Android系统源码阅读(15):Android 应用进程的启动
自己开心就好,何必管他人烦恼
1. 应用进程创建
ActivityManagerService负责管理应用进程的创建。这一节会讲述如何从ActivityManagerService申请创建一个app进程,然后从zygote克隆一个进程的过程。
1.1 ActivityManagerService.startProcessLocked
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java :
private final void startProcessLocked(ProcessRecord app, String hostingType, String hostingNameStr, String abiOverride, String entryPoint, String[] entryPointArgs) {
//...
try {
//...
int uid = app.uid;
int[] gids = null;
int mountExternal = Zygote.MOUNT_EXTERNAL_NONE;
//...
app.gids = gids;
app.requiredAbi = requiredAbi;
app.instructionSet = instructionSet;
// Start the process. It will either succeed and return a result containing
// the PID of the new process, or else throw a RuntimeException.
boolean isActivityProcess = (entryPoint == null);
//Android应用的进程入口android.app.ActivityThread
if (entryPoint == null) entryPoint = "android.app.ActivityThread";
//启动app进程
Process.ProcessStartResult startResult = Process.start(entryPoint,
app.processName, uid, uid, gids, debugFlags, mountExternal,
app.info.targetSdkVersion, app.info.seinfo, requiredAbi, instructionSet,
app.info.dataDir, entryPointArgs);
//...
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
// XXX do better error recovery.
//...
}
}1.2 Process.start
这一步直接交给下一步来处理。
1.3 Process.startViaZygote
frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/Process.java :
/**
* Starts a new process via the zygote mechanism.
*
* @param processClass Class name whose static main() to run
* @param niceName 'nice' process name to appear in ps
* @param uid a POSIX uid that the new process should setuid() to
* @param gid a POSIX gid that the new process shuold setgid() to
* @param gids null-ok; a list of supplementary group IDs that the
* new process should setgroup() to.
* @param debugFlags Additional flags.
* @param targetSdkVersion The target SDK version for the app.
* @param seInfo null-ok SELinux information for the new process.
* @param abi the ABI the process should use.
* @param instructionSet null-ok the instruction set to use.
* @param appDataDir null-ok the data directory of the app.
* @param extraArgs Additional arguments to supply to the zygote process.
* @return An object that describes the result of the attempt to start the process.
* @throws ZygoteStartFailedEx if process start failed for any reason
*/
private static ProcessStartResult startViaZygote(final String processClass,
final String niceName,
final int uid, final int gid,
final int[] gids,
int debugFlags, int mountExternal,
int targetSdkVersion,
String seInfo,
String abi,
String instructionSet,
String appDataDir,
String[] extraArgs)
throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {
synchronized(Process.class) {
ArrayList<String> argsForZygote = new ArrayList<String>();
//设置一些基本参数
// --runtime-args, --setuid=, --setgid=,
// and --setgroups= must go first
argsForZygote.add("--runtime-args");
argsForZygote.add("--setuid=" + uid);
argsForZygote.add("--setgid=" + gid);
//...
argsForZygote.add("--target-sdk-version=" + targetSdkVersion);
// --setgroups is a comma-separated list
if (gids != null && gids.length > 0) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("--setgroups=");
int sz = gids.length;
for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {
if (i != 0) {
sb.append(',');
}
sb.append(gids[i]);
}
argsForZygote.add(sb.toString());
}
if (niceName != null) {
argsForZygote.add("--nice-name=" + niceName);
}
if (seInfo != null) {
argsForZygote.add("--seinfo=" + seInfo);
}
if (instructionSet != null) {
argsForZygote.add("--instruction-set=" + instructionSet);
}
if (appDataDir != null) {
argsForZygote.add("--app-data-dir=" + appDataDir);
}
argsForZygote.add(processClass);
if (extraArgs != null) {
for (String arg : extraArgs) {
argsForZygote.add(arg);
}
}
//继续交给下一步处理,这里通过函数openZygoteSocketIfNeeded和Zygote建立了连接
return zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult(openZygoteSocketIfNeeded(abi), argsForZygote);
}
}函数openZygoteSocketIfNeeded会在zygote地址上建立一个socket连接,然后创建一个input stream和output stream。
1.4 Process.zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult
frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/Process.java :
/**
* Sends an argument list to the zygote process, which starts a new child
* and returns the child's pid. Please note: the present implementation
* replaces newlines in the argument list with spaces.
*
* @throws ZygoteStartFailedEx if process start failed for any reason
*/
private static ProcessStartResult zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult(
ZygoteState zygoteState, ArrayList<String> args)
throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {
try {
/**
* See com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit.readArgumentList()
* Presently the wire format to the zygote process is:
* a) a count of arguments (argc, in essence)
* b) a number of newline-separated argument strings equal to count
*
* After the zygote process reads these it will write the pid of
* the child or -1 on failure, followed by boolean to
* indicate whether a wrapper process was used.
*/
final BufferedWriter writer = zygoteState.writer;
final DataInputStream inputStream = zygoteState.inputStream;
//直接用已经建立好的input stream
writer.write(Integer.toString(args.size()));
writer.newLine();
//依次写入每个参数
int sz = args.size();
for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {
String arg = args.get(i);
if (arg.indexOf('\n') >= 0) {
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx(
"embedded newlines not allowed");
}
writer.write(arg);
writer.newLine();
}
writer.flush();
//获取创建进程的结果,如果进程pid小于0,则说明没有创建成功
// Should there be a timeout on this?
ProcessStartResult result = new ProcessStartResult();
result.pid = inputStream.readInt();
if (result.pid < 0) {
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("fork() failed");
}
result.usingWrapper = inputStream.readBoolean();
return result;
} catch (IOException ex) {
zygoteState.close();
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx(ex);
}
}1.5 ZygoteInit.runSelectLoop
ActivityManagerService通过socket将参数传递给zygote进程后,创建app进程的任务就交给zygote继续实现了。让我们再次回到zygote的循环中。
frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java :
private static void runSelectLoop(String abiList) throws MethodAndArgsCaller {
ArrayList<FileDescriptor> fds = new ArrayList<FileDescriptor>();
ArrayList<ZygoteConnection> peers = new ArrayList<ZygoteConnection>();
fds.add(sServerSocket.getFileDescriptor());
peers.add(null);
while (true) {
StructPollfd[] pollFds = new StructPollfd[fds.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < pollFds.length; ++i) {
pollFds[i] = new StructPollfd();
pollFds[i].fd = fds.get(i);
pollFds[i].events = (short) POLLIN;
}
try {
Os.poll(pollFds, -1);
} catch (ErrnoException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("poll failed", ex);
}
for (int i = pollFds.length - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
if ((pollFds[i].revents & POLLIN) == 0) {
continue;
}
if (i == 0) {
//ActivityManagerService和我建立连接
ZygoteConnection newPeer = acceptCommandPeer(abiList);
peers.add(newPeer);
fds.add(newPeer.getFileDesciptor());
} else {
//处理ActivityManagerService发送的请求
boolean done = peers.get(i).runOnce();
if (done) {
peers.remove(i);
fds.remove(i);
}
}
}
}
}1.6 ZygoteConnection.runOnce
frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteConnection.java :
/**
* Reads one start command from the command socket. If successful,
* a child is forked and a {@link ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller}
* exception is thrown in that child while in the parent process,
* the method returns normally. On failure, the child is not
* spawned and messages are printed to the log and stderr. Returns
* a boolean status value indicating whether an end-of-file on the command
* socket has been encountered.
*
* @return false if command socket should continue to be read from, or
* true if an end-of-file has been encountered.
* @throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller trampoline to invoke main()
* method in child process
*/
boolean runOnce() throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
String args[];
Arguments parsedArgs = null;
FileDescriptor[] descriptors;
try {
//读取传入的参数
args = readArgumentList();
descriptors = mSocket.getAncillaryFileDescriptors();
} catch (IOException ex) {
//...
}
if (args == null) {
// EOF reached.
closeSocket();
return true;
}
/** the stderr of the most recent request, if avail */
PrintStream newStderr = null;
if (descriptors != null && descriptors.length >= 3) {
newStderr = new PrintStream(
new FileOutputStream(descriptors[2]));
}
int pid = -1;
FileDescriptor childPipeFd = null;
FileDescriptor serverPipeFd = null;
try {
//...
//fork一个进程
pid = Zygote.forkAndSpecialize(parsedArgs.uid, parsedArgs.gid, parsedArgs.gids,
parsedArgs.debugFlags, rlimits, parsedArgs.mountExternal, parsedArgs.seInfo,
parsedArgs.niceName, fdsToClose, parsedArgs.instructionSet,
parsedArgs.appDataDir);
} catch (ErrnoException ex) {
//...
}
try {
if (pid == 0) {
// in child
IoUtils.closeQuietly(serverPipeFd);
serverPipeFd = null;
//在子进程中进一步处理
handleChildProc(parsedArgs, descriptors, childPipeFd, newStderr);
// should never get here, the child is expected to either
// throw ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller or exec().
return true;
} else {
// in parent...pid of < 0 means failure
IoUtils.closeQuietly(childPipeFd);
childPipeFd = null;
return handleParentProc(pid, descriptors, serverPipeFd, parsedArgs);
}
} finally {
IoUtils.closeQuietly(childPipeFd);
IoUtils.closeQuietly(serverPipeFd);
}
}1.7 ZygoteConnection.handleChildProc
frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteConnection.java :
/**
* Handles post-fork setup of child proc, closing sockets as appropriate,
* reopen stdio as appropriate, and ultimately throwing MethodAndArgsCaller
* if successful or returning if failed.
*
* @param parsedArgs non-null; zygote args
* @param descriptors null-ok; new file descriptors for stdio if available.
* @param pipeFd null-ok; pipe for communication back to Zygote.
* @param newStderr null-ok; stream to use for stderr until stdio
* is reopened.
*
* @throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller on success to
* trampoline to code that invokes static main.
*/
private void handleChildProc(Arguments parsedArgs,
FileDescriptor[] descriptors, FileDescriptor pipeFd, PrintStream newStderr)
throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
/**
* By the time we get here, the native code has closed the two actual Zygote
* socket connections, and substituted /dev/null in their place. The LocalSocket
* objects still need to be closed properly.
*/
closeSocket();
ZygoteInit.closeServerSocket();
if (parsedArgs.niceName != null) {
Process.setArgV0(parsedArgs.niceName);
}
// End of the postFork event.
//...
if (parsedArgs.invokeWith != null) {
WrapperInit.execApplication(parsedArgs.invokeWith,
parsedArgs.niceName, parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion,
VMRuntime.getCurrentInstructionSet(),
pipeFd, parsedArgs.remainingArgs);
} else {
//继续初始化进程
RuntimeInit.zygoteInit(parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion,
parsedArgs.remainingArgs, null /* classLoader */);
}
}1.8 RuntimeInit.zygoteInit
这里开始调用android.app.ActivityThread的main函数。
frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/RuntimeInit.java :
public static final void zygoteInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader)
throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
if (DEBUG) Slog.d(TAG, "RuntimeInit: Starting application from zygote");
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "RuntimeInit");
redirectLogStreams();
commonInit();
//启动Binder线程池,将在下面详细分析native部分
nativeZygoteInit();
//这里调用的不再是system的main函数了,而是ActivityThread的main函数,将在下面章节分析
applicationInit(targetSdkVersion, argv, classLoader);
}到这里一个Android app的进程就已经创建好了。
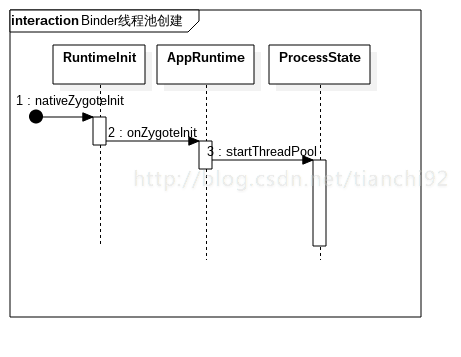
2. Binder线程池的启动
App进程创建过程中会建立一个Binder线程池,用来处理进程间的Binder通信。
2.1 RuntimeInit.nativeZygoteInit
frameworks/base/core/jni/AndroidRuntime.cpp :
这里直接调用了一个AndroidRuntime全局对象gCurRuntime的onZygoteInit函数。这个全局对象是在zygote进程中创建了,这里是通过复制zygote的进程获得的该对象。
2.2 AppRuntime.onZygoteInit
frameworks/base/cmds/app_main.cpp :
virtual void onZygoteInit()
{
sp<ProcessState> proc = ProcessState::self();
ALOGV("App process: starting thread pool.\n");
proc->startThreadPool();
}2.3 ProcessState.startThreadPool
启动Binder线程池线程, app进程从而具有进程间binder通信的能力。
frameworks/native/libs/binder/PorcessState.cpp :
void ProcessState::startThreadPool()
{
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
if (!mThreadPoolStarted) {
mThreadPoolStarted = true;
//启动一个Binder线程池的线程,从而可以支持Binder进程间通信了
spawnPooledThread(true);
}
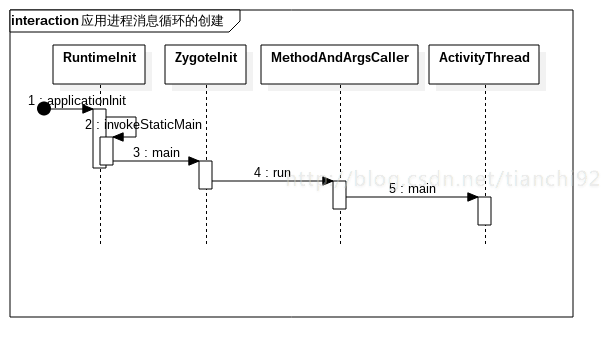
}3. App进程消息循环的创建
在1.8中,RuntimeInit调用函数applicationInit来启动ActivityThread的main函数。
3.1 RuntimeInit.applicationInit
设置了heap的目标使用率,然后调用了下一步的静态函数。
3.2 RuntimeInit.invokeStaticMain
这一步终于开始从这个创建的新进程中调用ActivityThread的main函数了。不过调用的方式有点奇怪,这里是通过抛出一个异常的形式,来清空当前栈中的积压的函数,直到回退到ZygoteInit.main函数中。因为该app进程是从zygote进程中fork出来的,所以栈的内容也是相同的,所以可以会退到ZygoteInit.main函数。
frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/RuntimeInit.java :
/**
* Invokes a static "main(argv[]) method on class "className".
* Converts various failing exceptions into RuntimeExceptions, with
* the assumption that they will then cause the VM instance to exit.
*
* @param className Fully-qualified class name
* @param argv Argument vector for main()
* @param classLoader the classLoader to load {@className} with
*/
private static void invokeStaticMain(String className, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader)
throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
Class<?> cl;
try {
//通过类名加载该类,这里就是ActivityThread类
cl = Class.forName(className, true, classLoader);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
//...
}
Method m;
try {
//获得ActivityThread的main方法
m = cl.getMethod("main", new Class[] { String[].class });
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
//...
}
//...
/*
* This throw gets caught in ZygoteInit.main(), which responds
* by invoking the exception's run() method. This arrangement
* clears up all the stack frames that were required in setting
* up the process.
* 这里通过抛出异常来回到stack中的某一个函数的做法还真是头一次见
*/
throw new ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller(m, argv);
}3.3 ZygoteInit.main
在Zygote进程里,会进入无限的循环。但是,在app进程里,进入这个循环是没有作用,所以需要跳出循环,继续前进。
public static void main(String argv[]) {
try {
//...
Log.i(TAG, "Accepting command socket connections");
//Zygote进程会一直在循环中
//虽然app进程在这个循环里创建,但是它需要跳出这个循环,才能继续执行
runSelectLoop(abiList);
closeServerSocket();
} catch (MethodAndArgsCaller caller) {
//所以app进程就跳到了这里
caller.run();
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
Log.e(TAG, "Zygote died with exception", ex);
closeServerSocket();
throw ex;
}
}3.4 MethodAndArgsCaller.run
这里就是回到ZygoteInit.main里调用ActivityThread的main函数,目的就是清理准备app进程中形成的调用堆栈。
public void run() {
try {
//就是调用了ActivityThread的main函数
mMethod.invoke(null, new Object[] { mArgs });
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
//...
}
}ActivityThread.main
这里就是回到我们熟悉的剧情了,不再赘述。

























 681
681

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








