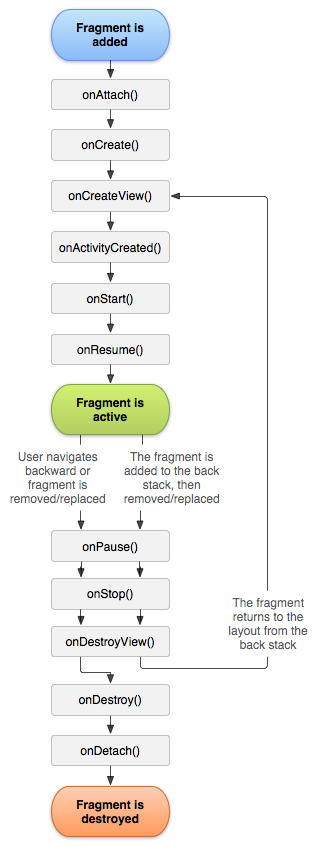
1.附上生命周期
1.执行如下方法后提交fragment
transaction.commit(); public int commit() {
return commitInternal(false);
}
public int commitAllowingStateLoss() {
return commitInternal(true);
}
int commitInternal(boolean allowStateLoss) {
if (mCommitted) throw new IllegalStateException("commit already called");
if (FragmentManagerImpl.DEBUG) {
Log.v(TAG, "Commit: " + this);
LogWriter logw = new LogWriter(TAG);
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(logw);
dump(" ", null, pw, null);
}
mCommitted = true;
if (mAddToBackStack) {
mIndex = mManager.allocBackStackIndex(this);
} else {
mIndex = -1;
}
mManager.enqueueAction(this, allowStateLoss);
return mIndex;
}由于BackStackRecord实现了runnable,所以就把它自己通过 mManager.enqueueAction(this, allowStateLoss);加入到了FragmentManagerImpl的mPendingActions中:
/**
* Adds an action to the queue of pending actions.
*
* @param action the action to add
* @param allowStateLoss whether to allow loss of state information
* @throws IllegalStateException if the activity has been destroyed
*/
public void enqueueAction(Runnable action, boolean allowStateLoss) {
if (!allowStateLoss) {
checkStateLoss();
}
synchronized (this) {
if (mDestroyed || mActivity == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Activity has been destroyed");
}
if (mPendingActions == null) {
mPendingActions = new ArrayList<Runnable>();
}
mPendingActions.add(action);
if (mPendingActions.size() == 1) {
mActivity.mHandler.removeCallbacks(mExecCommit);
mActivity.mHandler.post(mExecCommit);
}
}
} Runnable mExecCommit = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
execPendingActions();
}
};/**
* Only call from main thread!
*/
public boolean execPendingActions() {
if (mExecutingActions) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Recursive entry to executePendingTransactions");
}
if (Looper.myLooper() != mActivity.mHandler.getLooper()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Must be called from main thread of process");
}
boolean didSomething = false;
while (true) {
int numActions;
synchronized (this) {
if (mPendingActions == null || mPendingActions.size() == 0) {
break;
}
numActions = mPendingActions.size();
if (mTmpActions == null || mTmpActions.length < numActions) {
mTmpActions = new Runnable[numActions];
}
mPendingActions.toArray(mTmpActions);
mPendingActions.clear();
mActivity.mHandler.removeCallbacks(mExecCommit);
}
mExecutingActions = true;
for (int i=0; i<numActions; i++) {
mTmpActions[i].run();
mTmpActions[i] = null;
}
mExecutingActions = false;
didSomething = true;
}
if (mHavePendingDeferredStart) {
boolean loadersRunning = false;
for (int i=0; i<mActive.size(); i++) {
Fragment f = mActive.get(i);
if (f != null && f.mLoaderManager != null) {
loadersRunning |= f.mLoaderManager.hasRunningLoaders();
}
}
if (!loadersRunning) {
mHavePendingDeferredStart = false;
startPendingDeferredFragments();
}
}
return didSomething;
} synchronized (this) {
if (mPendingActions == null || mPendingActions.size() == 0) {
break;
}
numActions = mPendingActions.size();
if (mTmpActions == null || mTmpActions.length < numActions) {
mTmpActions = new Runnable[numActions];
}
mPendingActions.toArray(mTmpActions);
mPendingActions.clear();
mActivity.mHandler.removeCallbacks(mExecCommit);
}然后通过以下代码遍历执行BackStackRecord中的run方法执行:
for (int i=0; i<numActions; i++) {
mTmpActions[i].run();
mTmpActions[i] = null;
} public void run() {
if (FragmentManagerImpl.DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "Run: " + this);
if (mAddToBackStack) {
if (mIndex < 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("addToBackStack() called after commit()");
}
}
bumpBackStackNesting(1);
Op op = mHead;
while (op != null) {
switch (op.cmd) {
case OP_ADD: {
Fragment f = op.fragment;
f.mNextAnim = op.enterAnim;
mManager.addFragment(f, false);
} break;
case OP_REPLACE: {
Fragment f = op.fragment;
if (mManager.mAdded != null) {
for (int i=0; i<mManager.mAdded.size(); i++) {
Fragment old = mManager.mAdded.get(i);
if (FragmentManagerImpl.DEBUG) Log.v(TAG,
"OP_REPLACE: adding=" + f + " old=" + old);
if (f == null || old.mContainerId == f.mContainerId) {
if (old == f) {
op.fragment = f = null;
} else {
if (op.removed == null) {
op.removed = new ArrayList<Fragment>();
}
op.removed.add(old);
old.mNextAnim = op.exitAnim;
if (mAddToBackStack) {
old.mBackStackNesting += 1;
if (FragmentManagerImpl.DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "Bump nesting of "
+ old + " to " + old.mBackStackNesting);
}
mManager.removeFragment(old, mTransition, mTransitionStyle);
}
}
}
}
if (f != null) {
f.mNextAnim = op.enterAnim;
mManager.addFragment(f, false);
}
} break;
case OP_REMOVE: {
Fragment f = op.fragment;
f.mNextAnim = op.exitAnim;
mManager.removeFragment(f, mTransition, mTransitionStyle);
} break;
case OP_HIDE: {
Fragment f = op.fragment;
f.mNextAnim = op.exitAnim;
mManager.hideFragment(f, mTransition, mTransitionStyle);
} break;
case OP_SHOW: {
Fragment f = op.fragment;
f.mNextAnim = op.enterAnim;
mManager.showFragment(f, mTransition, mTransitionStyle);
} break;
case OP_DETACH: {
Fragment f = op.fragment;
f.mNextAnim = op.exitAnim;
mManager.detachFragment(f, mTransition, mTransitionStyle);
} break;
case OP_ATTACH: {
Fragment f = op.fragment;
f.mNextAnim = op.enterAnim;
mManager.attachFragment(f, mTransition, mTransitionStyle);
} break;
default: {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown cmd: " + op.cmd);
}
}
op = op.next;
}
mManager.moveToState(mManager.mCurState, mTransition,
mTransitionStyle, true);
if (mAddToBackStack) {
mManager.addBackStackState(this);
}
} static final int OP_NULL = 0;
static final int OP_ADD = 1;
static final int OP_REPLACE = 2;
static final int OP_REMOVE = 3;
static final int OP_HIDE = 4;
static final int OP_SHOW = 5;
static final int OP_DETACH = 6;
static final int OP_ATTACH = 7;对应commit之前调用的方法:
transaction.add
transaction.replace
transaction.remove
transaction.hide
transaction.show
transaction.detach
transaction.attach首先会调用mManager.addFragment(f, false);
public void addFragment(Fragment fragment, boolean moveToStateNow) {
if (mAdded == null) {
mAdded = new ArrayList<Fragment>();
}
if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "add: " + fragment);
makeActive(fragment);
if (!fragment.mDetached) {
if (mAdded.contains(fragment)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Fragment already added: " + fragment);
}
mAdded.add(fragment);
fragment.mAdded = true;
fragment.mRemoving = false;
if (fragment.mHasMenu && fragment.mMenuVisible) {
mNeedMenuInvalidate = true;
}
if (moveToStateNow) {
moveToState(fragment);
}
}
} void makeActive(Fragment f) {
if (f.mIndex >= 0) {
return;
}
if (mAvailIndices == null || mAvailIndices.size() <= 0) {
if (mActive == null) {
mActive = new ArrayList<Fragment>();
}
f.setIndex(mActive.size(), mParent);
mActive.add(f);
} else {
f.setIndex(mAvailIndices.remove(mAvailIndices.size()-1), mParent);
mActive.set(f.mIndex, f);
}
if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "Allocated fragment index " + f);
}if (moveToStateNow) {
moveToState(fragment);
}而是通过run方法最后的代码来执行
mManager.moveToState(mManager.mCurState, mTransition,
mTransitionStyle, true);






















 948
948

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








