环境
Java:1.8+
前言
最近研究解析数据报文,总结了一些,经过实践且高效的方法;
代码
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
*
* @author yutao
* @version $Id: ByteUtils.java, v 0.1 2022-07-05 15:26 yutao Exp $$
*/
public class ByteUtils {
private static final Map<String, String> DIGIT_MAP = new HashMap<>();
static {
DIGIT_MAP.put("0","0000");
DIGIT_MAP.put("1","0001");
DIGIT_MAP.put("2","0010");
DIGIT_MAP.put("3","0011");
DIGIT_MAP.put("4","0100");
DIGIT_MAP.put("5","0101");
DIGIT_MAP.put("6","0110");
DIGIT_MAP.put("7","0111");
DIGIT_MAP.put("8","1000");
DIGIT_MAP.put("9","1001");
DIGIT_MAP.put("a","1010");
DIGIT_MAP.put("b","1011");
DIGIT_MAP.put("c","1100");
DIGIT_MAP.put("d","1101");
DIGIT_MAP.put("e","1110");
DIGIT_MAP.put("f","1111");
}
private static final char[] HEX_DIGITS = "0123456789abcdef".toCharArray();
/**
* 16进制转二进制
* @param hex
* @return
*/
public static String hexToBin(String hex) {
char[] hexChar = hex.toCharArray();
StringBuilder binaryStr = new StringBuilder();
for (char h : hexChar) {
binaryStr.append(DIGIT_MAP.get(String.valueOf(h)));
}
return binaryStr.toString();
}
/**
* 将16进制转换为二进制
*
* @param hexString
* @return
*/
public static String hexToBinaryString(String hexString) {
int len = hexString.length() * 4;
//16进制转10进制
BigInteger sint = new BigInteger(hexString, 16);
//10进制转2进制
String result = sint.toString(2);
if(result.length() < len){
int diff = len - result.length();
String pad ="";
for(int i = 0; i < diff; ++i){
pad = pad.concat("0");
}
result = pad.concat(result);
}
//字符串反转
// return new StringBuilder(result).reverse().toString();
return result;
}
/**
* 十六进制转字节数组
* @param hexStr
* @return
*/
public static byte[] hexToBytes(String hexStr) {
hexStr = hexStr.toLowerCase();
int length = hexStr.length() / 2;
char[] hexChars = hexStr.toCharArray();
byte[] d = new byte[length];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
int pos = i * 2;
d[i] = (byte) (charToByte(hexChars[pos]) << 4 | charToByte(hexChars[pos + 1]));
}
return d;
}
/**
* Convert char to byte
* @param c char
* @return byte
*/
private static byte charToByte(char c) {
return (byte) "0123456789abcdef".indexOf(c);
}
/**
* 字节数组转16进制
* @param data
* @return
*/
public static String byteToHex(byte[] data) {
char[] chars = new char[data.length * 2];
for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
chars[i * 2] = HEX_DIGITS[(data[i] >> 4) & 0xf];
chars[i * 2 + 1] = HEX_DIGITS[data[i] & 0xf];
}
return new String(chars);
}
/**
* 字节数组 转 二进制
* @param bytes 高位 到 低位
* @return
*/
public static String byteToBinStr(byte[] bytes) {
int len = bytes.length * 8;
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder(new BigInteger(bytes).toString(2));
// StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder(new BigInteger(1, bytes).toString(2));
int diff = len - s.length();
for (int i = 0; i < diff; i++) {
s.insert(0, "0");
}
return s.toString();
}
/**
* 字节数组 转 二进制字符串
* @param bytes 高位 到 低位
* @return
*/
public static String byteToBinStr2(byte[] bytes) {
StringBuilder s1 = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length; i++) {
s1.append(Long.toBinaryString((bytes[i] & 0xFF) + 0x100).substring(1));
}
return s1.toString();
}
/**
* int 转 byte数组
* @param n
* @return
*/
public static byte[] intToByte(int n) {
byte[] b = new byte[4];
b[0] = (byte) (n & 0xff);
b[1] = (byte) (n >> 8 & 0xff);
b[2] = (byte) (n >> 16 & 0xff);
b[3] = (byte) (n >> 24 & 0xff);
return b;
}
/**
* long 转 byte数组
* 最低位到最高位,暂时别用,因为byteToLong需要高位到低位。
* @param n
* @return
*/
@Deprecated
public static byte[] longToByte(long n) {
byte[] b = new byte[8];
b[0] = (byte) (n & 0xff);
b[1] = (byte) (n >>> 8 & 0xff);
b[2] = (byte) (n >>> 16 & 0xff);
b[3] = (byte) (n >>> 24 & 0xff);
b[4] = (byte) (n >>> 32 & 0xff);
b[5] = (byte) (n >>> 40 & 0xff);
b[6] = (byte) (n >>> 48 & 0xff);
b[7] = (byte) (n >>> 56 & 0xff);
return b;
}
/**
* long 转 byte数组
* 最高位到最低位
* @param s
* @return
*/
public static byte[] longToByteArray(long s) {
byte[] targets = new byte[8];
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
int offset = (targets.length - 1 - i) * 8;
targets[i] = (byte) ((s >>> offset) & 0xff);
}
return targets;
}
/**
* byte数组转换为int整数
*
* @param bytes byte数组 期望 高位 到 低位
* @return int整数
*/
public static int byteToInt(byte[] bytes) {
if (bytes == null || bytes.length > 4) {
throw new RuntimeException("byte数组不能为null且长度不能超过4");
}
int length = bytes.length;
int r = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
//左移 8 位
r = r | (bytes[i] & 0xff) << 8 * (length - 1 - i);
}
return r;
}
/**
*
* 遇到{-25, -15, 51, -90}:值3891344294超过int的上限;这时就需要改用long
* 之所以要强转,因为Java默认在对byte进行移位操作前会转换为int类型
* @param bytes 期望的字节数组是 高位 到 低位
* @return
*/
public static long byteToLong(byte[] bytes) {
if (bytes == null || bytes.length > 8) {
throw new RuntimeException("byte数组不能为null且长度不能超过4");
}
int length = bytes.length;
long r = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
//左移 8 位
r = r | ((long) bytes[i] & 0xff) << 8 * (length - 1 - i);
}
return r;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*byte[] aa = new byte[]{-25, -15, 51, -90};
System.out.println(byteToHex(aa));
System.out.println((aa[0] & 0xff) << 8 * 3 | (aa[1] & 0xff) << 8*2 | (aa[2] & 0xff) << 8 | (aa[3] & 0xff));
System.out.println(byteToInt(aa));
System.out.println(byteToLong(aa));*/
System.out.println(byteToBinStr(new byte[]{-128}));
System.out.println(byteToBinStr2(new byte[]{-128}));
}
/**
* 获取指定的字节数组
* @param bytes
* @param len
* @return
*/
public static byte[] getByte(byte[] bytes, int offset, int len) {
byte[] newB = new byte[len];
System.arraycopy(bytes, offset, newB, 0, newB.length);
return newB;
}
/**
* 获取指定的字节数组
* @param bytes
* @param offset
* @return
*/
public static byte[] getByte(byte[] bytes, int offset) {
int i = bytes.length - offset;
if (i < 0) {
return new byte[0];
}
byte[] newB = new byte[i];
System.arraycopy(bytes, offset, newB, 0, newB.length);
return newB;
}
/**
* 二进制转10进制
*
* @param
* @return
*/
public static int binaryToInt(String binaryStr) {
// BigInteger sint = new BigInteger(binaryStr, 2);
// return sint.intValue();
return Integer.parseInt(binaryStr, 2);
}
/**
* 二进制转10进制
* @param binaryStr
* @return
*/
public static long binaryToLong(String binaryStr) {
return Long.parseLong(binaryStr, 2);
}
}
下面说明下容易出现,但是网上又千篇一律推荐的问题:
字节数组 转 二进制字符串
方法一:强烈推荐
/**
* 字节数组 转 二进制字符串
* @param bytes 高位 到 低位
* @return
*/
public static String byteToBinStr2(byte[] bytes) {
StringBuilder s1 = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length; i++) {
s1.append(Long.toBinaryString((bytes[i] & 0xFF) + 0x100).substring(1));
}
return s1.toString();
}
Long.toBinaryString((bytes[i] & 0xFF) + 0x100).substring(1)的原理是,字节是8位,+0x100即256,那就是9位(二进制),也就是每次用9位来转换。然后将转换后的字符串,截取到最高位(加上去的256),这样就得到了8位的二进制。
如果不这样做的话,上面的方法Long.toBinaryString(),1转为二进制还是1,而不是00000001(期望是这个)。
方法二:一般推荐
注意下面👇🏻:new BigInteger(1, bytes) 这里重点注意,指定了符号位
/**
* 字节数组 转 二进制
* @param bytes 高位 到 低位
* @return
*/
public static String byteToBinStr(byte[] bytes) {
int len = bytes.length * 8;
//new BigInteger(1, bytes) 这里重点注意,指定了符号位
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder(new BigInteger(1, bytes).toString(2));
int diff = len - s.length();
for (int i = 0; i < diff; i++) {
s.insert(0, "0");
}
return s.toString();
}
方法2的基础上不指定符号位
变成如下:
//网上千篇一律是这种写法,但是是错误的。
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder(new BigInteger(bytes).toString(2));
如果不指定符号位,那么在解析-128时,会解析为负数:
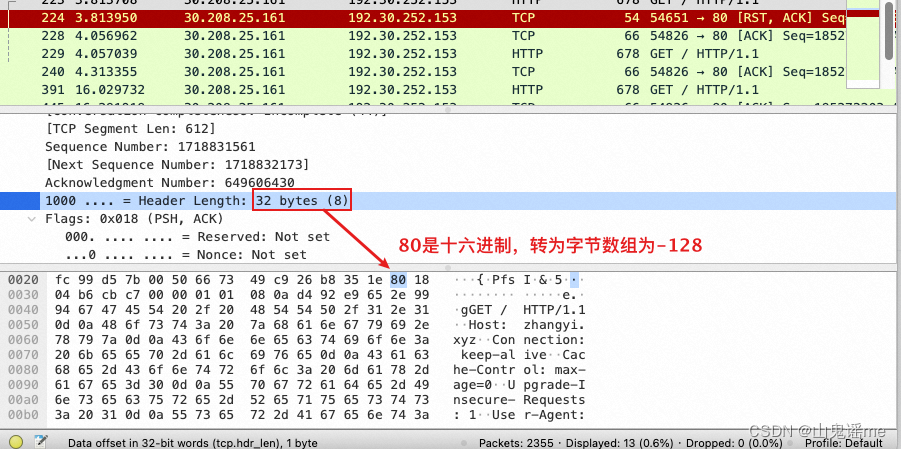

所以这里:
强烈建议使用方法一;
强烈建议使用方法一;
强烈建议使用方法一;
参考地址:

























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










