(参考离散数学及其应用,P732,带输出的有限状态机)
在管理系统中,我们经常涉及父子系统中不同状态的转换。现定义有限状态机 M = (S , I , O, f , g ,s0),其中有限状态集合S,转移函数f( f(原状态,输入) = 新状态 ),输出函数g( g(原状态,输入) = 输出 )有限输入字母表I,有限输出字母表O,初始状态s0 。
现设计学生信息系统:
该系统有三个子系统,为添加学生信息,删除学生信息,查找学生信息。任意时刻输入exit可以返回上级系统。到达最上级后继续exit会返回错误信息。
写出状态图:
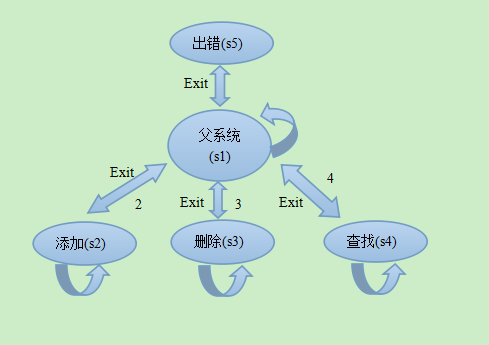
不难写出状态转移函数:
#define EXIT_ON(variable, back_status) {if (strcmp((variable), "exit") == 0) {status = (back_status); break;}}其中status 为全局状态变量。
具体代码实现:(其中有些函数存在student.h中,和状态机无关联,请自行替换。
//
// main.c
// gcc 编译通过
// Copyright (c) 2015年 XiaoJSoft. All rights reserved.
//
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "student.h"
#define EXIT_ON(variable, back_status) {if (strcmp((variable), "exit") == 0) {status = (back_status); break;}}
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
STUDENT_TREE students;
StudentTreeInitialize(&students);
char buf[250], buf1[250], buf2[250];
int status = 1;
while(1) {
switch(status) {
case 1:
printf("+: Add a student\n");
printf("-: Add a student\n");
printf("S: Add a student\n");
scanf("%s", buf);
if (strcmp(buf, "+") == 0) {
status = 2;
} else if (strcmp(buf, "-") == 0) {
status = 3;
} else if (strcmp(buf, "s") == 0 || strcmp(buf, "S") == 0) {
status = 4;
} else if (strcmp(buf, "exit") == 0) {
status = 5;
}
break;
case 2:
printf("Name: ");
scanf("%s", buf1);
EXIT_ON(buf1, 1);
printf("Key: ");
scanf("%s", buf2);
EXIT_ON(buf2, 1);
StudentTreeAdd(&students, buf2, buf1); // printf("StudentTreeAdd\n");
break;
case 3:
printf("Key: ");
scanf("%s", buf2);
EXIT_ON(buf2, 1);
StudentTreeDelete(&students, buf2); //printf("StudentTreeDelete\n");
break;
case 4:
printf("Key: ");
scanf("%s", buf2);
EXIT_ON(buf2, 1);
STUDENT_TREE_NODE *searched = StudentTreeSearch(&students, buf2); //printf("StudentTreeSearch\n");
if (searched) {
printf("Name: %s\n", searched->name);
} else {
printf("No such student.\n");
}
break;
case 5:
goto hehe;
}
}
hehe:
StudentTreeFinalize(&students); //printf("Error");
return 0;
}






















 524
524

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








