该路径存在负环。
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2010, M = 10010;
int n, m;
int h[N], w[M], e[M], ne[M], idx;
int dist[N], cnt[N];
bool st[N];
void add(int a, int b, int c)
{
e[idx] = b, w[idx] = c, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx ++ ;
}
bool spfa()
{
queue<int> q;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
st[i] = true;
q.push(i);
}
while (q.size())
{
int t = q.front();
q.pop();
st[t] = false;
for (int i = h[t]; i != -1; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if (dist[j] > dist[t] + w[i])
{
dist[j] = dist[t] + w[i];
cnt[j] = cnt[t] + 1;
if (cnt[j] >= n) return true;
if (!st[j])
{
q.push(j);
st[j] = true;
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
while (m -- )
{
int a, b, c;
scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c);
add(a, b, c);
}
if (spfa()) puts("Yes");
else puts("No");
return 0;
}
2.5 Floyd算法
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 210, INF = 1e9;
int n, m, Q;
int d[N][N];
void floyd()
{
for (int k = 1; k <= n; k ++ )
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ )
d[i][j] = min(d[i][j], d[i][k] + d[k][j]);
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &Q);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ )
if (i == j) d[i][j] = 0;
else d[i][j] = INF;
while (m -- )
{
int a, b, c;
scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c);
d[a][b] = min(d[a][b], c);
}
floyd();
while (Q -- )
{
int a, b;
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
int t = d[a][b];
if (t > INF / 2) puts("impossible");
else printf("%d\n", t);
}
return 0;
}






















 880
880











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








