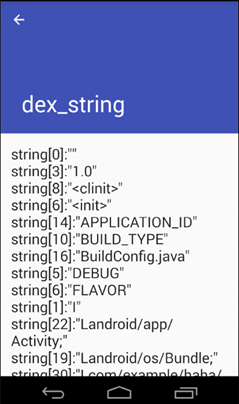
先学习dex文件格式,如图所示(图片来源于网络):
思路:
1.apk文件应用名称写死,修改为dex.zip,保存在固定的目录下,download目录下,使用函数获取路径
2.使用java中的zip类来实现dex.zip文件的解压,得到dex文件数据,并保存在内存中,java解析zip方法参考源码注释。
3.通过点击floatbutton加载classes.dex文件即可
4.进行解析
4.1先设计每个结构体都封装一个java bean类,每个类中有响应的字段解析方法,
4.2再在界面显示
--------------------------------
思路简化:
1.直接将classes.dex文件复制到download目录下
2.读取文件内容保存到byte数组中
3.通过点击floatbutton加载classes.dex文件即可
4.进行解析
4.1先设计每个结构体都封装一个java bean类,每个类中有响应的字段解析方法,
4.2再在界面显示
--------------------------------
目的在于熟悉dex文件格式,所以没有实现复杂文件操作,直接写死的路径,通过直接在程序初始化时初始化对象,所以需要将dex文件复制到downloa目录下,且命名为classes.dex,否则程序直接退出。其中使用了android文件相关操作,一些路径的标准写法
Environment.getDataDirectory()= /data
Environment.getDownloadCacheDirectory()= /cache
Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory()= /mnt/sdcard
Environment.getRootDirectory()= /system
context.getCacheDir()= /data/data/com.mt.mtpp/cache
context.getExternalCacheDir()= /mnt/sdcard/Android/data/com.mt.mtpp/cache
context.getFilesDir()= /data/data/com.mt.mtpp/files
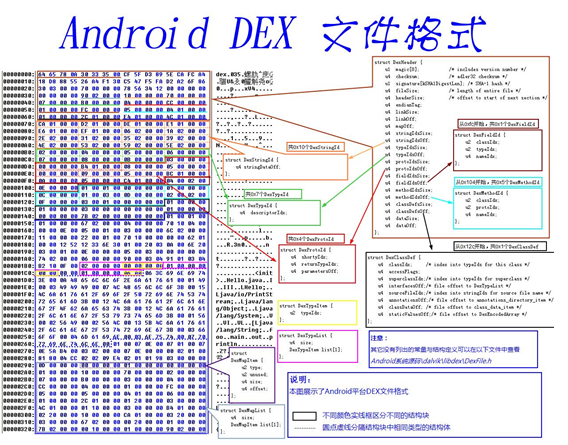
实现功能如图所示(部分截图):


1.解析dexHeader
public dexHeader()throws IOException{
//1.获取文件路径,
String dexPath = GetDexFilePath();
//2.获取zip文件中的classes.dex,并读取字节
//2.打开dex文件,并读取头部数据到byte中
List<Byte> byteList = new ArrayList<Byte>();
byteList = getDexHeard(dexPath);
//3.需要判断魔数是否为合法dex文件64 65 78
if (!(byteList.get(0) == 0x64
&& byteList.get(1) == 0x65
&& byteList.get(2) == 0x78)){
IOException e = null;
throw e;
}
//4.将缓冲区内容按格式分别存储到对应的结构(javabean)对象中
//解析dex_header并保存各节的数据到对应的javabean对象中
ParseDexHeader(byteList);
} public String GetDexFilePath() {
String path = null;
//获取安卓download文件下的dex.zip文件路径
File inRoot = Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory();
path = inRoot.getPath() + "/"
+ Environment.DIRECTORY_DOWNLOADS + "/classes.dex";
return path;
}
private List<Byte> getDexHeard(String dexPath) throws IOException{
File dexfile = new File(dexPath);
InputStream in = null;
List<Byte> bytelist = new ArrayList<Byte>();
// 一次读一个字节
in = new FileInputStream(dexfile);
int tempbyte;
//dex头大小为0x70
int count = 0x70;
while (count != 0) {
tempbyte = in.read();
bytelist.add((byte) tempbyte);
count--;
}
in.close();
return bytelist;
}2.解析dexString
public dexString(dexHeader dexheader){
//从头部获取偏移和大小
this.byteStrSize = dexheader.stringsize;
this.byteStrOff = dexheader.stringoff;
//转换成int型
byte[] tempSize = new byte[4];
byte[] tempOff = new byte[4];
tempSize = bytereverse(byteStrSize);
tempOff = bytereverse(byteStrOff);
int intStrSize = byte2int(tempSize);
//偏移
int intStrOff = byte2int(tempOff);
//保存偏移值到stringID中
for (int i = 0; i < intStrSize; i++){
stringOffList.add(intStrOff);
intStrOff += 4;
}
try {
StringID strid = new StringID();
strIntsize = strid.getStrDataList();
strStringValue = strid.getStrStringList();
setStrIntsize(strIntsize);
setStrStringValue(strStringValue);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("解析String出错!");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}3.解析dexType
public dexType(dexHeader dexheader, dexString dexstring) throws IOException {
//从头部对象中获取type的大小和偏移
this.typeSize = dexheader.typesize;
this.typeOff = dexheader.typeoff;
//将获取的大小和偏移转化成int型
byte[] tempSize = new byte[4];
byte[] tempOff = new byte[4];
tempSize = bytereverse(typeSize);
tempOff = bytereverse(typeOff);
int intTypeSize = byte2int(tempSize);
//偏移,
int intTypeOff = byte2int(tempOff);
//保存到typeOffList中
//这个偏移里面保存了字符串表中的索引
for (int i = 0; i < intTypeSize; i++){
typeOffList.add(intTypeOff);
intTypeOff += 4;
}
//读文件取出索引值
for (int i = 0; i < typeOffList.size(); i++){
byte[] tmp = new byte[4];
int off = typeOffList.get(i);
List<Byte> tByte = readDexString(GetDexFilePath(), off);
//将byte转成int
tmp[0] = tByte.get(0);
tmp[1] = tByte.get(1);
tmp[2] = tByte.get(2);
tmp[3] = tByte.get(3);
tmp = bytereverse(tmp);
int StrIndex = byte2int(tmp);
//保存index值用于显示
intindex.add(StrIndex);
//在通过索引值在字符串表中找到对应字符串
String strRes = dexstring.getStrStringValue().get(StrIndex);
typeStringList.add(strRes);
}
setIntindex(intindex);
setTypeStringList(typeStringList);
}4.解析dexProto
//构造方法
public dexProto(dexHeader dexheader, dexString dexstring, dexType dextype) throws IOException {
//dexheader获得偏移
//4字节短类型保存在dexString表中
//4字节返回值类型保存在dexType表中
//4字节参数偏移,找到参数的数量和索引
//参数数量,该原型有几个参数
//参数类型索引,通过类型索引在type表中找到类型值
//从头部对象中获取type的大小和偏移
this.protoSize = dexheader.protosize;
this.protoOff = dexheader.protooff;
//将获取的大小和偏移转化成int型
byte[] tempSize = new byte[4];
byte[] tempOff = new byte[4];
tempSize = bytereverse(protoSize);
tempOff = bytereverse(protoOff);
int intProtoSize = byte2int(tempSize);
//偏移,
int intProtoOff = byte2int(tempOff);
//保存到typeOffList中
//这个偏移里面保存了字符串表中的索引
for (int i = 0; i < intProtoSize; i++){
protoOffList.add(intProtoOff);
intProtoOff += 12;
}
//分别计算不同字段的偏移
for (int i = 0; i < protoOffList.size(); i++){
int off = protoOffList.get(i);
List<Byte> tByte = readDexString(GetDexFilePath(), off);
//将byte转成int
byte[] protoShort = new byte[4];
protoShort[0] = tByte.get(0);
protoShort[1] = tByte.get(1);
protoShort[2] = tByte.get(2);
protoShort[3] = tByte.get(3);
protoShort = bytereverse(protoShort);
int shortidx = byte2int(protoShort);
protoShortList.add(shortidx);
byte[] protoReturn = new byte[4];
protoReturn[0] = tByte.get(4);
protoReturn[1] = tByte.get(5);
protoReturn[2] = tByte.get(6);
protoReturn[3] = tByte.get(7);
protoReturn = bytereverse(protoReturn);
int Returnidx = byte2int(protoReturn);
protoReturnList.add(Returnidx);
byte[] protoParam = new byte[4];
protoParam[0] = tByte.get(8);
protoParam[1] = tByte.get(9);
protoParam[2] = tByte.get(10);
protoParam[3] = tByte.get(11);
protoParam = bytereverse(protoParam);
int Paramoff = byte2int(protoParam);
protoParamList.add(Paramoff);
}
//读文件分别获取不同字段的值
//获取短类型在dexString中的索引
//读文件取出短类型索引值
for (int i = 0; i < protoShortList.size(); i++){
int value = protoShortList.get(i);
//在通过索引值在字符串表中找到对应字符串
String strRes = dexstring.getStrStringValue().get(value);
protoShortStringList.add(strRes);
}
//读文件取出返回值索引值
for (int i = 0; i < protoReturnList.size(); i++){
int value = protoReturnList.get(i);
//在通过索引值在type表中找到对应字符串
String strRes = dextype.getTypeStringList().get(value);
protoReturnStringList.add(strRes);
}
//读文件取出参数偏移
for (int i = 0; i < protoParamList.size(); i++){
byte[] tmp = new byte[4];
int off = protoParamList.get(i);
List<Byte> tByte = new ArrayList<Byte>();
if (off == 0){
ParamNumList.add(0);
parambyteList.add(tByte);
continue;
}
tByte = readDexString2(GetDexFilePath(), off);
//将byte转成int
tmp[0] = tByte.get(0);
tmp[1] = tByte.get(1);
tmp[2] = tByte.get(2);
tmp[3] = tByte.get(3);
tmp = bytereverse(tmp);
int paramnum = byte2int(tmp);
//在通过索引值读文件在文件偏移处找到对应参数个数,参数索引
//参数个数list
ParamNumList.add(paramnum);
//保存参数list
//保存参数的字节,然后再更具参数个数进行解析
//需要偏移4个字节后开始读,字节数 = 索引2字节 * 个数(paramnum的值)
tByte = readDexString3(GetDexFilePath(), off + 4, paramnum);
parambyteList.add(tByte);
}
//再根据参数个数的list来解析参数的值
for (int i = 0; i < ParamNumList.size(); i++){
if (ParamNumList.get(i) == 1){
//直接保存参数索引
byte[] tmp2 = new byte[2];
tmp2[0] = parambyteList.get(i).get(0);
tmp2[1] = parambyteList.get(i).get(1);
tmp2 = bytereverse2(tmp2);
int paramidx = byte2int_2(tmp2);
String paramString = dextype.getTypeStringList().get(paramidx);
paramStringList.add(paramString);
}
else if (ParamNumList.get(i) == 0)
{
paramStringList.add("void");
}
else
{
//参数总字节数/参数个数 = 需要分解的参数个数
int count = (parambyteList.get(i).size())/(ParamNumList.get(i));
String paramString2 = "";
while(count != 0){
//一次读2个字节,保存参数索引
byte[] tmp2 = new byte[2];
tmp2[0] = parambyteList.get(i).get(0);
tmp2[1] = parambyteList.get(i).get(1);
tmp2 = bytereverse2(tmp2);
int paramidx = byte2int_2(tmp2);
paramString2 = paramString2 + dextype.getTypeStringList().get(paramidx);
count--;
}
paramStringList.add(paramString2);
}
}
}5.解析dexField
//构造函数中获取field的偏移和大小
public dexField(dexHeader dexheader, dexString dexstring, dexType dextype) throws IOException {
//从头部对象中获取type的大小和偏移
this.fieldSize = dexheader.fieldsize;
this.fieldOff = dexheader.fieldoff;
//将获取的大小和偏移转化成int型
byte[] tempSize = new byte[4];
byte[] tempOff = new byte[4];
tempSize = bytereverse(fieldSize);
tempOff = bytereverse(fieldOff);
int intFiledSize = byte2int(tempSize);
//偏移,
int intFieldOff = byte2int(tempOff);
//保存到typeOffList中
//这个偏移里面保存了字符串表中的索引
for (int i = 0; i < intFiledSize; i++){
FieldOffList.add(intFieldOff);
intFieldOff += 8;
}
//根据偏移读取对应字段的值
for (int i = 0; i < FieldOffList.size(); i++){
int off = FieldOffList.get(i);
List<Byte> tByte = readDexString(GetDexFilePath(), off);
//将byte转成int
//保存classid的索引
byte[] classid = new byte[2];
classid[0] = tByte.get(0);
classid[1] = tByte.get(1);
classid = bytereverse2(classid);
int classindex = byte2int_2(classid);
FieldclassidList.add(classindex);
//保存typeid的索引
byte[] typeid = new byte[2];
typeid[0] = tByte.get(2);
typeid[1] = tByte.get(3);
typeid = bytereverse2(typeid);
int typeidindex = byte2int_2(typeid);
FieldtypeidList.add(typeidindex);
//保存nameid的索引
byte[] nameid = new byte[4];
nameid[0] = tByte.get(4);
nameid[1] = tByte.get(5);
nameid[2] = tByte.get(6);
nameid[3] = tByte.get(7);
nameid = bytereverse(nameid);
int nameindex = byte2int(nameid);
FieldnameidList.add(nameindex);
}
//根据索引获取classid字符串
for (int i = 0; i < FieldclassidList.size(); i++){
String classStr = dextype.getTypeStringList().get(FieldclassidList.get(i));
FiledClassStrList.add(classStr);
}
//根据索引获取typeid字符串
for (int i = 0; i < FieldtypeidList.size(); i++){
String typeStr = dextype.getTypeStringList().get(FieldtypeidList.get(i));
FiledTypeStrList.add(typeStr);
}
//根据索引获取nameid字符串
for (int i = 0; i < FieldnameidList.size(); i++){
String nameStr = dexstring.getStrStringValue().get(FieldnameidList.get(i));
FiledNameStrList.add(nameStr);
}
}
6.解析dexMethod
//构造函数中获取field的偏移和大小
public dexMethod(dexHeader dexheader, dexString dexstring,
dexType dextype, dexProto dexproto) throws IOException {
//从头部对象中获取method的大小和偏移
this.methodSize = dexheader.methodsize;
this.methodOff = dexheader.methodoff;
//将获取的大小和偏移转化成int型
byte[] tempSize = new byte[4];
byte[] tempOff = new byte[4];
tempSize = bytereverse(methodSize);
tempOff = bytereverse(methodOff);
int intMethodSize = byte2int(tempSize);
//偏移,
int intMethodOff = byte2int(tempOff);
//保存到methodOffList中
//这个偏移里面保存了字符串表中的索引
for (int i = 0; i < intMethodSize; i++){
MethodOffList.add(intMethodOff);
intMethodOff += 8;
}
//根据偏移读取对应字段的值
for (int i = 0; i < MethodOffList.size(); i++){
int off = MethodOffList.get(i);
List<Byte> tByte = readDexString(GetDexFilePath(), off);
//将byte转成int
//保存classid的索引
byte[] classid = new byte[2];
classid[0] = tByte.get(0);
classid[1] = tByte.get(1);
classid = bytereverse2(classid);
int classindex = byte2int_2(classid);
MethodclassidList.add(classindex);
//保存typeid的索引
byte[] protoid = new byte[2];
protoid[0] = tByte.get(2);
protoid[1] = tByte.get(3);
protoid = bytereverse2(protoid);
int protoidindex = byte2int_2(protoid);
MethodprotoidList.add(protoidindex);
//保存nameid的索引
byte[] nameid = new byte[4];
nameid[0] = tByte.get(4);
nameid[1] = tByte.get(5);
nameid[2] = tByte.get(6);
nameid[3] = tByte.get(7);
nameid = bytereverse(nameid);
int nameindex = byte2int(nameid);
MethodnameidList.add(nameindex);
}
//根据索引获取classid字符串
for (int i = 0; i < MethodclassidList.size(); i++){
String classStr = dextype.getTypeStringList().get(MethodclassidList.get(i));
MethodClassStrList.add(classStr);
}
//根据索引获取protoid字符串
for (int i = 0; i < MethodprotoidList.size(); i++){
//保存参数
String protoStr = dexproto.getParamStringList().get(MethodprotoidList.get(i));
MethodprotoStrList.add(protoStr);
//保存返回值
String protoreturnStr = dexproto.getProtoReturnStringList().get(MethodprotoidList.get(i));
MethodprotoReturnStrList.add(protoreturnStr);
}
//根据索引获取nameid字符串
for (int i = 0; i < MethodnameidList.size(); i++){
String nameStr = dexstring.getStrStringValue().get(MethodnameidList.get(i));
MethodNameStrList.add(nameStr);
}
}7.解析dexClass,未实现完整,给出类型转换函数的实现
//转换uleb128转uint
// 解码uleb
int byteindex = 0;
public int decodeUleb128(byte[] byteAry) {
int index = 0, cur;
int result = byteAry[index];
index++;
if (result > 0x7f) { // 判断第一个字节是否大于 0x7f
cur = byteAry[index]; // 读取第二个字节
result = (result & 0x7f) | ((cur & 0x7f) << 7); //前两个字节合并
index++;
if (cur > 0x7f) {//判断第二个字节是否大于0x7f
cur = byteAry[index];//读取第三个字节
result |= (cur & 0x7f) << 14;
index++;
if (cur > 0x7f) {//判断第三个字节是否大于0x7f
cur = byteAry[index];//读取第四个字节
result |= (cur & 0x7f) << 21;
index++;
if (cur > 0x7f) {//判断第四个字节是否大于0x7f
cur = byteAry[index];//读取第五个字节
result |= cur << 28;
}
}
}
}
this.byteindex = index;
return result;
}有更好的实现方式可以交流学习。






















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








