import pandas as pd
titanic = pd.read_csv('http://biostat.mc.vanderbilt.edu/wiki/pub/Main/DataSets/titanic.txt')
#titanic = pd.read_csv('../Datasets/Breast-Cancer/titanic.txt')
X=titanic[['pclass','age','sex']]
y=titanic['survived']
X.info()
X['age'].fillna(X['age'].mean(),inplace=True)
X.info()
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(X,y,test_size=0.25,random_state=33)
from sklearn.feature_extraction import DictVectorizer
vec = DictVectorizer(sparse=False)
X_train=vec.fit_transform(X_train.to_dict(orient='record'))
print(vec.feature_names_)
X_test=vec.transform(X_test.to_dict(orient='record'))
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
dtc = DecisionTreeClassifier()
dtc.fit(X_train,y_train)
dtc_y_pred=dtc.predict(X_test)
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
rfc = RandomForestClassifier()
rfc.fit(X_train,y_train)
rfc_y_pred=rfc.predict(X_test)
from sklearn.ensemble import GradientBoostingClassifier
gbc = GradientBoostingClassifier()
gbc.fit(X_train,y_train)
gbc_y_pred = gbc.predict(X_test)
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
print('The accuracy of decision tree is',dtc.score(X_test,y_test))
print(classification_report(dtc_y_pred,y_test))
print('The accuracy of random decision tree is',rfc.score(X_test,y_test))
print(classification_report(rfc_y_pred,y_test))
print('The accuracy of gradient forest tree is',gbc.score(X_test,y_test))
print(classification_report(gbc_y_pred,y_test))
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
def show_values(pc, fmt="%.2f", **kw):
'''
Heatmap with text in each cell with matplotlib's pyplot
Source: https://stackoverflow.com/a/25074150/395857
By HYRY
'''
global zip
import itertools
zip = getattr(itertools, 'izip', zip)
pc.update_scalarmappable()
ax = pc.axes
for p, color, value in zip(pc.get_paths(), pc.get_facecolors(), pc.get_array()):
x, y = p.vertices[:-2, :].mean(0)
if np.all(color[:3] > 0.5):
color = (0.0, 0.0, 0.0)
else:
color = (1.0, 1.0, 1.0)
ax.text(x, y, fmt % value, ha="center", va="center", color=color, **kw)
def cm2inch(*tupl):
'''
Specify figure size in centimeter in matplotlib
Source: https://stackoverflow.com/a/22787457/395857
By gns-ank
'''
inch = 2.54
if type(tupl[0]) == tuple:
return tuple(i/inch for i in tupl[0])
else:
return tuple(i/inch for i in tupl)
def heatmap(AUC, title, xlabel, ylabel, xticklabels, yticklabels, figure_width=40, figure_height=20, correct_orientation=False, cmap='RdBu'):
'''
Inspired by:
- https://stackoverflow.com/a/16124677/395857
- https://stackoverflow.com/a/25074150/395857
'''
# Plot it out
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
#c = ax.pcolor(AUC, edgecolors='k', linestyle= 'dashed', linewidths=0.2, cmap='RdBu', vmin=0.0, vmax=1.0)
c = ax.pcolor(AUC, edgecolors='k', linestyle= 'dashed', linewidths=0.2, cmap=cmap)
# put the major ticks at the middle of each cell
ax.set_yticks(np.arange(AUC.shape[0]) + 0.5, minor=False)
ax.set_xticks(np.arange(AUC.shape[1]) + 0.5, minor=False)
# set tick labels
#ax.set_xticklabels(np.arange(1,AUC.shape[1]+1), minor=False)
ax.set_xticklabels(xticklabels, minor=False)
ax.set_yticklabels(yticklabels, minor=False)
# set title and x/y labels
plt.title(title)
plt.xlabel(xlabel)
plt.ylabel(ylabel)
# Remove last blank column
plt.xlim( (0, AUC.shape[1]) )
# Turn off all the ticks
ax = plt.gca()
for t in ax.xaxis.get_major_ticks():
t.tick1On = False
t.tick2On = False
for t in ax.yaxis.get_major_ticks():
t.tick1On = False
t.tick2On = False
# Add color bar
plt.colorbar(c)
# Add text in each cell
show_values(c)
# Proper orientation (origin at the top left instead of bottom left)
if correct_orientation:
ax.invert_yaxis()
ax.xaxis.tick_top()
# resize
fig = plt.gcf()
#fig.set_size_inches(cm2inch(40, 20))
#fig.set_size_inches(cm2inch(40*4, 20*4))
fig.set_size_inches(cm2inch(figure_width, figure_height))
def plot_classification_report(classification_report, title='Classification report ', cmap='RdBu'):
'''
Plot scikit-learn classification report.
Extension based on https://stackoverflow.com/a/31689645/395857
'''
lines = classification_report.split('\n')
classes = []
plotMat = []
support = []
class_names = []
for line in lines[2 : (len(lines) - 2)]:
t = line.strip().split()
if len(t) < 2: continue
classes.append(t[0])
v = [float(x) for x in t[1: len(t) - 1]]
support.append(int(t[-1]))
class_names.append(t[0])
print(v)
plotMat.append(v)
print('plotMat: {0}'.format(plotMat))
print('support: {0}'.format(support))
xlabel = 'Metrics'
ylabel = 'Classes'
xticklabels = ['Precision', 'Recall', 'F1-score']
yticklabels = ['{0} ({1})'.format(class_names[idx], sup) for idx, sup in enumerate(support)]
figure_width = 25
figure_height = len(class_names) + 7
correct_orientation = False
heatmap(np.array(plotMat), title, xlabel, ylabel, xticklabels, yticklabels, figure_width, figure_height, correct_orientation, cmap=cmap)
#传入相应的report结果
def main():
sampleClassificationReport =classification_report(dtc_y_pred,y_test)
plot_classification_report(sampleClassificationReport)
plt.savefig('decision_tree_report.png', dpi=200, format='png', bbox_inches='tight')
plt.close()
sampleClassificationReport1 =classification_report(rfc_y_pred,y_test)
plot_classification_report(sampleClassificationReport1)
plt.savefig('radom_forest_classifier_report.png', dpi=200, format='png', bbox_inches='tight')
plt.close()
sampleClassificationReport2 =classification_report(gbc_y_pred,y_test)
plot_classification_report(sampleClassificationReport2)
plt.savefig('gradient_tree_classifier_report.png', dpi=200, format='png', bbox_inches='tight')
plt.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
#cProfile.run('main()') # if you want to do some profiling
输出结果如下:
File "D:\Python35\lib\urllib\request.py", line 1256, in do_open
raise URLError(err)
urllib.error.URLError: <urlopen error [WinError 10060] 由于连接方在一段时间后没有正确答复或连接的主机没有反应,连接尝试失败。>
修改数据连接文件:titanic = pd.read_csv('../Datasets/Breast-Cancer/titanic.txt')最后输出结果如下:
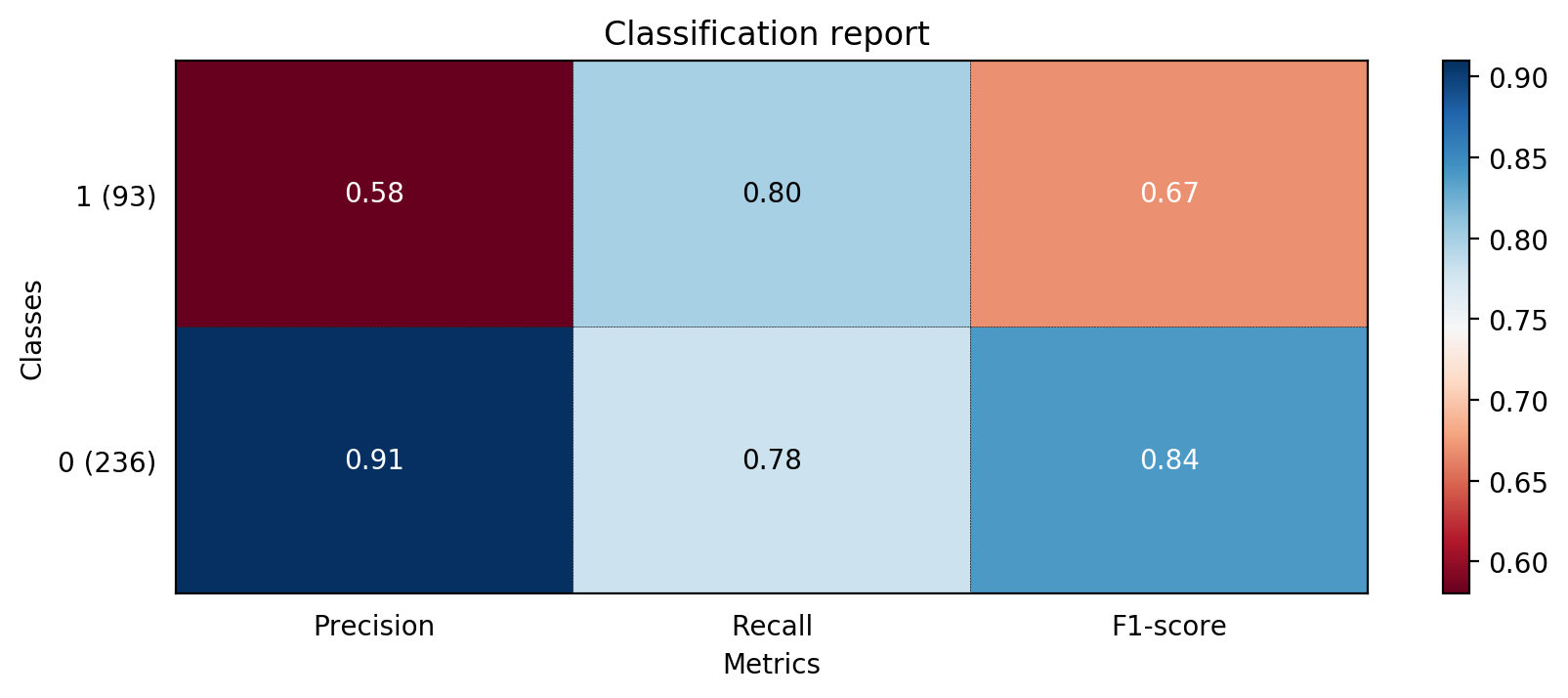
The accuracy of decision tree is 0.7811550151975684
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.91 0.78 0.84 236
1 0.58 0.80 0.67 93
avg / total 0.81 0.78 0.79 329
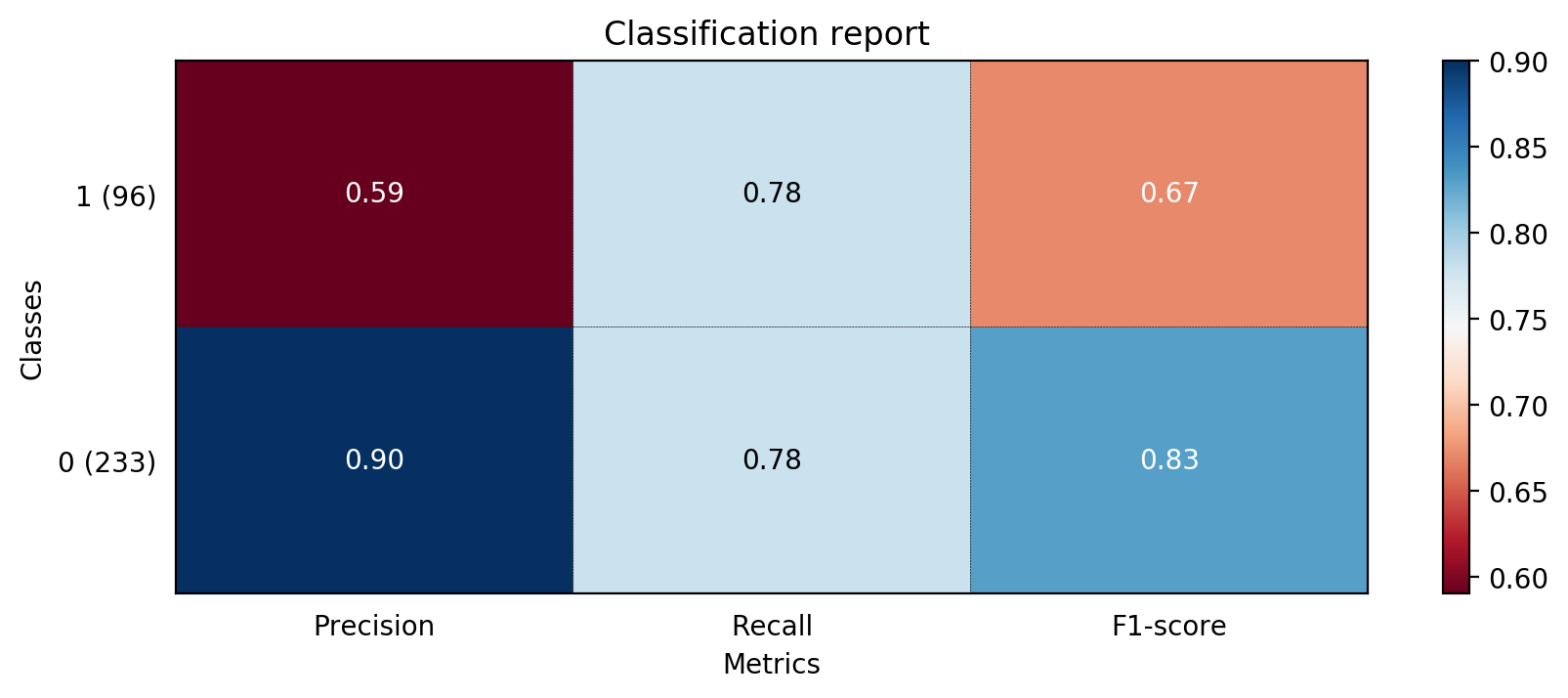
The accuracy of random decision tree is 0.7781155015197568
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.90 0.78 0.83 233
1 0.59 0.78 0.67 96
avg / total 0.81 0.78 0.79 329
The accuracy of gradient forest tree is 0.790273556231003
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.92 0.78 0.84 239
1 0.58 0.82 0.68 90
avg / total 0.83 0.79 0.80 329可视化分析如下图所示:























 843
843

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








