文章目录
1.原型链继承
1.1 实现方式
function Person(sing) {
this.sing = sing;
this.jump = function () {
console.log("jump");
};
}
Person.prototype.rap = function () {
console.log("rap");
};
function Children() {}
// 将 Person 构造函数的实例对象赋值给 Children 构造函数的原型,Children 就能拿到 Person 中所有的属性及方法
Children.prototype = new Person("sing");
const c1 = new Children();
const c2 = new Children();
console.log(c1.sing);
c1.jump();
c1.rap();
输出结果:
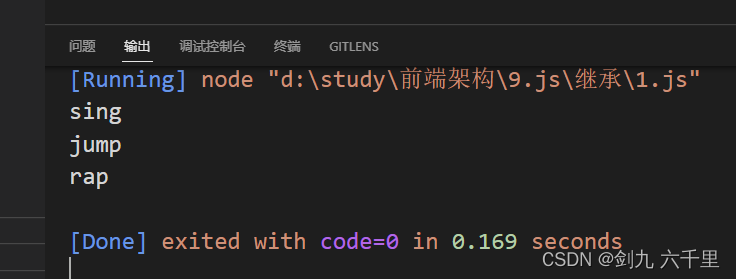
1.2 优缺点
- 优点:实现简单,一行代码
- 缺点:数据共享了,c1和c2共享了同一个原型对象
2.借用构造函数继承
1.实现方式
function Person(sing) {
this.sing = sing;
this.jump = function () {
console.log("jump");
};
}
function Children(sing) {
// this -> Children 的实例对象
Person.call(this, sing);
}
const c1 = new Children("sing1");
const c2 = new Children("sing2");
console.log(c1.sing);
console.log(c2.sing);
c1.jump();
输出结果:
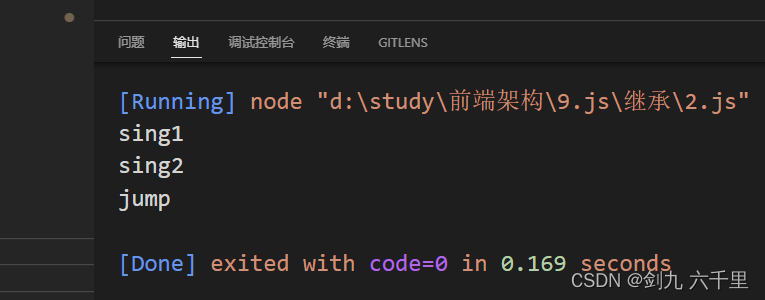
2.2 优缺点
- 优点:
- 避免了引用类型的属性被所有的实例共享;
- 可以在
Children中向Person传参
- 缺点:
- 方法都在构造函数中定义,每次创建实例都会创建一遍方法;
- 不能继承
Person原型上的方法/属性
Person.prototype.rap = function () { console.log("rap"); }; c1.rap(); // 这样去使用的话会报错 rap 未定义
3.组合继承
3.1.实现方式
Person.call(this, sing); // 借用构造器Children.prototype = new Person(); // 原型链继承,能继承原型上的方法Children.prototype.constructor = Children; // 将构造函数引用指向 Children
function Person(sing) {
this.sing = sing;
this.jump = function () {
console.log("jump");
};
}
Person.prototype.rap = function () {
console.log("rap");
};
function Children(sing, ball) {
// this -> Children 的实例对象
Person.call(this, sing); // 借用构造器
this.ball = ball;
}
Children.prototype = new Person(); // 原型链继承,能继承原型上的方法
/**
* 如果不显式地将 Children.prototype.constructor 设置为 Children,
* 那么 Children.prototype.constructor 将会指向 Parent,
* 因为 Children.prototype 是基于 Parent.prototype 创建的。
* 这显然是不正确的,因为 Children.prototype 应该与 Children 构造函数相关联。
*/
Children.prototype.constructor = Children; // 将构造函数引用指向 Children
const c1 = new Children("sing1");
const c2 = new Children("sing2");
console.log(c1.sing);
console.log(c2.sing);
c1.jump();
c1.rap();
3.2 优缺点
- 融合原型链继承和构造函数的优点,是
JavaScript中最常用的继承模式
4.寄生式继承
4.1.实现方式
function createObj(o) {
var clone = Object.create(o);
clone.sayName = function () {
console.log("hi");
};
return clone;
}
let c = createObj({
hello: "world",
});
console.log(c.hello); // world
c.sayName(); // hi
输出结果:

5. ES6中的 class 继承
5.1 基本实现
- 通过
class关键字声明类 - 子类通过
extends关键字继承父类
class Person {
constructor(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
say() {
console.log("say");
}
}
class Children extends Person {}
let c1 = new Children("嘎子", 18);
let c2 = new Children("英子", 22);
console.log(c1.name);
console.log(c1.age);
console.log(c1.say);
console.log(c2.name);
console.log(c2.say);
- 输出结果




























 520
520

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










