def gpu_remap(numpy_img,map_tensor):
# 准备图像数据
img_tensor = torch.from_numpy(numpy_img).contiguous().cuda(non_blocking=True)
img_tensor = img_tensor.permute(2,0,1).unsqueeze(0).float()
res = torch.nn.functional.grid_sample(img_tensor,map_tensor,
mode='bilinear',
padding_mode='zeros',
align_corners=None)
res = res.char()
res = res[0].permute(1,2,0)
res = res.cpu()
res = res.numpy()
res = np.uint8(res)
return resdef cpu_remap(numpy_img,mapx,mapy):
return cv2.remap(numpy_img,mapx,mapy,cv2.INTER_LINEAR)if __name__=='__main__':
mtx = np.asarray(
[[1.45400077e+03,0.00000000e+00,8.91370579e+02],
[0.00000000e+00,1.20949778e+03,3.22130436e+02],
[0.00000000e+00,0.00000000e+00,1.00000000e+00]])
dist =np.asarray([[-0.45415106,0.42747461,0.04382156,0.003691,-0.29239333]])
w,h = 1920,1080
# 准备map
mapx, mapy = cv2.initUndistortRectifyMap(mtx, dist, None, mtx, (w, h), 5)
# 准备grid数据
mapx_tensor = torch.from_numpy(mapx).unsqueeze(2)/1920*2-1
mapy_tensor = torch.from_numpy(mapy).unsqueeze(2)/1080*2-1
map_tensor = torch.cat([mapx_tensor,mapy_tensor],dim=2).unsqueeze(0).cuda()
img_org = cv2.imread('test.jpg')
for i in range(100):
cpu_res = cpu_remap(img_org,mapx,mapy)
for i in range(100):
cpu_res = gpu_remap(img_org,map_tensor)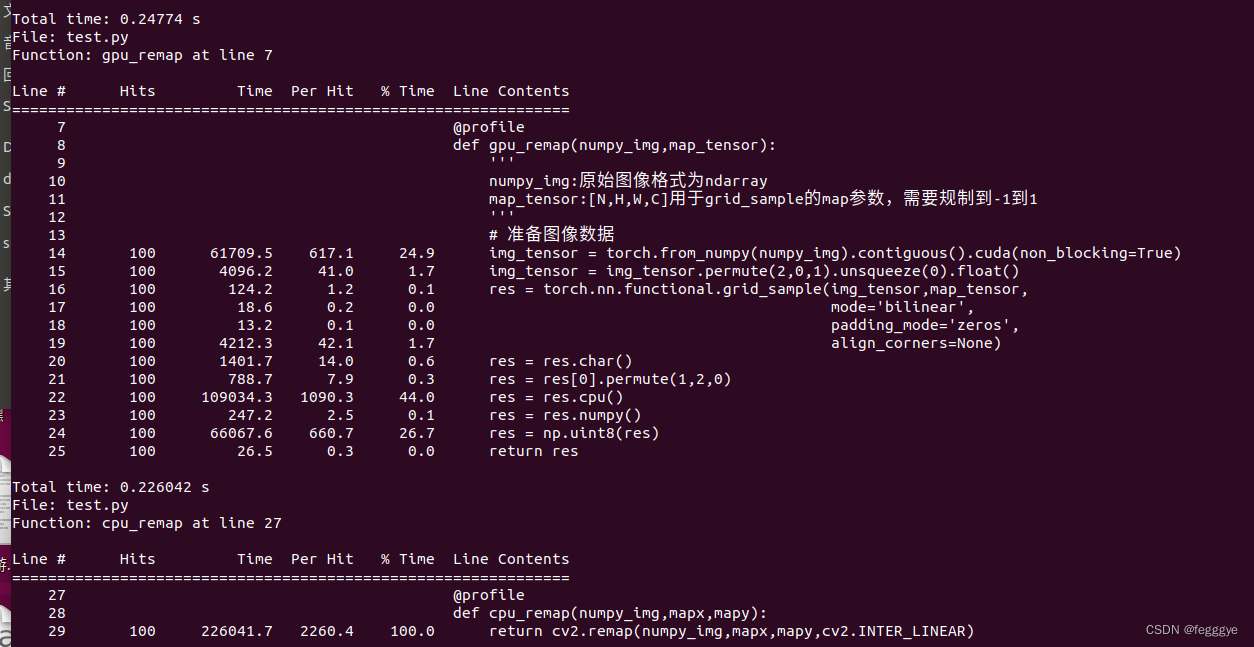
计算了下耗时,结果发现还是CPU->GPU数据拷贝是瓶颈。。。但是计算耗时确实少很多,后续看看如何优化吧。。。




















 9371
9371











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








