Lotka–Volterra equation
The
Lotka–Volterra equations
, also known as the
predator–prey equations
, are a pair of first-order,
non-linear
,
differential equations
frequently used to describe the
dynamics
of
biological systems
in which two species interact, one as a predator and the other as prey. The populations change through time according to the pair of equations:

where
- x is the number of prey (for example, rabbits);
- y is the number of some predator (for example, foxes);
 and
and  represent the growth rates of the two populations over time;
represent the growth rates of the two populations over time;- t represents time; and
 ,
, 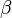 ,
, 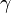 and
and 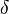 are parameters describing the interaction of the two species.
are parameters describing the interaction of the two species.
Competitive Lotka–Volterra equations
The
competitive Lotka–Volterra equations
are a simple model of the
population dynamics
of species competing for some common resource. They can be further
generalised
to include trophic interactions.
The form is similar to the Lotka–Volterra equations for predation in that the equation for each species has one term for self-interaction and one term for the interaction with other species. In the equations for predation, the base population model is exponential. For the competition equations, the logistic equationis the basis.
Given two populations, x1 and x2, with logistic dynamics, the Lotka–Volterra formulation adds an additional term to account for the species' interactions. Thus the competitive Lotka–Volterra equations are:
























 4513
4513











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








