概述
之前的文章SURF和SIFT算子实现特征点检测简单地讲了利用SIFT和SURF算子检测特征点,在检测的基础上可以使用SIFT和SURF算子对特征点进行特征提取并使用匹配函数进行特征点的匹配。具体实现是首先采用SurfFeatureDetector检测特征点,再使用SurfDescriptorExtractor计算特征点的特征向量,最后采用BruteForceMatcher暴力匹配法或者FlannBasedMatcher选择性匹配法(二者的不同)来进行特征点匹配。
实验所用环境是opencv2.4.0+vs2008+win7,需要注意opencv2.4.X版本中SurfFeatureDetector是包含在opencv2/nonfree/features2d.hpp中,BruteForceMatcher是包含在opencv2/legacy/legacy.hpp中,FlannBasedMatcher是包含在opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp中。
BruteForce匹配法
首先使用BruteForceMatcher暴力匹配法,代码如下:
/**
* @采用SURF算子检测特征点,对特征点进行特征提取,并使用BruteForce匹配法进行特征点的匹配
* @SurfFeatureDetector + SurfDescriptorExtractor + BruteForceMatcher
* @author holybin
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/nonfree/features2d.hpp" //SurfFeatureDetector实际在该头文件中
#include "opencv2/legacy/legacy.hpp" //BruteForceMatcher实际在该头文件中
//#include "opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp" //FlannBasedMatcher实际在该头文件中
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
Mat src_1 = imread( "D:\\opencv_pic\\cat3d120.jpg", CV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE );
Mat src_2 = imread( "D:\\opencv_pic\\cat0.jpg", CV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE );
if( !src_1.data || !src_2.data )
{
cout<< " --(!) Error reading images "<<endl;
return -1;
}
//-- Step 1: 使用SURF算子检测特征点
int minHessian = 400;
SurfFeatureDetector detector( minHessian );
vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1, keypoints_2;
detector.detect( src_1, keypoints_1 );
detector.detect( src_2, keypoints_2 );
cout<<"img1--number of keypoints: "<<keypoints_1.size()<<endl;
cout<<"img2--number of keypoints: "<<keypoints_2.size()<<endl;
//-- Step 2: 使用SURF算子提取特征(计算特征向量)
SurfDescriptorExtractor extractor;
Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2;
extractor.compute( src_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1 );
extractor.compute( src_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2 );
//-- Step 3: 使用BruteForce法进行暴力匹配
BruteForceMatcher< L2<float> > matcher;
vector< DMatch > matches;
matcher.match( descriptors_1, descriptors_2, matches );
cout<<"number of matches: "<<matches.size()<<endl;
//-- 显示匹配结果
Mat matchImg;
drawMatches( src_1, keypoints_1, src_2, keypoints_2, matches, matchImg );
imshow("matching result", matchImg );
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
实验结果:
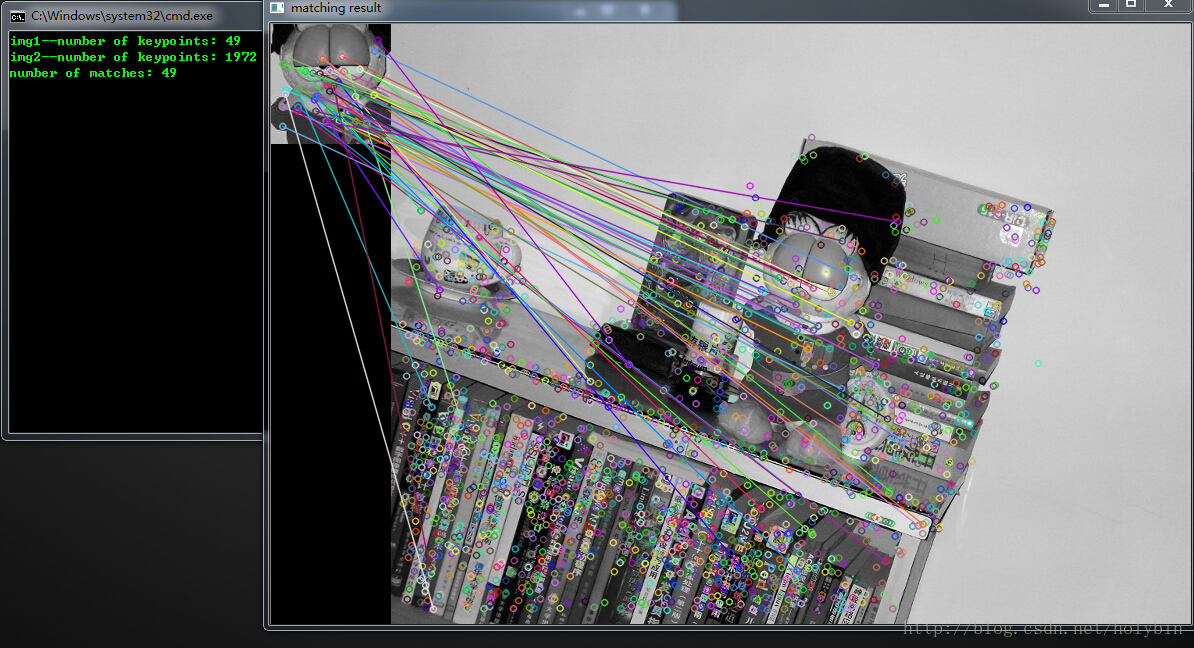
FLANN匹配法
使用暴力匹配的结果不怎么好,下面使用FlannBasedMatcher进行特征匹配,只保留好的特征匹配点,代码如下:
/**
* @采用SURF算子检测特征点,对特征点进行特征提取,并使用FLANN匹配法进行特征点的匹配
* @SurfFeatureDetector + SurfDescriptorExtractor + FlannBasedMatcher
* @author holybin
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/nonfree/features2d.hpp" //SurfFeatureDetector实际在该头文件中
//#include "opencv2/legacy/legacy.hpp" //BruteForceMatcher实际在该头文件中
#include "opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp" //FlannBasedMatcher实际在该头文件中
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
Mat src_1 = imread( "D:\\opencv_pic\\cat3d120.jpg", CV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE );
Mat src_2 = imread( "D:\\opencv_pic\\cat0.jpg", CV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE );
if( !src_1.data || !src_2.data )
{
cout<< " --(!) Error reading images "<<endl;
return -1;
}
//-- Step 1: 使用SURF算子检测特征点
int minHessian = 400;
SurfFeatureDetector detector( minHessian );
vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1, keypoints_2;
detector.detect( src_1, keypoints_1 );
detector.detect( src_2, keypoints_2 );
cout<<"img1--number of keypoints: "<<keypoints_1.size()<<endl;
cout<<"img2--number of keypoints: "<<keypoints_2.size()<<endl;
//-- Step 2: 使用SURF算子提取特征(计算特征向量)
SurfDescriptorExtractor extractor;
Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2;
extractor.compute( src_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1 );
extractor.compute( src_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2 );
//-- Step 3: 使用FLANN法进行匹配
FlannBasedMatcher matcher;
vector< DMatch > allMatches;
matcher.match( descriptors_1, descriptors_2, allMatches );
cout<<"number of matches before filtering: "<<allMatches.size()<<endl;
//-- 计算关键点间的最大最小距离
double maxDist = 0;
double minDist = 100;
for( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{
double dist = allMatches[i].distance;
if( dist < minDist )
minDist = dist;
if( dist > maxDist )
maxDist = dist;
}
printf(" max dist : %f \n", maxDist );
printf(" min dist : %f \n", minDist );
//-- 过滤匹配点,保留好的匹配点(这里采用的标准:distance<2*minDist)
vector< DMatch > goodMatches;
for( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{
if( allMatches[i].distance < 2*minDist )
goodMatches.push_back( allMatches[i]);
}
cout<<"number of matches after filtering: "<<goodMatches.size()<<endl;
//-- 显示匹配结果
Mat matchImg;
drawMatches( src_1, keypoints_1, src_2, keypoints_2,
goodMatches, matchImg, Scalar::all(-1), Scalar::all(-1),
vector<char>(),
DrawMatchesFlags::NOT_DRAW_SINGLE_POINTS //不显示未匹配的点
);
imshow("matching result", matchImg );
//-- 输出匹配点的对应关系
for( int i = 0; i < goodMatches.size(); i++ )
printf( " good match %d: keypoints_1 [%d] -- keypoints_2 [%d]\n", i,
goodMatches[i].queryIdx, goodMatches[i].trainIdx );
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
实验结果:

从第二个实验结果可以看出,经过过滤之后特征点数目从49减少到33,匹配的准确度有所上升。当然也可以使用SIFT算子进行上述两种匹配实验,只需要将SurfFeatureDetector换成SiftFeatureDetector,将SurfDescriptorExtractor换成SiftDescriptorExtractor即可。
拓展
在FLANN匹配法的基础上,还可以进一步利用透视变换和空间映射找出已知物体(目标检测),具体来说就是利用findHomography函数利用匹配的关键点找出相应的变换,再利用perspectiveTransform函数映射点群。具体可以参考这篇文章:OpenCV中feature2D学习——SIFT和SURF算法实现目标检测。























 4342
4342

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








