时钟机制是驱动Linux内核运转的核心组件,他的工作方式有两种,periodic(周期性的)和NO_HZ_FULL(IDLE).在不同的模式下,时钟周期的精度是不同的,下面做实验验证一下.
测试用例如下,pselect不传入文件列表参数,将导致等待超时返回,行为上和一个定时器没有任何区别。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<time.h>
#include<sys/time.h>
#include<errno.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/select.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
unsigned int nTimeTestSec = 0;
unsigned int nTimeTest = 0;
struct timeval tvBegin;
struct timeval tvNow;
int ret = 0;
unsigned int nDelay = 0;
struct timeval tv;
int fd = 1;
int i = 0;
struct timespec req;
unsigned int delay[20] =
{500000, 100000, 50000, 10000, 1000, 900, 500, 100, 10, 1, 0};
int nReduce = 0; //误差
fprintf(stderr, "%19s%12s%12s%12s\n", "fuction", "time(usec)", "realtime", "reduce");
fprintf(stderr, "----------------------------------------------------\n");
for (i = 0; i < 20; i++)
{
if (delay[i] <= 0)
break;
nDelay = delay[i];
//test sleep
gettimeofday(&tvBegin, NULL);
ret = usleep(nDelay);
if(ret == -1)
{
fprintf(stderr, "usleep error, errno=%d [%s]\n", errno, strerror(errno));
}
gettimeofday(&tvNow, NULL);
nTimeTest = (tvNow.tv_sec - tvBegin.tv_sec) * 1000000 + tvNow.tv_usec - tvBegin.tv_usec;
nReduce = nTimeTest - nDelay;
fprintf (stderr, "\t usleep %8u %8u %8d\n", nDelay, nTimeTest,nReduce);
//test nanosleep
req.tv_sec = nDelay/1000000;
req.tv_nsec = (nDelay%1000000) * 1000;
gettimeofday(&tvBegin, NULL);
ret = nanosleep(&req, NULL);
if (-1 == ret)
{
fprintf (stderr, "\t nanousleep %8u not support\n", nDelay);
}
gettimeofday(&tvNow, NULL);
nTimeTest = (tvNow.tv_sec - tvBegin.tv_sec) * 1000000 + tvNow.tv_usec - tvBegin.tv_usec;
nReduce = nTimeTest - nDelay;
fprintf (stderr, "\t nanosleep %8u %8u %8d\n", nDelay, nTimeTest,nReduce);
//test select
tv.tv_sec = 0;
tv.tv_usec = nDelay;
gettimeofday(&tvBegin, NULL);
ret = select(0, NULL, NULL, NULL, &tv);
if (-1 == ret)
{
fprintf(stderr, "select error. errno = %d [%s]\n", errno, strerror(errno));
}
gettimeofday(&tvNow, NULL);
nTimeTest = (tvNow.tv_sec - tvBegin.tv_sec) * 1000000 + tvNow.tv_usec - tvBegin.tv_usec;
nReduce = nTimeTest - nDelay;
fprintf (stderr, "\t select %8u %8u %8d\n", nDelay, nTimeTest,nReduce);
//pselcet
req.tv_sec = nDelay/1000000;
req.tv_nsec = (nDelay%1000000) * 1000;
gettimeofday(&tvBegin, NULL);
ret = pselect(0, NULL, NULL, NULL, &req, NULL);
if (-1 == ret)
{
fprintf(stderr, "select error. errno = %d [%s]\n", errno, strerror(errno));
}
gettimeofday(&tvNow, NULL);
nTimeTest = (tvNow.tv_sec - tvBegin.tv_sec) * 1000000 + tvNow.tv_usec - tvBegin.tv_usec;
nReduce = nTimeTest - nDelay;
fprintf (stderr, "\t pselect %8u %8u %8d\n", nDelay, nTimeTest,nReduce);
fprintf (stderr, "--------------------------------\n");
}
return 0;
}在使用高精度定时器的情况下测试开关PREEMPT的情况:
关闭CONFIG_PREEMPT的情况下


打开CONFIG_PREEMPT
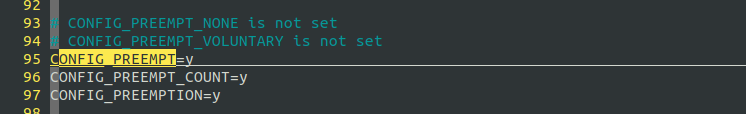
重新编译和安装内核:

貌似改善不多,可以得出CONFIG_PREEMPT和精度关系不大的结论,我们继续.打开周期定时器:

关闭高精度定时器:
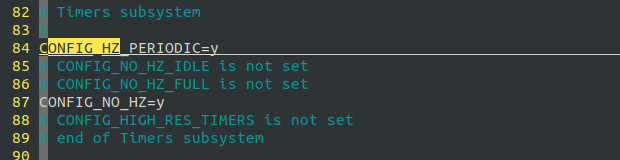
运行用例验证,可以明显发现,由于时钟模式变为periodic的了,时钟粒度瞬间缩减为4ms=4000us,所以例子中即便睡眠1个us,也需要等到4ms后才会被唤醒,和没有打开periodic的模式有显著区别.超时时间将ceiling到系统时钟粒度。


CONFIG_HZ修改为100,看有没有变化:
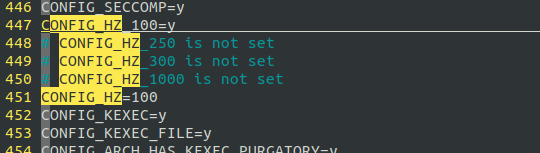
重新编译内核,发现时钟粒度再次变大,CONFIG_HZ从250变为100. 时钟粒度则从4ms变为10ms成反比关系.

打开CONFIG_HIGH_RES_TIMERS
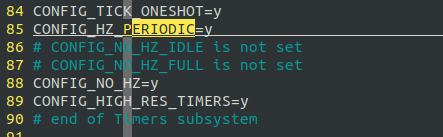
重新编译,运行用例:

可以看到,打开高精度定时器,时间精度恢复了原始的比较精确的误差范围.
关闭CONFIG_NO_HZ

发现时间精度仍然是高精度的范围

所以看起来,控制高精度定时器的是CONFIG_HIGH_RES_TIMERS.
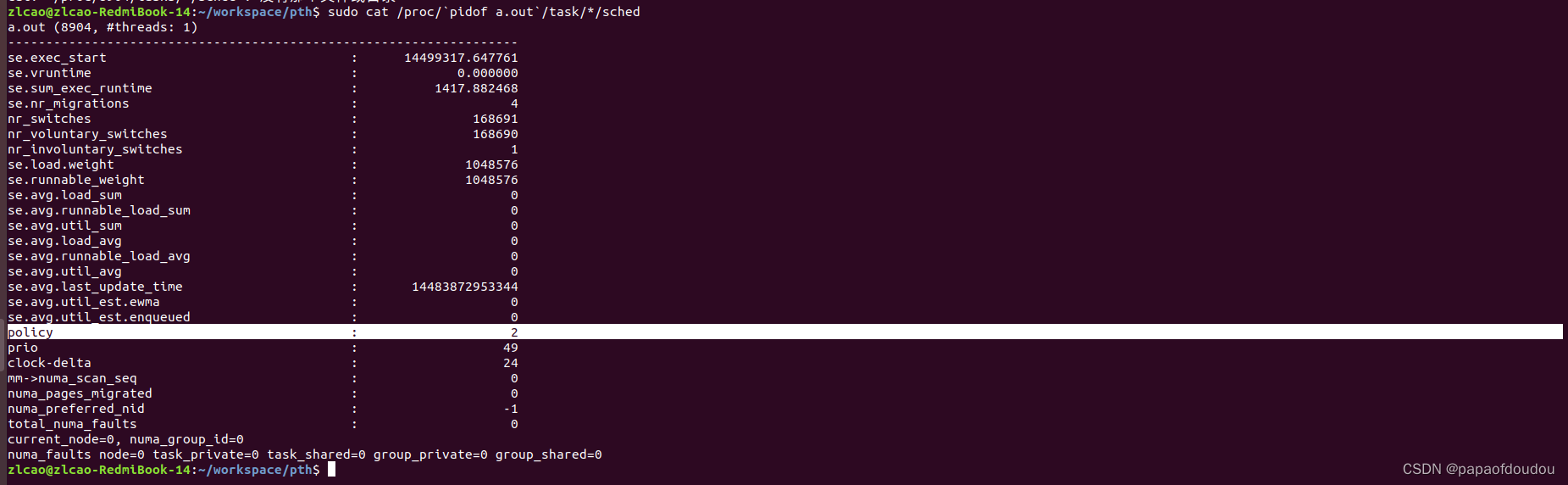
线程优先级对于时钟精度的影响
测试代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <chrono>
#include<thread>
#include <pthread.h>
using namespace std;
int get_thread_info(void)
{
pthread_t self = pthread_self();
int policy;
struct sched_param param;
if (pthread_getschedparam(self, &policy, ¶m) != 0) {
printf("%s line %d, pthread_getschedparam error.\n",
__func__, __LINE__);
return -1;
}
switch (policy) {
case SCHED_FIFO:
printf("SCHED_FIFO\n");
break;
case SCHED_RR:
printf("SCHED_RR\n");
break;
case SCHED_OTHER:
printf("SCHED_OTHER\n");
break;
default:
printf("unknown.\n");
break;
}
printf("current thread priority:%d\n", param.sched_priority);
return 0;
}
void adjust_priority(void)
{
struct sched_param params;
params.sched_priority = 50; // 50是优先级值,可以根据需求设置
if(pthread_setschedparam(pthread_self(), SCHED_RR, ¶ms) != 0) {
printf("%s line %d, error, failure.\n", __func__, __LINE__);
} else {
printf("%s line %d, set priority success.\n", __func__, __LINE__);
}
get_thread_info();
return;
}
int main(void)
{
int nTimerValue = 100; //wait for 100 ms
adjust_priority();
for (int i = 0; /*i < 500*/; ++i) {
auto start = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::microseconds(nTimerValue));
auto clock_end = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
long lElapsetimeMs = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::microseconds>(clock_end - start).count();
char szBuff[255];
sprintf(szBuff, "[%d] slept Time: %ld MiroSec\n", i, lElapsetimeMs);
cout << szBuff;
}
cout << "system clock : ";
cout << chrono::system_clock::period::num << "/" << chrono::system_clock::period::den << "s" << endl;
cout << "steady clock : ";
cout << chrono::steady_clock::period::num << "/" << chrono::steady_clock::period::den << "s" << endl;
cout << "high resolution clock : ";
cout << chrono::high_resolution_clock::period::num << "/" << chrono::high_resolution_clock::period::den << "s" << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}编译代码:
g++ xxx.c -lpthread
在CFS调度器的情况下,睡眠100微妙,实际上的睡眠事件可能在150+

设置RR优先级,用SUDO模式运行,时间精度缩小到如下值:

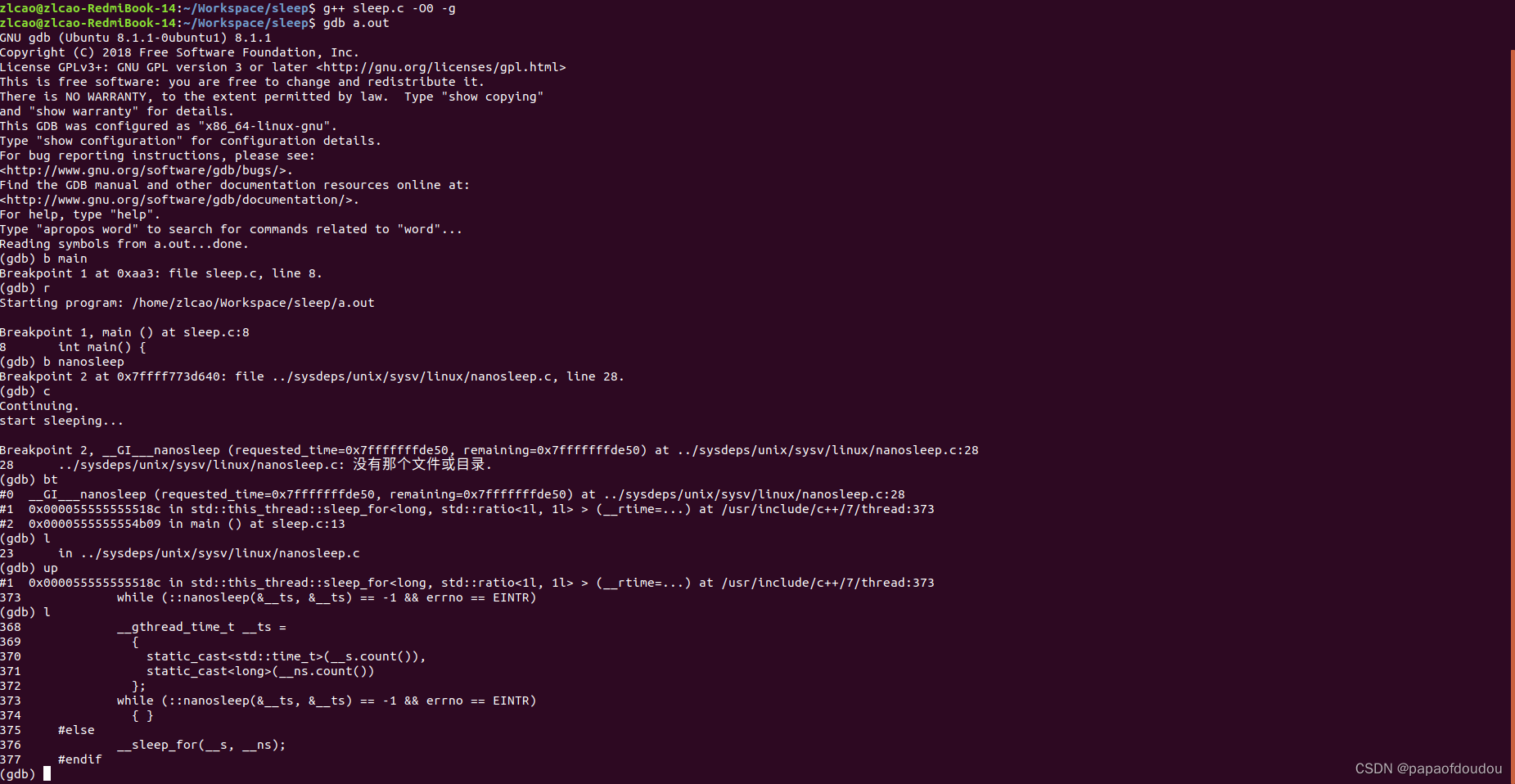
c++标准中的sleep_for用的就是nanosleep:
在musl中,usleep就是用nanosleep实现的:

打开CONFIG_HIGH_RES_TIMERS和关闭下,HRTIMER唤醒的区别
CONFIG_HIGH_RES_TIMERS打开:

CONFIG_HZ_PERIODIC打开,CONFIG_HIGH_RES_TIMERS关闭,则hrtimer_wakeup在周期中断下调度:
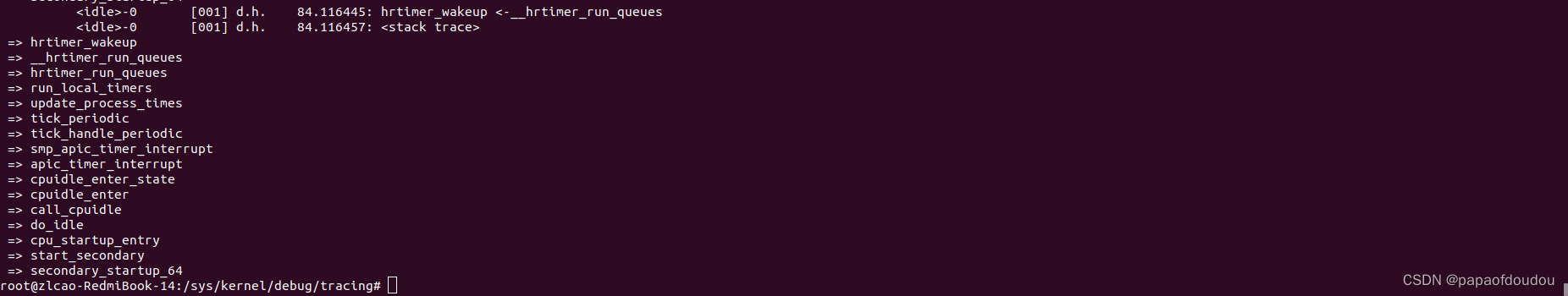
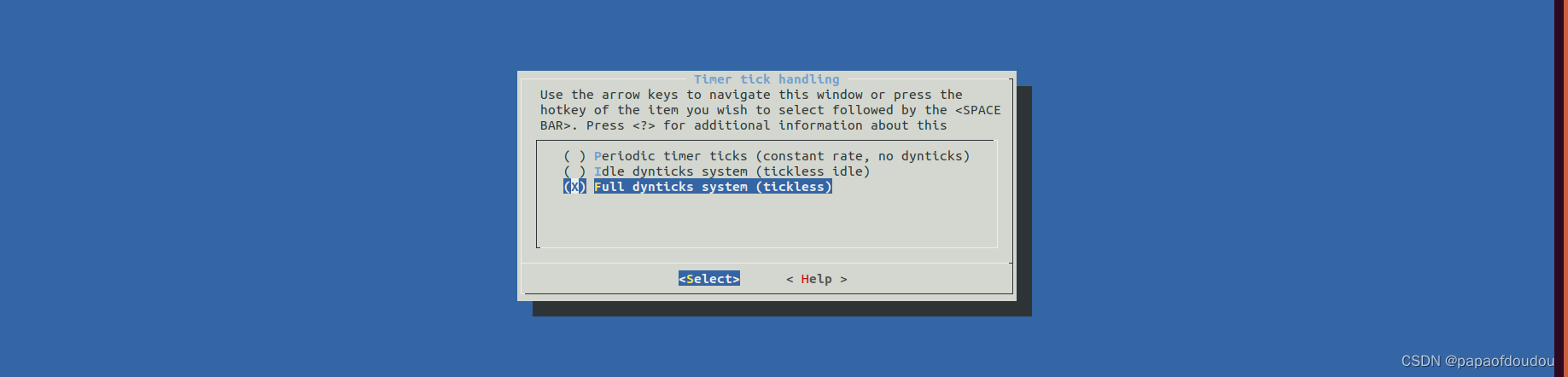
CONFIG_HZ_PERIODIC关闭,CONFIG_HIGH_RES_TIMERS关闭,CONFIG_NO_HZ_FULL关闭,CONFIG_NO_HZ_IDLE=y。
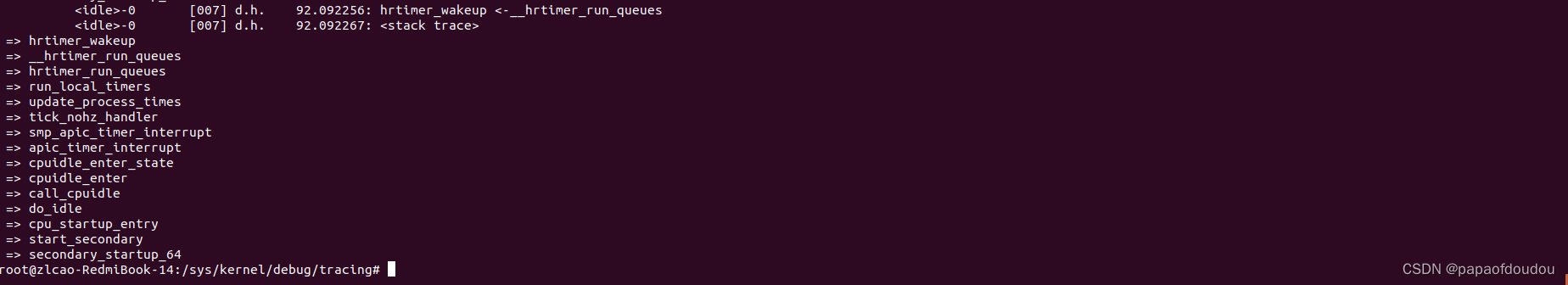
CONFIG_NO_HZ_FULL=y,CONFIG_HZ_PERIODIC关闭,CONFIG_NO_HZ_IDLE关闭,CONFIG_HIGH_RES_TIMERS关闭。
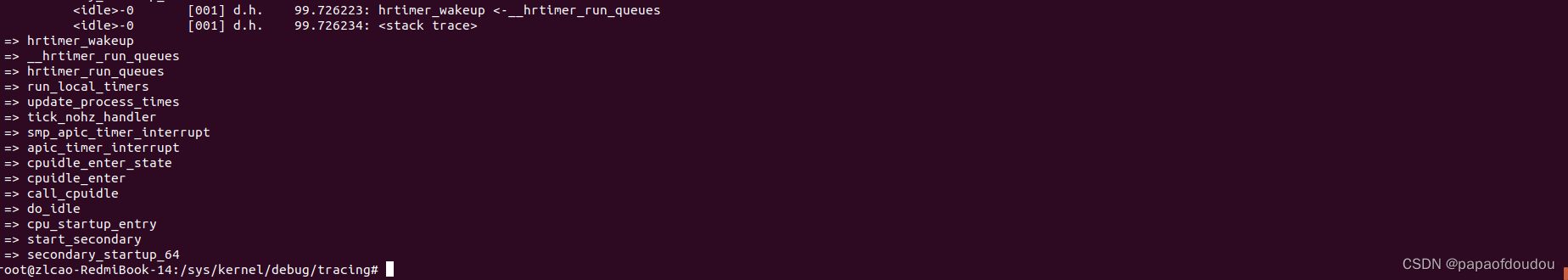
CONFIG_NO_HZ_FULL/CONFIG_NO_HZ_IDLE/CONFIG_HZ_PERIODIC 是互斥关系,只能三选1。
CONFIG_HZ配置
关于CONFIG_HZ的影响,以REDHAT企业版为例,RH企业版的CONFIG_HZ参数设置为1000,而其他服务器发行版,比如UBUNTU是250,这样运行RH的系统会有比较大的系统时钟负荷,在某些场景下,会影响场景的效率,一种解决方案是在启动参数中设置divider=xx,意思是1/XX的CONFIG_HZ 频率,详细解释如下:

























 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










