f开头的函数(下)
本篇介绍C语言中f开头的函数(下)
21. floor,floorf,floorl
21.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
double floor (double x); | 获取小于或等于 x 的最大整数(double)。 |
float floorf (float x); | 获取小于或等于 x 的最大整数(float)。 |
long double floorl (long double x) | 获取小于或等于 x 的最大整数(long double)。 |
21.2 演示示例
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
int main()
{
double x = 10.24;
printf("floor(%.2lf) = %.2lf\n", x, floor(x));
float xf = 5.63;
printf("floorf(%.2f) = %.2f\n", xf, floorf(xf));
long double xL = 2.89;
printf("floorl(%.2Lf) = %.2Lf\n", xL, floorl(xL));
return 0;
}
21.3 运行结果
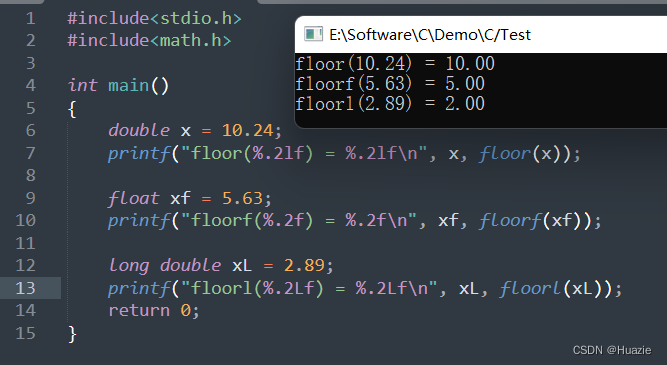
22. _flushall
22.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int _flushall(void); | 清除所有缓冲区,返回打开的流(输入和输出)的数量 |
22.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
FILE *stream = fopen("STU.FIL", "w");
// 清除所有缓冲区
// 返回打开的流(输入和输出)的数量
printf("%d streams were flushed.\n", _flushall());
fclose(stream);
return 0;
}
22.3 运行结果
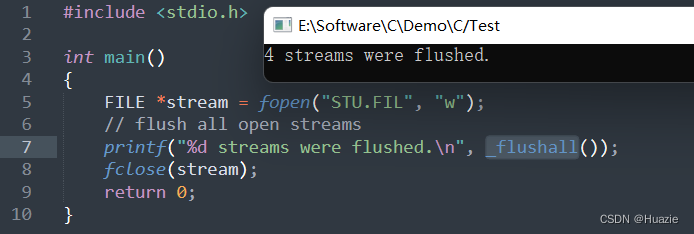
23. fma,fmaf,fmal
23.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
double fma (double x, double y, double z); | 计算x*y+z的值,并将结果四舍五入(double)。 |
float fmaf (float x, float y, float z ); | 计算x*y+z的值,并将结果四舍五入(float )。 |
long double fmal (long double x, long double y, long double z); | 计算x*y+z的值,并将结果四舍五入(double)。 |
23.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main() {
double x = 2.0, y = 3.0, z = 4.0;
float xf = 2.0, yf = 3.0, zf = 4.0;
long double xL = 2.0, yL = 3.0, zL = 4.0;
printf("fma(%lf, %lf, %lf) = %lf\n", x, y, z, fma(x, y, z));
printf("fmaf(%f, %f, %f) = %f\n", xf, yf, zf, fmaf(xf, yf, zf));
printf("fmal(%Lf, %Lf, %Lf) = %Lf\n", xL, yL, zL, fmal(xL, yL, zL));
return 0;
}
23.3 运行结果
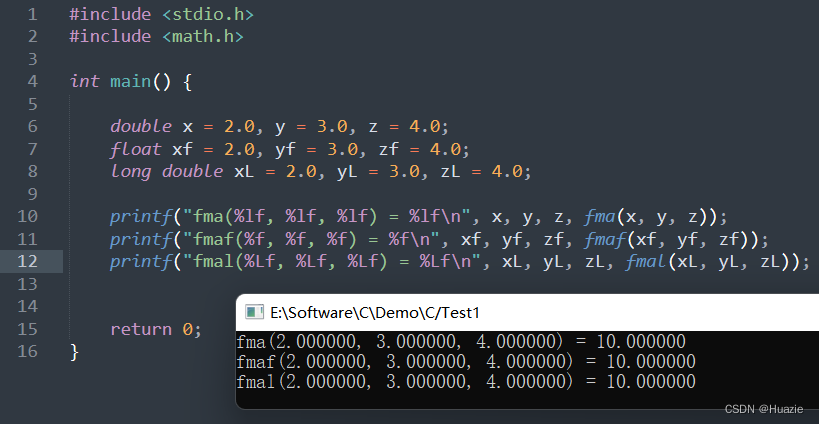
24. fmax,fmaxf,fmaxl
24.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
double fmax (double x, double y); | 获取 x 和 y 中的最大值(double) |
float fmaxf (float x, float y); | 获取 x 和 y 中的最大值(float) |
long double fmaxl (long double x, long double y); | 获取 x 和 y 中的最大值(long double) |
24.2 演示示例
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
int main()
{
double x = 10.24, y = 5.63;
printf("fmax(%.2lf, %.2lf) = %.2lf\n", x, y, fmax(x, y));
float xf = 5.63, yf = 2.89;
printf("fmaxf(%.2f, %.2f) = %.2f\n", xf, yf, fmaxf(xf, yf));
long double xL = 2.89, yL = 4.56;
printf("fmaxl(%.2Lf, %.2Lf) = %.2Lf\n", xL, yL, fmaxl(xL, yL));
return 0;
}
24.3 运行结果
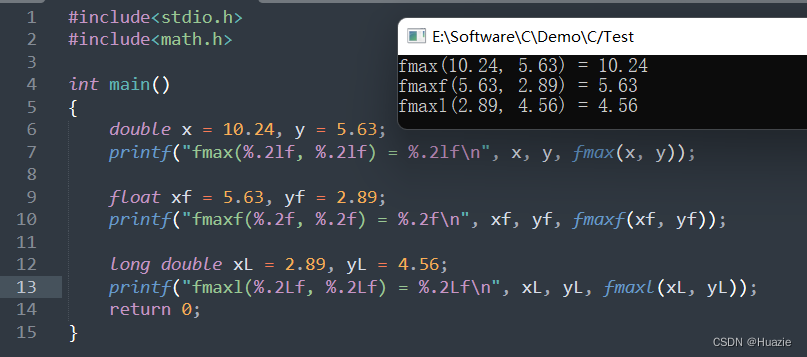
25. fmin,fminf,fminl
25.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
double fmin (double x, double y); | 获取 x 和 y 中的最小值(double) |
float fminf (float x, float y); | 获取 x 和 y 中的最小值(float) |
long double fminl (long double x, long double y); | 获取 x 和 y 中的最小值(long double) |
25.2 演示示例
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
int main()
{
double x = 10.24, y = 5.63;
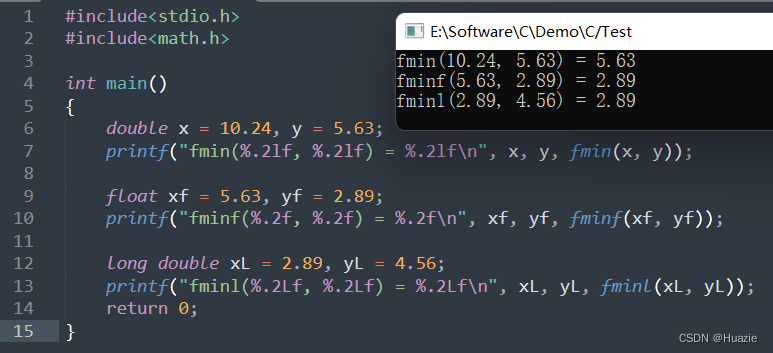
printf("fmin(%.2lf, %.2lf) = %.2lf\n", x, y, fmin(x, y));
float xf = 5.63, yf = 2.89;
printf("fminf(%.2f, %.2f) = %.2f\n", xf, yf, fminf(xf, yf));
long double xL = 2.89, yL = 4.56;
printf("fminl(%.2Lf, %.2Lf) = %.2Lf\n", xL, yL, fminl(xL, yL));
return 0;
}
25.3 运行结果
26. fmod,fmodf,fmodl
26.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
double fmod (double x, double y); | 计算 x 除以 y 的余数(double)。 |
float fmodf (float x, float y); | 计算 x 除以 y 的余数(float)。 |
long double fmodl (long double x, long double y); | 计算 x 除以 y 的余数(long double)。 |
26.2 演示示例
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
int main()
{
double x = 10.24, y = 5.63;
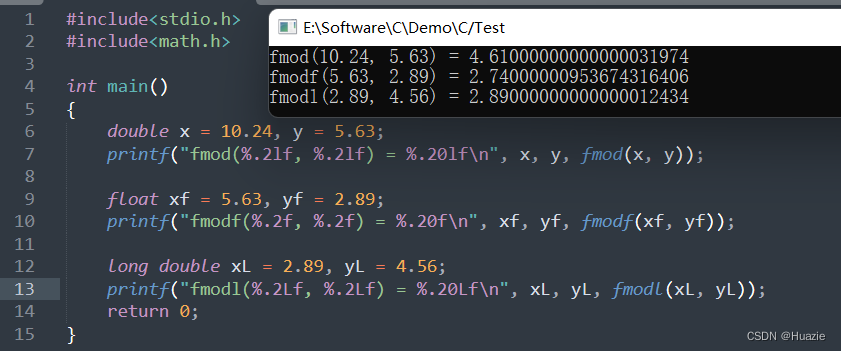
printf("fmod(%.2lf, %.2lf) = %.20lf\n", x, y, fmod(x, y));
float xf = 5.63, yf = 2.89;
printf("fmodf(%.2f, %.2f) = %.20f\n", xf, yf, fmodf(xf, yf));
long double xL = 2.89, yL = 4.56;
printf("fmodl(%.2Lf, %.2Lf) = %.20Lf\n", xL, yL, fmodl(xL, yL));
return 0;
}
26.3 运行结果
27. fopen
27.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
FILE *fopen(const char *filename, const char *mode); | 使用给定的模式mode打开filename所指向的文件。 |
参数:
filename: 要打开的文件全路径名
mode: 文件访问模式
返回值:
如果文件顺利打开后,指向该流的文件指针就会被返回;否则文件打开失败则返回 NULL,并把错误代码存在 error 中。
文件访问模式
| 文件访问模式 | 说明 |
|---|---|
"r" | 以只读模式打开文件,该文件必须存在。 |
"w" | 以只写模式打开文件。若文件不存在则创建该文件。若文件存在则其现有内容将被清除。 |
"a" | 以追加模式打开只写文件。若文件不存在则创建该文件;如果文件存在,则新写入的数据会被加到文件尾后。 |
"r+" | 以读写模式打开文件,该文件必须存在。 |
"w+" | 以读写模式打开文件。若文件不存在则创建该文件。若文件存在则其内容将被清除。 |
"a+" | 以追加模式打开可读写文件。若文件不存在则创建该文件;如果文件存在,则新写入的数据会被加到文件尾后。 |
"rb" | 以只读模式打开一个二进制文件。 |
"wb" | 以只写模式打开或新建一个二进制文件。 |
"ab" | 以追加模式打开一个二进制文件,并在文件末尾写入数据。 |
"rb+" | 以读写模式打开一个二进制文件,该文件必须存在。 |
"wb+" | 以读写模式打开或创建一个二进制文件。 |
"ab+" | 以追加模式打开一个二进制文件,以便在文件末尾写入数据。该文件也是可读的。 |
"rt" | 以只读模式打开一个文本文件。 |
"wt" | 以只读模式打开或创建文本文件。 |
"at" | 以追加模式打开一个文本文件,并在文件末尾写入数据。 |
"rt+" | 以读写模式打开一个文本文件。 |
"wt+" | 以读写模式打开或创建文本文件。 |
"at+" | 以追加模式打开文本文件,以便在文件末尾写入数据。该文件也是可读的。 |
27.2 演示示例
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
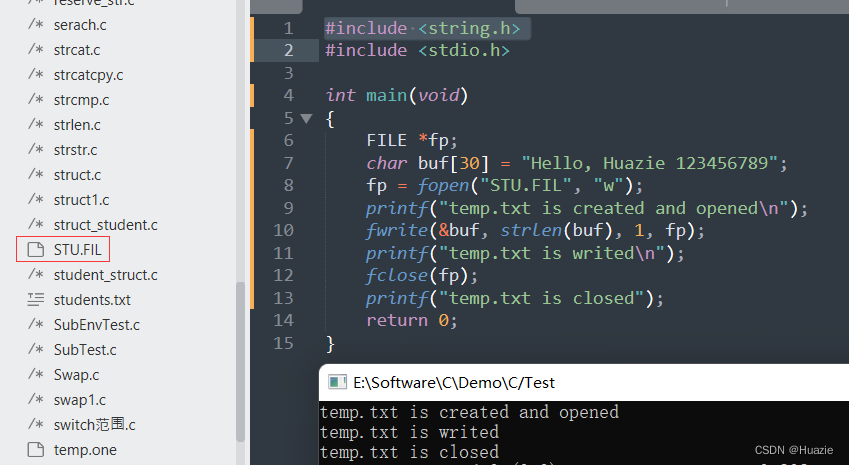
FILE *fp;
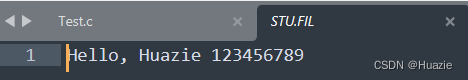
char buf[30] = "Hello, Huazie 123456789";
fp = fopen("STU.FIL", "w");
printf("temp.txt is created and opened\n");
fwrite(&buf, strlen(buf), 1, fp);
printf("temp.txt is writed\n");
fclose(fp);
printf("temp.txt is closed");
return 0;
}
27.3 运行结果
28. fprintf
28.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int fprintf(FILE *stream, char *format[, argument,...]); | 格式化输出到一个流文件中 |
28.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
FILE *stream;
stream = fopen("temp.txt", "w");
fprintf(stream, "%s:%d\n", "Hello Huazie", 456);
fclose(stream);
return 0;
}
28.3 运行结果
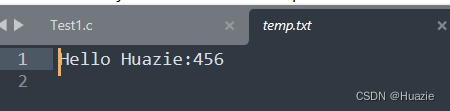
29. fputc
29.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int fputc(int ch, FILE *stream); | 将字符【ch为字符的ascii码】写到文件指针stream所指向的文件的当前写指针的位置 |
注意: 在正常调用情况下,函数返回写入文件的字符的 ASCII 码值,出错时,返回 EOF(-1)。当正确写入一个字符或一个字节的数据后,文件内部写指针会自动后移一个字节的位置。EOF是在头文件 stdio.h中定义的宏。
29.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
char msg[] = "Hello Huazie";
int i = 0;
while (msg[i])
{
fputc(msg[i], stdout);
i++;
}
return 0;
}
29.3 运行结果
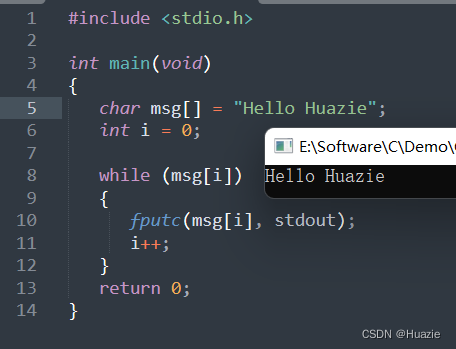
30. fputchar
30.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int fputchar(char ch); | 送一个字符到标准输出流(stdout)中,出错则返回EOF |
30.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
char msg[] = "This is a test";
int i = 0;
while (msg[i])
{
fputchar(msg[i]);
i++;
}
return 0;
}
30.3 运行结果
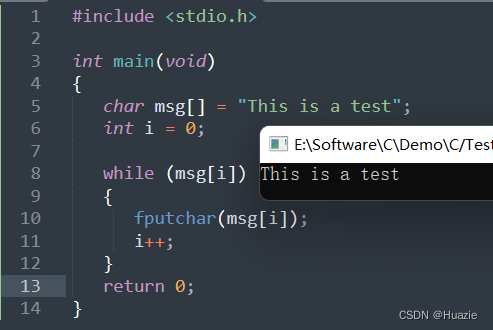
31. fputs
31.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int fputs(const char *str, FILE *stream); | 把字符串写入到指定的流( stream) 中,但不包括空字符。 |
注意: fputs 函数如果成功则返回 0,如果发生错误则返回 EOF(-1)
31.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int result = fputs("Hello Huazie\n1234", stdout);
printf("\nresult = %d", result);
return 0;
}
31.3 运行结果
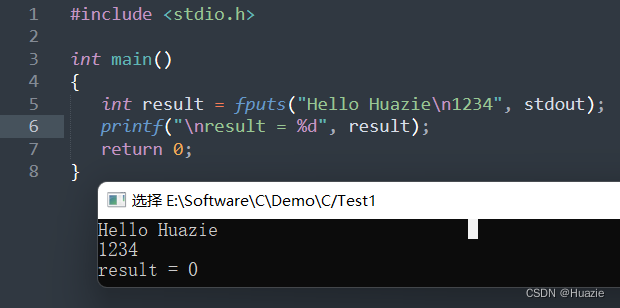
32. fread
32.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int fread(void *buffer, int size, int count, FILE *stream); | 从给定输入流stream读取最多count个对象到数组buffer中 |
参数:
buffer : 指向要读取的数组中首个对象的指针
size : 每个对象的大小(单位是字节)
count : 要读取的对象个数
stream : 指定输入流
返回值:
返回成功读取的对象个数,若出现错误或到达文件末尾,则可能小于count。
若 size 或 count 为零,则 fread 返回零且不进行其他动作。
fread 不区分文件尾和错误,因此调用者必须用 feof 和 ferror 才能判断发生了什么。
注意: 如果读取成功,流的文件位置指示器前进读取的字节数;否则出现错误,则流的文件位置指示器的位置不确定。同样若没有完整地读入最后一个元素,则其值也不确定。
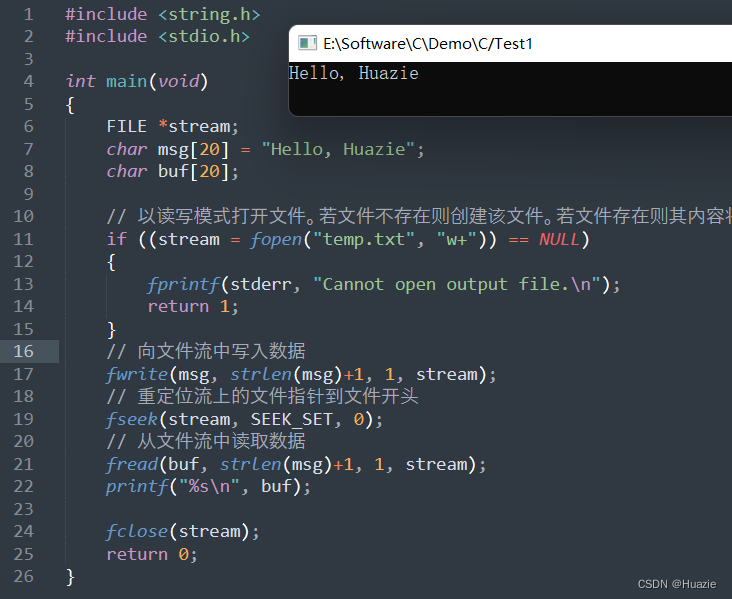
32.2 演示示例
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
FILE *stream;
char msg[20] = "Hello, Huazie";
char buf[20];
// 以读写模式打开文件。若文件不存在则创建该文件。若文件存在则其内容将被清除。
if ((stream = fopen("temp.txt", "w+")) == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Cannot open output file.\n");
return 1;
}
// 向文件流中写入数据
fwrite(msg, strlen(msg)+1, 1, stream);
// 重定位流上的文件指针到文件开头
fseek(stream, SEEK_SET, 0);
// 从文件流中读取数据
fread(buf, strlen(msg)+1, 1, stream);
printf("%s\n", buf);
fclose(stream);
return 0;
}
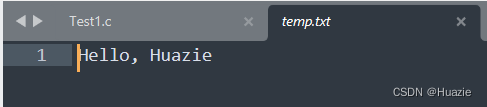
32.3 运行结果
33. free
33.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
void free(void *ptr); | 释放ptr指向的存储空间 |
注意: 被释放的空间通常被送入可用存储区池,以后可以在调用 malloc、realloc 以及 calloc 函数来再分配。
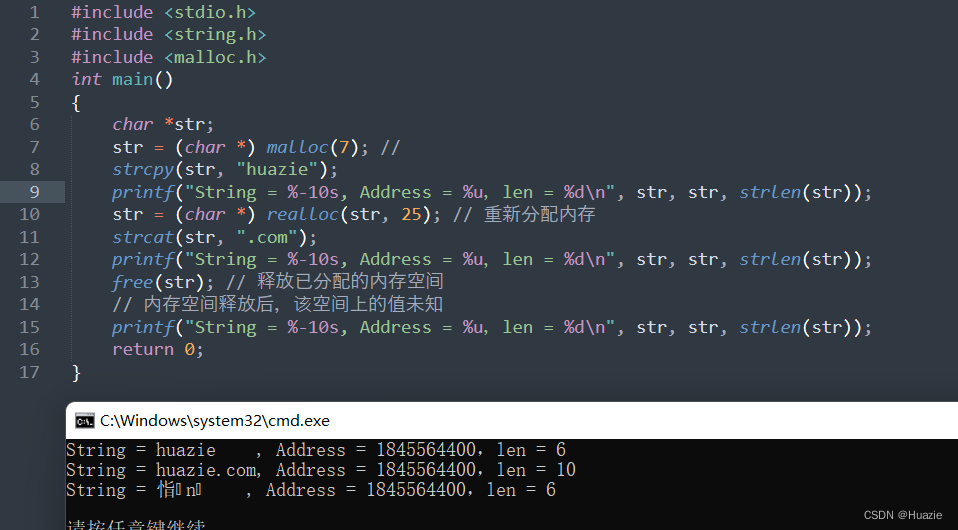
33.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <malloc.h>
int main()
{
char *str;
str = (char *) malloc(7);
strcpy(str, "huazie");
printf("string = %-10s, Address = %u, len = %d\n", str, str, strlen(str));
str = (char *) realloc(str,25); //重新分配内存
strcat(str, ".com");
printf("string = %-10s, Address = %u, len = %d\n", str, str, strlen(str));
free(str);// 释放已分配的内存空间
//内存空间释放后,该空间上的值未知
printf("string = %-10s, Address = %u, len = %d\n", str, str, strlen(str));
return 0;
}
33.3 运行结果
34. freopen
34.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
FILE * freopen(const char *filename, const char *mode, FILE *stream); | 以指定模式重新指定到另一个文件 |
参数:
filename: 需要重定向到的文件名或文件路径。
mode: 代表文件访问权限的字符串。 参见 27 fopen
stream: 需要被重定向的文件流。
34.2 演示示例
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
if(freopen("temp.txt", "w", stdout) == NULL)
fprintf(stderr,"error redirecting stdout\n");
printf("Hello, %s", "Huazie");
fclose(stdout);
return 0;
}
34.3 运行结果
35. frexp,frexpf,frexpl
35.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
double frexp (double x, int * exp); | 将x 分解为有效位 和 2 的整数指数。(double)。 |
float frexpf (float x, int * exp); | 将x 分解为有效位 和 2 的整数指数。(float)。 |
long double frexpl (long double x, int * exp); | 将x 分解为有效位 和 2 的整数指数。(long double)。 |
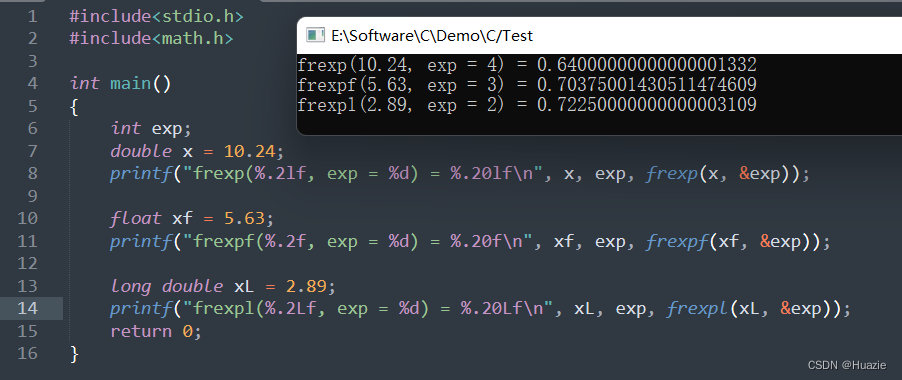
注意: 有效位的绝对值范围为 0.5(包括) 到 1(不包括)。x = 有效位 * 2 e x p 2^{exp} 2exp
35.2 演示示例
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
int main()
{
int exp;
double x = 10.24;
printf("frexp(%.2lf, exp = %d) = %.20lf\n", x, exp, frexp(x, &exp));
float xf = 5.63;
printf("frexpf(%.2f, exp = %d) = %.20f\n", xf, exp, frexpf(xf, &exp));
long double xL = 2.89;
printf("frexpl(%.2Lf, exp = %d) = %.20Lf\n", xL, exp, frexpl(xL, &exp));
return 0;
}
35.3 运行结果
36. fscanf
36.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int fscanf(FILE *stream, char *format[,argument...]); | 从一个流中执行格式化输入 |
注意: fscanf 遇到空格和换行时结束。它与 fgets 有区别,fgets 遇到空格不结束。
36.2 演示示例
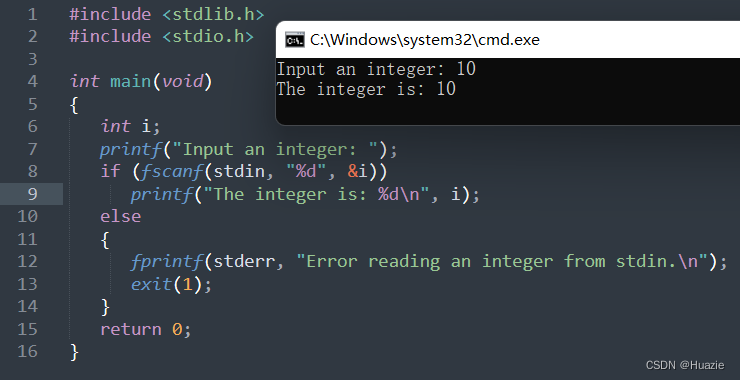
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int i;
printf("Input an integer: ");
if (fscanf(stdin, "%d", &i))
printf("The integer is: %d\n", i);
else
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error reading an integer from stdin.\n");
exit(1);
}
return 0;
}
36.3 运行结果
37. fseek
37.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int fseek(FILE *stream, long offset, int fromwhere); | 重定位流上的文件指针位置 |
注意: 如果执行成功,stream 将指向以 fromwhere【偏移起始位置:文件头 0(SEEK_SET),当前位置 1(SEEK_CUR),文件尾2(SEEK_END) 】为基准,偏移 offset(指针偏移量)个字节的位置。如果执行失败(比如 offset 超过文件自身大小),则不改变 stream 指向的位置。
37.2 演示示例
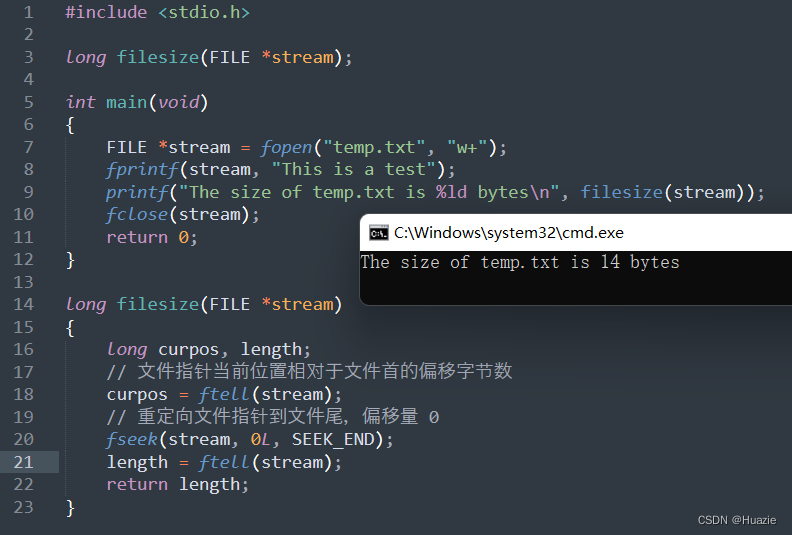
#include <stdio.h>
long filesize(FILE *stream);
int main(void)
{
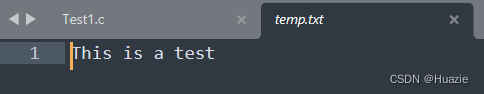
FILE *stream = fopen("temp.txt", "w+");
fprintf(stream, "This is a test");
printf("The size of temp.txt is %ld bytes\n", filesize(stream));
fclose(stream);
return 0;
}
long filesize(FILE *stream)
{
long curpos, length;
// 文件指针当前位置相对于文件首的偏移字节数
curpos = ftell(stream);
// 重定向文件指针到文件尾,偏移量 0
fseek(stream, 0L, SEEK_END);
length = ftell(stream);
return length;
}
37.3 运行结果
38. fsetpos
38.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int fsetpos(FILE *stream, const fpos_t *pos); | 将文件指针定位在pos指定的位置上。如果成功返回0,否则返回非0。 |
38.2 演示示例
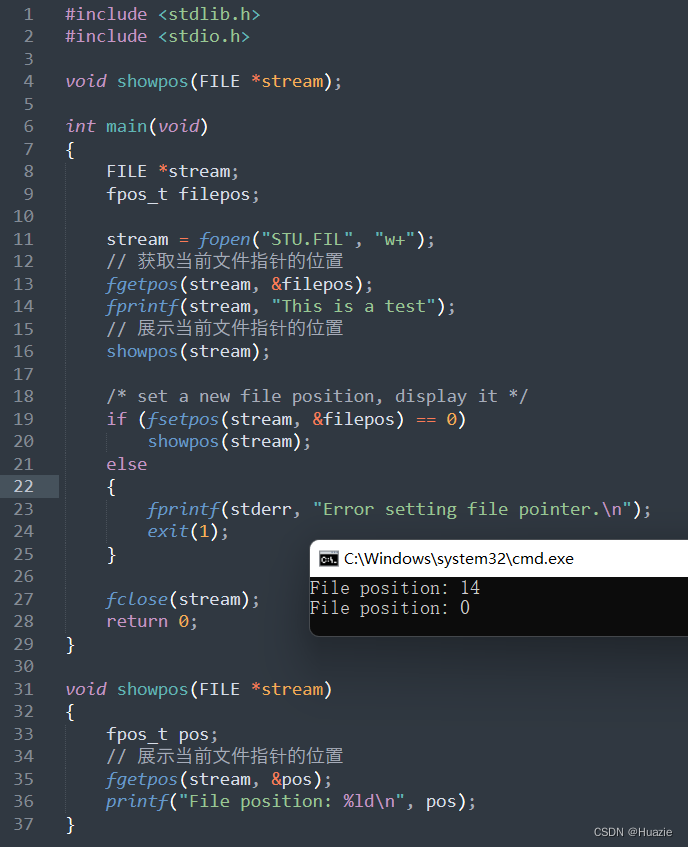
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
void showpos(FILE *stream);
int main(void)
{
FILE *stream;
fpos_t filepos;
stream = fopen("STU.FIL", "w+");
// 获取当前文件指针的位置
fgetpos(stream, &filepos);
fprintf(stream, "This is a test");
// 展示当前文件指针的位置
showpos(stream);
/* set a new file position, display it */
if (fsetpos(stream, &filepos) == 0)
showpos(stream);
else
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error setting file pointer.\n");
exit(1);
}
fclose(stream);
return 0;
}
void showpos(FILE *stream)
{
fpos_t pos;
// 展示当前文件指针的位置
fgetpos(stream, &pos);
printf("File position: %ld\n", pos);
}
38.3 运行结果
39. fstat
39.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int fstat(int handle,struct stat *buf); | 由文件描述符获取文件状态 |
39.2 演示示例
#include <sys\stat.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
int main()
{
struct stat statbuf;
FILE *stream;
if ((stream = fopen("STU.FIL", "w+")) == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Cannot open output file.\n");
exit(1);
}
fprintf(stream, "This is a test");
fflush(stream);
// get information about the file
fstat(fileno(stream), &statbuf);
fclose(stream);
if (statbuf.st_mode & S_IFCHR)
printf("Handle refers to a device.\n");
if (statbuf.st_mode & S_IFREG)
printf("Handle refers to an ordinary file.\n");
if (statbuf.st_mode & S_IREAD)
printf("User has read permission on file.\n");
if (statbuf.st_mode & S_IWRITE)
printf("User has write permission on file.\n");
// 不知道为啥,我这里文件的驱动号是空
printf("Drive letter of file: %c\n", statbuf.st_dev);
printf("Size of file in bytes: %ld\n", statbuf.st_size);
printf("Time file last opened: %s\n", ctime(&statbuf.st_ctime));
return 0;
}
39.3 运行结果
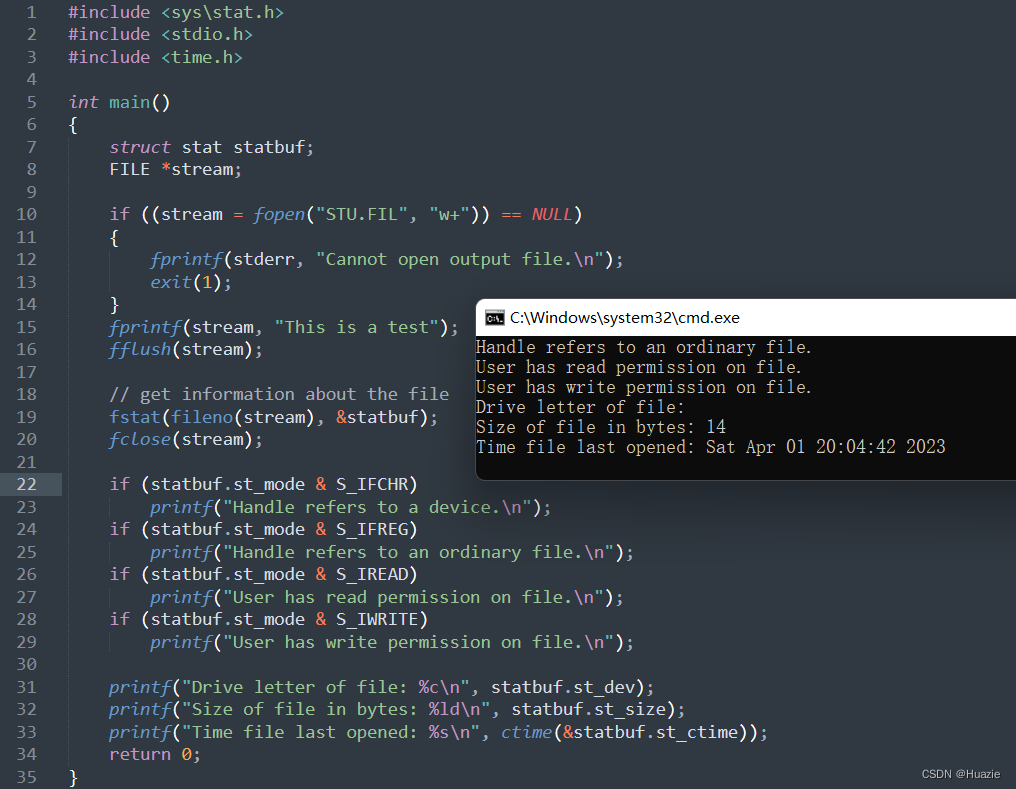
40. ftell
40.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
long ftell(FILE *stream); | 获取文件指针当前位置相对于文件首的偏移字节数 |
40.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
FILE *stream = fopen("temp.txt", "w+");
fprintf(stream, "This is a test");
printf("The file pointer is at byte %ld\n", ftell(stream));
fclose(stream);
return 0;
}
40.3 运行结果
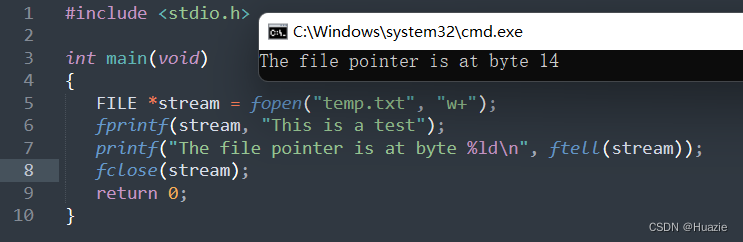
41. fwrite
41.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 | 函数功能 |
|---|---|
int fwrite(const void *ptr, int size, int nitems, FILE *stream); | 把ptr所指向的数组中的数据写入到给定流stream中 |
参数:
ptr: 指向要被写入的元素数组的指针。
size: 要被写入的每个元素的大小,以字节为单位。
nitems: 元素的个数,每个元素的大小为 size 字节。
stream: 指向 FILE 对象的指针,该 FILE 对象指定了一个输出流。
注意: 如果写入成功,fwrite 返回一个 size_t 对象,表示元素的总数,该对象是一个整型数据类型。如果该数字与 nitems 参数不同,则会显示一个错误。
41.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
struct mystruct
{
int i;
char ch;
};
int main(void)
{
FILE *stream;
struct mystruct s;
// 以只写模式打开或新建一个二进制文件。
if ((stream = fopen("test.txt", "wb")) == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Cannot open output file.\n");
return 1;
}
s.i = 0;
s.ch = 'A';
fwrite(&s, sizeof(s), 1, stream);
fclose(stream);
// 以只读模式打开或新建一个二进制文件。
if ((stream = fopen("test.txt", "rb")) == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Cannot open output file.\n");
return 1;
}
struct mystruct s1;
fread(&s1, sizeof(s1), 1, stream);
printf("%d %c", s1.i, s1.ch);
fclose(stream);
return 0;
}
41.3 运行结果
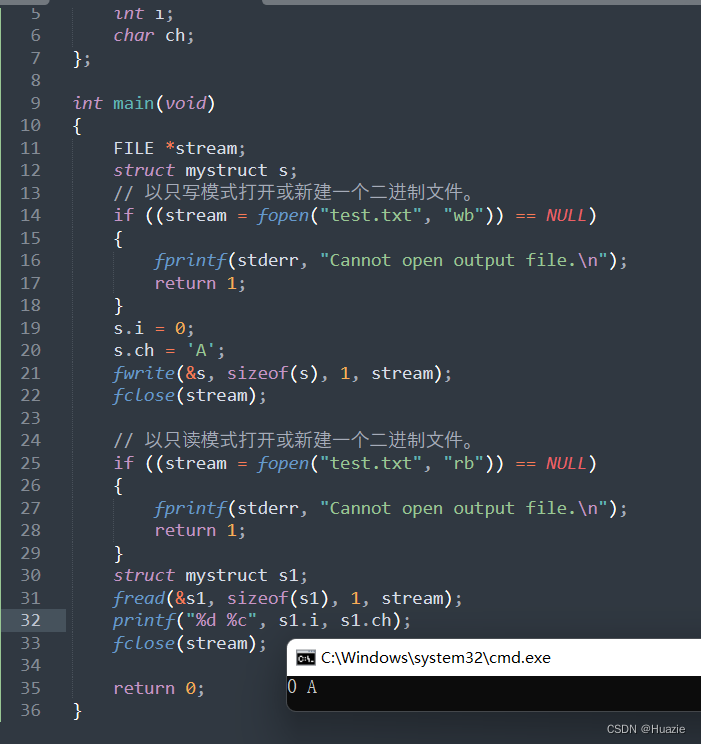























 848
848











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










