注:本文主题《OSPF 和 IS-IS 路由协议比较》,几篇合集,英文部分机翻,未校。
OSPF VS ISIS — huawei
umaryaqub 乌马里亚库布 Created: 2019-09-25 07:16:26
Latest reply: 2022-10-27 06:11:28
I have come across some questions on the differences and similarities between OSPF and IS-IS. Here are some of the similarities and differences between both. I hope this is helpful.
我遇到了一些关于 OSPF 和 IS-IS 之间异同的问题。以下是两者之间的一些相似之处和不同之处。
Similarities between OSPF and IS-IS Routing Protocols
OSPF 和 IS-IS 路由协议之间的相似之处
There are a lot of similarities between the OSPF and IS-IS routing protocols. The following are some of the major similarities that one should keep in mind while implementing the OSPF or IS-IS routing protocol.
OSPF 和 IS-IS 路由协议之间有很多相似之处。以下是在实施 OSPF 或 IS-IS 路由协议时应牢记的一些主要相似之处。
-
Both routing protocols are Interior Gateway Protocols (IGP).
-
两种路由协议都是内部网关协议(IGP)。
-
Both routing protocols can only be used to distribute routing information between routers belonging to the same Autonomous System (AS).
两种路由协议只能用于在属于同一自治系统(AS)的路由器之间分发路由信息。
-
Both routing protocols are link-state protocols.
两种路由协议都是链路状态协议。
-
Both routing protocols maintain a link-state database and run the Dijkstra SPF algorithm to compute the shortest path.
两种路由协议都维护一个链路状态数据库,并运行 Dijkstra SPF 算法来计算最短路径。
-
Both routing protocols use Hello packets to create and maintain adjacencies between the neighboring routers.
两种路由协议都使用 Hello 数据包在相邻路由器之间创建和维护邻接关系。
-
Both routing protocols use areas to create a hierarchical structure.
两种路由协议都使用区域来创建分层结构。
-
Both routing protocols are classless routing protocols and support CIDR, VLSM, and discontinuous networks.
这两种路由协议都是无类别路由协议,支持 CIDR、VLSM 和不连续网络。
-
Both routing protocols elect a designated router in the broadcast networks.
两种路由协议都会在广播网络中选择一个指定的路由器。
-
Both routing protocols support authentication mechanisms.
两种路由协议都支持身份验证机制。
-
Both routing protocols support the unlimited number of hops count.
两种路由协议都支持无限数量的跃点计数。
Differences between OSPF and IS-IS Routing Protocols
OSPF 和 IS-IS 路由协议之间的差异
Apart from these similarities, both routing protocols differ from each other with many features. Both routing protocols have some key differences that one should keep in mind because many people think (better to say confused) that both are the same protocols and the implementation of any protocol will not affect network performance a lot. But the following list will help you to distinguish both routing protocols.
除了这些相似之处之外,两种路由协议在许多功能上都有所不同。这两种路由协议都有一些关键差异,应该牢记这些差异,因为许多人认为(最好说是困惑)两者都是相同的协议,任何协议的实施都不会对网络性能产生太大影响。但以下列表将帮助您区分这两种路由协议。
-
OSPF supports NBMA and point-to-multipoint links, whereas IS-IS does not support them.
OSPF 支持 NBMA 和点对多点链路,而 IS-IS 不支持它们。
-
IS-IS runs on the data link layer, whereas OSPF runs on the network layer.
IS-IS 运行在数据链路层,而 OSPF 运行在网络层。
-
OSPF supports virtual links, whereas IS-IS does not support them.
OSPF 支持虚拟链路,而 IS-IS 不支持虚拟链路。
-
OSPF elects a DR and BDR, whereas IS-IS elects only a single DR called DIS.
OSPF 选择 DR 和 BDR,而 IS-IS 只选择一个名为 DIS 的 DR。
-
OSPF defines a backbone area called area 0 for inter-area advertisements, whereas IS-IS categorizes the domain into two layers.
OSPF 定义了一个称为区域 0 的中枢区域,用于区域间通告,而 IS-IS 将域分为两层。
-
An OSPF router can belong to multiple areas whereas an IS-IS router can belong to only one area.
OSPF 路由器可以属于多个区域,而 IS-IS 路由器只能属于一个区域。
-
OSPF uses Router ID, whereas IS-IS uses System ID to identify each router on the network.
OSPF 使用路由器 ID,而 IS-IS 使用系统 ID 来识别网络上的每个路由器。
OSPF and IS-IS Terminology
OSPF 和 IS-IS 术语
Apart from these similarities and differences between the OSPF and IS-IS routing protocols, one should also be familiar with the terminology used to refer to the basic terms for both routing protocols.
除了 OSPF 和 IS-IS 路由协议之间的这些相似之处和不同之处之外,还应熟悉用于指代两种路由协议的基本术语的术语。
The following table list some of the basic terms used to refer to the components of the OSPF and IS-IS routing protocols.
下表列出了用于指代 OSPF 和 IS-IS 路由协议组件的一些基本术语。
| Sr. No. | OSPF Terms | IS-IS Terms |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Router | End System |
| 2. | Link | Circuit |
| 3. | Designated Router | Designated IS |
| 4. | Backup DR | N/A |
| 5. | Link State Advertisement(LSA) | Link-State PDU (LSP) |
| 6. | Hello Packet | IS-IS Hello(IIH) |
| 7. | Area | Sub domain |
| 8. | Area Border Router(ABR) | L1/L2 Router |
In this post, we have learned the similarities and differences between the OSPF and IS-IS routing protocols. Let us know if you have something that can help us to improve the article. Please let me know if there are any further confusions, and I’ll try to answer them one by one.
在本文中,我们了解了 OSPF 和 IS-IS 路由协议之间的异同。
OSPF vs ISIS: Detailed Comparison
OSPF 与 ISIS:详细比较
Rashmi Bhardwaj | 拉什米·巴德瓦吉 |
OSPF stands for Open Shortest Path First and ISIS stands for Intermediate System to Intermediate System. OSPF and ISIS both are routing protocols for Internet Protocol Networks.
OSPF 代表开放式最短路径优先,ISIS 代表中间系统到中间系统。OSPF 和 ISIS 都是互联网协议网络的路由协议。
What is OSPF?
什么是 OSPF?
OSPF is a link-state routing protocol that is used to route IP packets within an autonomous system. It was designed as a scalable alternative to RIP (Routing Information Protocol). OSPF routers exchange link state advertisements (LSAs) to build a topology map of the network. Each router then uses the Dijkstra algorithm to calculate the shortest path to each destination.
OSPF 是一种链路状态路由协议,用于在自治系统内路由 IP 数据包。它被设计为 RIP(路由信息协议)的可扩展替代方案。OSPF 路由器交换链路状态通告(LSA)以构建网络的拓扑图。然后,每个路由器使用 Dijkstra 算法计算到每个目的地的最短路径。
What is ISIS?
什么是 ISIS?
ISIS is a link-state routing protocol that uses a hierarchical network structure to route data within an autonomous system (AS). It was originally developed for use in the ISO OSI protocol suite but was adapted for IP routing. ISIS routers exchange information about their links and build a complete network topology. Each router then independently calculates the best path to each destination using the Shortest Path First (SPF) algorithm.
ISIS 是一种链路状态路由协议,它使用分层网络结构在自治系统(AS)内路由数据。它最初是为在 ISO OSI 协议套件中使用而开发的,但后来也适用于 IP 路由。ISIS 路由器交换有关其链路的信息并构建完整的网络拓扑。然后,每个路由器使用最短路径优先(SPF)算法独立计算到每个目的地的最佳路径。
Similarities between OSPF and ISIS
OSPF 和 ISIS 之间的相似之处
Before going into the details of differences between OSPF and ISIS, let’s explore some similarities:
在详细介绍 OSPF 和 ISIS 之间的差异之前,让我们先了解一些相似之处:
-
OSPF and ISIS both are Link State Routing Protocols using the Dijkstra SPF Algorithm.
OSPF 和 ISIS 都是使用 Dijkstra SPF 算法的链路状态路由协议。
-
Both are Interior Gateway Protocols (IGP) that distribute routing information between routers belonging to a single Autonomous System (AS).
两者都是内部网关协议(IGP),可在属于单个自治系统(AS)的路由器之间分配路由信息。
-
Both use Hello packets to create and maintain adjacencies between the neighboring routers.
两者都使用 Hello 数据包在相邻路由器之间创建和维护邻接关系。
-
Both the protocols are classless protocols and support classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) and Variable Subnet Length Masking (VLSM)
这两种协议都是无类别协议,都支持无类别域间路由(CIDR)和可变子网长度掩码(VLSM)
-
Both support Authentication Mechanism.
两者都支持身份验证机制
-
Both support multipath.
两者都支持多路径。
-
Both support IP unnumbered links.
两者都支持 IP 未编号的链接。
Differences between OSPF and ISIS
OSPF 和 ISIS 之间的差异
-
OSPF operates on the top of IP layer whereas ISIS operates over Layer 2.
OSPF 在 IP 层上运行,而 ISIS 在第 2 层上运行。
-
OSPF can support virtual links but ISIS can not support (as it operates on Layer 2 directly).
OSPF 可以支持虚拟链路,但 ISIS 不支持(因为它直接在第 2 层上运行)。
-
OSPF elects a DR and BDR on broadcast networks which can not be pre-empted however, ISIS elects a single DIS which can be pre-empted.
OSPF 在广播网络上选择一个 DR 和 BDR,该网络无法被抢占,但是,ISIS 会选择一个可以被抢占的 DIS。
-
IP connectivity between the routers to share the routing information is required in case of OSPF, while ISIS doesn’t require IP connectivity as the updates are sent via CLNS instead of IP.
在 OSPF 的情况下,路由器之间需要 IP 连接以共享路由信息,而 ISIS 不需要 IP 连接,因为更新是通过 CLNS 而不是 IP 发送的。
-
OSPF is prone to attacks hence security overheads are required for protection. The possibility of attacks is very less in case of ISIS as it runs over Layer 2.
OSPF 容易受到攻击,因此需要安全开销进行保护。如果 ISIS 在第 2 层上运行,因此攻击的可能性非常小。
-
OSPF designates a backbone area and standard or non-backbone area for inter-area advertisements whereas ISIS organizes the domain into different levels.
OSPF 为区域间通告指定主干区域和标准或非主干区域,而 ISIS 将域组织为不同的级别。
-
To identify a router on the network, OSPF uses Router ID and ISIS uses System ID.
为了识别网络上的路由器,OSPF 使用路由器 ID,而 ISIS 使用系统 ID。
-
OSPF is less flexible with more strict requirements for forming neighbor adjacencies. The hello and dead intervals, and the subnet mask must match (except on point-to-point links).
OSPF 的灵活性较低,对形成邻居邻接的要求更严格。你好间隔和死区间隔以及子网掩码必须匹配(点对点链路除外)。
Comparison Table: OSPF vs ISIS
对比表:OSPF 与 ISIS
Below table enumerates the differences between OSPF and ISIS protocols
下表列举了 OSPF 和 ISIS 协议之间的差异
| Parameter | OSPF | ISIS |
|---|---|---|
| Administrative Distance | 110 | 115 |
| Standard | RFC 2328(OSPFv2) | ISO 10589, RFC1195 |
| Operating OSI Layer | OSPF operates on top of IP Layer | ISIS operates over L2 |
| Virtual Links Supported | Yes | No |
| DR/BDR election | OSPF elects a DR and BDR on broadcast networks | ISIS elects a single DIS on broadcast networks |
| IP connectivity | OSPF requires IP connectivity between the routers to share the routing information | ISIS doesn’t require IP connectivity between the routers as updates are sent via CLNS instead of IP. |
| Security | Prone to attack and hence requires more security overheads for protection. | Since ISIS runs on Layer 2, hence very unlikely possibility of attack |
| Area/Level Types | ● Backbone Area ● Standard Area(Non Backbone Area) | Different Levels used in place of area ● Level 1 ● Level 2 ● Level 1/2 Areas |
| Identification | OSPF uses router id to identify a router on network | ISIS uses System ID to identify a router on the network. |
| Table Refresh | OSPF refreshes the entire routing table after 30 minutes. | ISIS doesn’t refresh the entire SPF table periodically like OSPF. |
| Related terms | Area,non-Backbone Area, Backbone Area,ABR,ASBR,Host | IS,Level-1,Level-2,L1/L2,Sub Domain,ES |
| Flexibility | Less flexible than ISIS | More flexible to use than OSPF especially in provider domain |
| Scalability | Less scalable than ISIS | More scalable than OSPF |
Related FAQs
相关常见问题解答
Q.1 What is an OSPF designated router (DR) and why is it important?
Q.1 什么是 OSPF 指定路由器(DR),为什么它很重要?
In OSPF, a DR is elected on multi-access networks to act as a central point for exchanging routing information, reducing the amount of data traffic and improving efficiency.
在 OSPF 中,在多址网络上选举一个 DR 作为交换路由信息的中心点,从而减少数据流量并提高效率。
Q.2 How does OSPF handle route summarization?
Q.2 OSPF 如何处理路由摘要?
OSPF allows route summarization at area boundaries to reduce the size of the routing table and improve network performance. This is typically done at ABRs (Area Border Routers).
OSPF 允许在区域边界进行路由汇总,以减小路由表的大小并提高网络性能。这通常在 ABR(区域边界路由器)上完成。
Q.3 What are the differences between Level 1 and Level 2 routing in ISIS?
Q.3 ISIS 中的 1 级和 2 级路由有什么区别?
Level 1 routers route within a single area, while Level 2 routers can route between different areas. Level 2 routers act as the backbone of an IS-IS network.
1 级路由器在单个区域内路由,而 2 级路由器可以在不同区域之间路由。2 级路由器充当 IS-IS 网络的主干。
Q.4 What are TLVs in ISIS?Q.4 ISIS 中的 TLV 是什么?
TLV (Type-Length-Value) is a flexible encoding method used in ISIS to carry various types of routing information. This extensibility allows ISIS to be easily updated to support new features.
TLV(Type-Length-Value)是 ISIS 中用于传输各种路由信息的灵活编码方法。这种可扩展性使 ISIS 可以轻松更新以支持新功能。
OSPF Vs ISIS
OSPF 与 ISIS
In this article, we will discuss the similarities and differences between OSPF and ISIS Protocols.
在本文中,将讨论 OSPF 和 ISIS 协议之间的异同。
OSPF and ISIS Similarities
OSPF 和 ISIS 的相似之处
In this article we will compare OSPF and ISIS and discuss their similarities and some key differences between them.
在本文中,我们将比较 OSPF 和 ISIS,并讨论它们的相似之处和它们之间的一些主要区别。
There are many similarities between the OSPF and ISIS. Below are few main similarities between both protocols.
OSPF 和 ISIS 之间有许多相似之处。以下是两种协议之间的一些主要相似之处。
-
Both OSPF and ISIS are Interior Gateway Protocols and used for routing in internal domains or autonomous systems.
OSPF 和 ISIS 都是内部网关协议,用于内部域或自治系统中的路由。
-
Both the routing protocols are link-state protocols.
两种路由协议都是链路状态协议。
-
Both OSPF and ISIS maintain a link-state database (LSDB) and run the Dijkstra SPF algorithm to compute the shortest path.
OSPF 和 ISIS 都维护一个链路状态数据库(LSDB)并运行 Dijkstra SPF 算法来计算最短路径。
-
Both the routing protocols use Hello packets to create and maintain adjacency between the neighboring nodes.
两种路由协议都使用 Hello 数据包在相邻节点之间创建和维护邻接关系。
-
Both OSPF and ISIS use areas to maintain a hierarchical structure.
OSPF 和 ISIS 都使用区域来维护层次结构。
-
Both the routing protocols are classless routing protocols and support CIDR, VLSM, and discontinuous network.
这两种路由协议都是无类路由协议,支持 CIDR、VLSM 和不连续网络。
-
Both the routing protocols elect a designated router in the broadcast networks. However, ISIS only elects a DIS (Designated IS). There is no backup DIS.
两种路由协议都会在广播网络中选择一个指定的路由器。但是,ISIS 只选择 DIS(指定 IS)。没有备份 DIS。
-
Both the IGPs support authentication mechanisms.
两种 IGP 都支持身份验证机制。
-
Both the IGPs support the unlimited number of hops count.
两种 IGP 都支持无限数量的跃点计数。
-
Both the IGPs support Classless Inter Domain Routing, Variable Length Subnet Mask, IP unnumbered links, Authentication, and Multi-paths.
两种 IGP 都支持无类别域间路由、可变长度子网掩码、IP 未编号链路、身份验证和多路径。
OSPF and ISIS Dissimilarities
OSPF 和 ISIS 的差异
Apart from the similarities explained above, both the routing protocols also have some dissimilarities as explained below:
除了上面解释的相似之处外,两种路由协议也有一些不同之处,如下所述:
-
The default administrative distance of OSPF is 110 and ISIS is 115.
OSPF 的默认管理距离为 110,ISIS 的默认管理距离为 115。
-
OSPF behaves differently with different kind of networks for example NBMA and point-to-multipoint links, whereas IS-IS only supports two type of networks (Broadcast and Point-to-Point)
OSPF 在不同类型的网络(例如 NBMA 和点对多点链路)上的行为不同,而 IS-IS 仅支持两种类型的网络(广播和点对点)
-
ISIS runs on top of data link layer(encapsulated in Data link layer), whereas OSPF runs on top of IP (Protocol no. 89), i.e. at the Transport layer. To further elaborate, OSPF requires IP connectivity to form adjacency between two nodes, however, ISIS does not require any IP connectivity to for adjacency because it uses NSAP addresses (example 0049.0001.1111.1111.1111.00) which is a unique value per node configured under ISIS routing process. As ISIS on top of Data Link layer, it is not possible to attack ISIS at IP. NSAP fields are explained as below:
ISIS 运行在数据链路层(封装在数据链路层)之上,而 OSPF 运行在 IP(协议编号 89)之上,即传输层。进一步阐述,OSPF 需要 IP 连接才能在两个节点之间形成邻接关系,但是,ISIS 不需要任何 IP 连接来实现邻接关系,因为它使用 NSAP 地址(例如 0049.0001.1111.1111.1111.00),这是在 ISIS 路由进程下配置的每个节点的唯一值。由于 ISIS 位于数据链路层之上,因此无法在 IP 上攻击 ISIS。NSAP 字段说明如下:
49 – Private Domain
49 – 私有域0001 – Area
0001 – 区域1111.1111.1111 – System ID (like mac address)
111.1111.1111 – 系统 ID (如 mac 地址)00 – NSEL – Signifies that the node is a router. i.e if a node is router then nsel is 00
00 – NSEL – 表示节点是路由器。即,如果节点是 router,则 NSEL 为 00

-
OSPF supports virtual link to connect an remote area to backbone area 0, whereas IS-IS does not support virtual link concept.
OSPF 支持将远程区域连接到主干区域 0 的虚拟链路,而 IS-IS 不支持虚拟链路概念。
-
OSPF elects a DR and BDR in the shared network, whereas IS-IS elects only a single DR called DIS.
OSPF 在共享网络中选择一个 DR 和 BDR,而 IS-IS 只选择一个称为 DIS 的 DR。
-
OSPF refreshes its complete database table every 30 mins (or at max after 60 mins) however, ISIS doesn’t refresh its entire database periodically like OSPF.
OSPF 每 30 分钟刷新一次其完整的数据库表(或最多 60 分钟后刷新一次),但是,ISIS 不会像 OSPF 那样定期刷新其整个数据库。
-
Unlike OSPF, in the ISIS protocol, SPF is only used to calculate the reachability to routers based on their NSAP addresses. Once best paths are calculated, SPF in not run again when any network prefix goes down or fluctuates. SPF will only run again if a router/node goes down. ISIS uses another algorithm called partial route calculation (PRC) for IP routing table calculation.
与 OSPF 不同,在 ISIS 协议中,SPF 仅用于根据路由器的 NSAP 地址计算路由器的可达性。计算出最佳路径后,当任何网络前缀出现故障或波动时,SPF 不会再次运行。SPF 只有在路由器/节点宕机时才会再次运行。ISIS 使用另一种称为部分路由计算(PRC)的算法进行 IP 路由表计算。
-
OSPF defines a backbone area called area 0 for inter-area advertisements, whereas ISIS categorizes the domain uses various ISIS levels, for example L1, L1/L2, L2. The L2 routers (L2 routing information) form the backbone area in ISIS.
OSPF 为区域间通告定义了一个称为区域 0 的主干区域,而 ISIS 使用各种 ISIS 级别(例如 L1、L1/L2、L2)对域进行分类。L2 路由器(L2 路由信息)构成了 ISIS 中的主干区域。
-
An OSPF router can belong to multiple areas, for example, an ABR can be part of two or more areas at a time whereas an ISIS router can belong to only one area.
OSPF 路由器可以属于多个区域,例如,ABR 可以同时属于两个或多个区域,而 ISIS 路由器只能属于一个区域。
-
OSPF uses Router ID, whereas ISIS uses System ID to identify each router on the network.
OSPF 使用路由器 ID,而 ISIS 使用系统 ID 来识别网络上的每个路由器。
-
Compared to OSPF, ISIS is more easy to configure and flexible and scalable in operation and therefore is widely configured as an IGP in Service Provider core backbones.
与 OSPF 相比,ISIS 更易于配置,操作更灵活且可扩展,因此被广泛配置为服务提供商核心骨干网中的 IGP。
-
While migrating from IPv4 to IPv6, we have to jump from OSPFv2 to OSPFv3 at config level, however, ISIS simply requires addition of IPv6 address family and that’s it.
从 IPv4 迁移到 IPv6 时,我们必须在配置级别从 OSPFv2 跳转到 OSPFv3,但是,ISIS 只需要添加 IPv6 地址族,仅此而已。
ISIS vs OSPF
| OSPF | ISIS |
|---|---|
| Host | End System(ES) |
| Router | Intermediate System(IS) |
| Link | Circuit |
| Packet | Protocol Data Unit(PDU) |
| Designated router(DR) | Designated IS(DIS) |
| Backup DR(BDR) | No Backup DIS is elected in ISIS |
| Hello packet | IIH PDU |
| Database Description(DBD) | Complete sequence number PDU(CSNP) |
| Link State Request(LSR) | Partial Sequence Number PDUs(PSNP) |
| Link-State Update | Link-State PDU(LSP) |
| Link State Acknowledgement | PSNPs are also used to acknowledge receipt of an LSP |
| Area | Sub domain(area) |
| Non-backbone area | Level-1 area |
| Backbone area | Level-2 Sub domain(backbone) |
| Area Border Router(ABR) | L1 L2 router |
| Autonomous System Boundary Router(ASBR) | Any IS |
| Works at Transport Layer.i.e on top of IP Layer | Works at Link Layer(Not Possible to attack the IGP using IP as with OSPF) |
| Suits ISPs with central high speed core network linking regional PoPs | Suits ISPs with diverse infrastructure, not fitting central core model of OSPF |
IS-IS versus OSPF
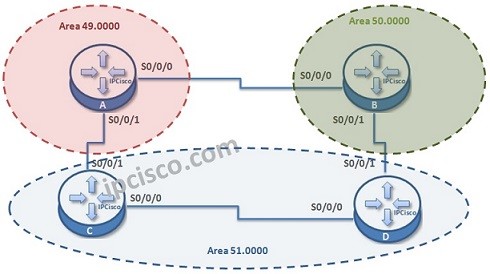
IS-IS Protocol and OSPF have some similarities and differences. In this lesson, we will focus on IS-IS versus OSPF and we will learn the similarities and differences between ospf and IS-IS Protocol.
IS-IS 协议和 OSPF 有一些相似之处和不同之处。在本文中,我们将重点介绍 IS-IS 与 OSPF,并将了解 ospf 和 IS-IS 协议之间的异同。
Lets firstly check the similarities of these two protocol one by one:
首先,让我们逐一检查这两个协议的相似之处:
-
IS-IS Protocol and OSPF are both Link-State Interior Gateway Protocols.
IS-IS 协议和 OSPF 都是链路状态内部网关协议。
-
Intermediate System to Intermediate System & OSPF are both uses Dijkstra SPF (Shortest Path First) algorithm.
中间系统到中间系统和OSPF都使用Dijkstra SPF(最短路径优先)算法。
-
These protocols have LSDBs and the LSDB similar structure
这些协议具有 LSDB 和 LSDB 类似的结构
-
Both support VLSM (Variable Length Subnet Mask)
两者都支持 VLSM(可变长度子网掩码)
-
Both are very scalable protocols
两者都是高度可扩展的协议
-
Open Shortest Path First and ISIS have fast convergence time after changes
开放最短路径优先和 ISIS 在更改后具有快速收敛时间
-
Both are open standards
两者都是开放标准
-
Both have hierarchical structures, there are two hierarchy level
两者都有层次结构,有两个层次结构级别
-
OSPF and Intermediate System to Intermediate System support LANs and point-to-point protocols in similar ways
OSPF 和中间系统到中间系统以类似的方式支持 LAN 和点对点协议
-
Both protocol use periodic Hello messages for neighbour establishment
两种协议都使用定期的 Hello 消息来建立邻居
After IS-IS versus OSPF similarities, now let’s check the differences of these two important protocols:
在 IS-IS 与 OSPF 相似之后,现在让我们检查一下这两个重要协议的差异:
IS-IS Protocol works above Layer 2 next to IP, OSPF works on top of IP.
IS-IS 协议在 IP 旁边的第 2 层之上工作,OSPF 在 IP 之上工作。
-
IS-IS routers belong to one area, OSPF routers belong multiple areas, links are in areas in Open Shortest Path First.
IS-IS 路由器属于一个区域,OSPF 路由器属于多个区域,链路位于开放最短路径优先的区域。
-
Intermediate System to Intermediate System uses DIS, OSPF uses DR and BDR.
中间系统到中间系统使用 DIS,OSPF 使用 DR 和 BDR。
-
OSPF has virtual-links, Intermediate System to Intermediate System does not support this.
OSPF 具有虚拟链路,中间系统到中间系统不支持此功能。
-
Open Shortest Path First uses opaque LSA extensions, ISIS can be extended more by TLVs.
开放最短路径优先使用不透明的 LSA 扩展,ISIS 可以通过 TLV 进行更多扩展。
-
Open Shortest Path First has efficient packet types, ISIS has untidy structure because of TLVs, but more granular.
开放最短路径优先具有高效的数据包类型,ISIS 由于 TLV 而具有不整洁的结构,但更精细。
-
In OSPF small changes causes small packets, in Intermediate System to Intermediate System even if small change, entire LSPs are sent.
在 OSPF 中,小的更改会导致小数据包,在中间系统到中间系统中,即使很小的更改,也会发送整个 LSP。
You can also see the summary of these differences in the shape.
可以在下图中查看这些差异的摘要。
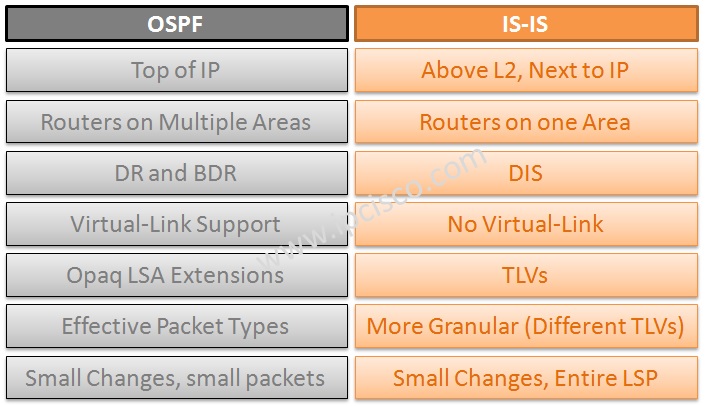
IS-IS Protocol versus OSPF ProtocolIS-IS 协议与 OSPF 协议
And lastly, let’s check the terminology of these two Link-State protocols. IS-IS Protocol terminology versus OSPF terminolog is showed below:
最后,让我们检查一下这两个 Link-State 协议的术语。IS-IS 协议术语与 OSPF 术语如下所示:

IS-IS Protocol and OSPF Protocol Terminology Comparison
IS-IS 协议和 OSPF 协议术语比较
Both of these routing protocols are very important for networking world. So, it is important to know the differences and simiarities of these routing protocols.
这两种路由协议对于网络世界都非常重要。因此,了解这些路由协议的差异和相似性非常重要。
Difference between OSPF and IS-IS :
OSPF 和 IS-IS 之间的区别:
| S.No. | Parameter 参数 | OSPF | IS-IS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Administrative Distance 管理距离 | 110 | 115 |
| 2. | Standard | RFC 2328 (OSPFv2) | ISO 10589, RFC 1195 |
| 3. | Operating OSI Layer 操作 OSI 层 | OSPF operates on the top of IP layer. OSPF 在 IP 层上运行。 | IS-IS operates over L2. IS-IS 在 L2 上运行。 |
| 4. | Virtual Links Supported 支持虚拟链接 | Yes 是 | No 不 |
| 5. | DR/BDR Election DR/BDR 选择 | OSPF elects a BDR and DR on broadcast networks. OSPF 在广播网络上选择 BDR 和 DR。 | IS-IS elects a single DIS on broadcast networks.IS-IS 在广播网络中选举单个 DIS。 |
| 6. | IP Connectivity IP 连接 | OSPF Requires the IP Connectivity between the routers to share the routing information. OSPF 要求路由器之间的 IP 连接共享路由信息。 | IS-IS doesn’t require IP connectivity between the routers as updates are sent via CLNS instead of IP. IS-IS 不需要路由器之间的 IP 连接,因为更新是通过 CLNS 而不是 IP 发送的。 |
| 7. | Support 支持 | OSPF supports NBMA and point to multipoint links. OSPF 支持 NBMA 和点对多点链路。 | IS-IS doesn’t support. IS-IS 不支持。 |
| 8. | Router Area 路由器区域 | OSPF router can belong to multiple areas. OSPF 路由器可以属于多个区域。 | IS-IS router can belong to only one area. IS-IS 路由器只能属于一个区域。 |
| 9. | Area/Level Types 区域/级别类型 | Backbone Area 骨干区 Standard Area (Non Backbone Area) 标准区(非主干区) | Level 1 Level 2 Level 1/2 Areas |
| 10. | Security 安全 | Prone to attack and hence requires more security overheads for protection. 容易受到攻击,因此需要更多的安全开销来提供保护。 | Since, IS-IS runs on level2, hence every unlikely possibility of attack. 因为 IS-IS 在 2 级上运行,因此不太可能受到攻击。 |
| 11. | Identification 鉴定 | OSPF uses Router id to identify a router on network. OSPF 使用 Router ID 来标识网络上的路由器。 | IS-IS uses System ID to identify a router on the network. IS-IS 使用 System ID 来识别网络上的路由器。 |
| 12. | Flexibility 灵活性 | Less Flexible than IS-IS. 不如 IS-IS 灵活。 | More Flexible to use than OSPF especially in provider domain. 比 OSPF 更灵活,尤其是在提供商域中。 |
| 13. | Table Refresh 表刷新 | OSPF refreshes the entire routing table after 30 minutes. OSPF 会在 30 分钟后刷新整个路由表。 | IS-IS doesn’t refresh the entire SPF Table Periodically like OSPF. IS-IS 不会像 OSPF 那样定期刷新整个 SPF 表。 |
| 14. | Related Terms 相关术语 | Area, Non Backbone Area, Backbone Area, ABR, ASBR, Host. 区域、非主干区域、主干区域、ABR、ASBR、主机。 | IS, Level 1, Level 2, L1/L2, Subdomain, ES. IS、级别 1、级别 2、L1/L2、子域、ES。 |
ISIS 与 OSPF 之差异比较
beloved818414 2016-10-18 21:01:17
由于 cisco 的引导,IS-IS 在网络中开始得到规模的应用,但 OSPF 在全球范围的应用更多。
从根本上讲 ISIS 和 OSPF 从基本功能与操作上都是如此的相似,以至于很难说使用其中一个就比另一个好的或者更有效。
当然,这两个协议也有不同之处,其中包括细微差异和重大差异。本文主要就 ISIS 与 OSPF 的差异展开讨论,为大家学习 ISIS 提供一定的参考。
一、 ISIS 与 OSPF 差异比较说明
ISIS 与 OSPF 之间的细节差异众多,其主要差异见下表:
| ISIS | OSPF |
|---|---|
| ISIS 是支持 ISOCLNP 和 IP 双重路由 | 仅支持 IP 包 |
| ISIS 封装在链路层中 | 封装在 IP 包中 |
| ISIS 是 ISO3 个网络层协议之一 | 不是网络层协议,在 IP 上运行 |
| ISIS 可以忽略不支持的 TLV 类型 | 网络中所有 OSPF 路由器必须识别所有使用的扩展和 LSA 选项 |
| ISIS 可以承载多个 tlv 字段,只有一个包头节省带宽 | 所有 OSPFLSA 都有自己的包头,type1 和 2 的 LSA 可以有多个 ip 前缀,type3,4 和 5 的 LSA 仅可以承载单个 ip 前缀 |
| ISIS 仅支持广播和点到点类型 | OSPF 支持:点到点,广播,NBMA,点到多点,按需电路 |
| 最初数据库同步在邻接关系建立后进行 | 数据库同步在邻接建立以前进行 |
| ISIS 路由器只属于一个特定区域 | OSPF 路由器可以属于多个区域 |
| 在链路上划分边界 | 在路由器上划分边界 |
| 默认下 ISIS 是 stub 区域,层 2 不能向层 1 泄漏路由信息 | 默认不是 stub 区域 |
| DIS 无备份,DIS 可以被抢占 | DR 有备份,DR 不能被抢占 |
| ISIS 可以进行 PRC 计算 | OSPF 要进行完全 SPF 计算 |
| ISIS 仅在点到点链路上进行可靠扩散,在广播链路上是不可靠的 | OSPF 保证在所有链路上上扩散的可靠性 |
二、ISIS 与 OSPF 差异深入讨论
1.集成 ISIS 协议作为网络层协议直接运行在链路层上,ISIS 数据包在以太网中通过其协议类型 0xFEFE 被链路层承认。IP 类型是 0x0800。
在链路层上运行 ISIS 协议的好处是可以避免受到 ip 数据包欺骗与 DoS 攻击,不利之处在于不能在 ATM 上运行。
OSPF 在 ip 上运行,协议号为 89,在 IP 中封装意味着 OSPF 报文会遭到 IP 包欺骗与拒绝服务攻击。
2.ISIS 大量使用可变长报文来通告路由选择信息。所有的 ISIS 报文均使用了 tlv 字段,从而每类 ISIS 报文都可以扩展。并且 ISIS 路由器可以忽略自身不支持的 tlv 类型。OSPF 报文报文格式不可以扩展。OSPF 使用各种不同类型的 LSA 来通告信息。LSA 是可扩展的。和 ISIS 不同的是,那些没有得到接收认可的 LSA 类型不会扩散到邻接路由器。
3.为了建立邻接,OSPF 和 ISIS 都需要通知路由器获取匹配的最大传输单元的大小。ISIS 协议在 hello 报文中填充 mtu 大小,而 OSPF 则在数据库描述报文中通告接口 mtu。ISIS 可以手工禁止 mtu 的填充报文。
4.在 ISIS 和 OSPF 中都是通过周期性地传送和接收 hello 报文来实现的,ISIS 的 hello 报文被通告到第二层广播地址上,比如以太网广播地址是 0180.c200.0014 和 0180.c200.0015。OSPF 被广播到 224.0.0.5 和 DR224.0.0.6。
5.ISIS 和 OSPF 在邻接关系建立上存在重大的差异,ISIS 协议在通过交换 hello 报文建立双方通信后建立邻接关系,在建立邻接后就会同步双方的 lsdb,由于邻接关系建立先于数据库同步从而可能引起的瞬时路由选择问题可以通过使用 ISIS 超载位来解决。
OSPF 采用了一个复杂的进程,该进程要求路由器在建立邻接之前同步他们的 lsdb,这样就可以避免那些当相邻的还不具备完全转发能力的路由器吸收了中转流量时可能会发生的瞬时路由选择问题。
6.ISIS 和 OSPF 都有指定路由器的概念,用来限制在广播链路中,路由器之间交换的链路状态信息的数量。ISIS 只要求选举一台 DIS,不需要备份,而且允许抢占,DIS 通告 hello 报文的速度比其他路由器要快,缺省时其他节点的 3 倍。OSPF 选举一台 DR 和 BDR,DR 不能被抢占。
7.扩散是链路状态协议用来在网络中分发链路状态信息的一种手段,通过扩散来共享链路状态信息使得所有路由器都拥有一致的网络拓扑信息,从而可以计算通往网络中目标地址的无环路由。ISIS 只有在点到点链路才能保证可靠扩散,在广播链路中可以通过 dis 来实现路由信息的同步。
OSPF 在点到点链路和广播链路中都能实现可靠的扩散。
8.ISIS 报文中的剩余生存时间使一个从 1200 秒开始倒数的定时器。
OSPF 则使用了一种正向技术的计数器,用来表示 lsa 被产生以来所经过的时间。
ISIS 允许设置最大生存时间为 18.7 小时
OSPF 生存时间使一个固定值为 1 小时
为了将一个过期的 lsp 清除,ISIS 路由器可以把该 lsp 的剩余时间设置为 0 并广播到网络中。
ISIS 允许任何路由器都可以从网络中清除被破坏的 lsp。
OSPF 只允许路由器提早清除那些自己产生的未过期 LSA,这样可以避免 ISIS 的 LSP 破坏风暴。
ISIS 和 OSPF 都会周期刷新再 LSP 来刷新现存的 LSP,即使没有过期。
ISIS 每 15 分钟刷一次,OSPF 是每 30 分钟刷新一次,具有禁止老化的 LSA 在 LSDB 中不会老化,所以不需要每 30 分钟刷新一次,然而如果这样的 LSA 在保持了 60 分钟后而且在这段时间内其源路由器也不能连通,那么将被清除。
9.ISIS 路由携带了度量信息,cisco 只支持缺省度量。
ISIS 默认为窄度量,使用 6bit,最大度量为 63,并且路径度量最大不能超过 1023。宽度量支持更大更灵活的度量值,在扩展 ip tlv(135)宽度量占 32bit。
ISIS 接口默认度量为 10,ISIS 度量可以通过设置 I/E 字段表示是内部度量还是外部度量,如果该字段被设置(即外部度量)那么度量的通告值要加 64(有些 IOS 要加 128)。
OSPF 同样使用与带宽成反比的度量。OSPF 接口 cost 取值范围为 0-1024,一个网络的 metric 达到 65535 认为不可达。
10.ISIS 和 OSPF 都是用 spf 计算路由,所以他们的收敛时间大致相同,实际上每个方面都差不多,但是,由于 ISIS 采用 prc 计算,ip 前缀作为最短路径树的叶子节点,这就为 ISIS 协议在网络事件只影响到 ip 前缀而没有涉及基本的拓扑结构的情况下运行只需消耗少量 CPU 资源的部分路由计算提供了更多的机会。
OSPF 是围绕链路而建立的,所以在某个区域内任何 IP 前缀变化都会引发整个 SPF 算法的运行。
11.一个 IGP 能够支持多大的区域是许多人都感兴趣的问题。ISIS 在 1000 台路由器的域中没有出过重大问题,目前世界顶级的 ISP 运行在 ISIS 的单个域中都超过 500 台,OSPF 也可以配置到 350 台,不过数据不是绝对的。
IS-IS 与 OSPF 生存时间相关机制及影响(对比)
| 对比项目 | IS-IS | OSPF |
|---|---|---|
| 最大生存时间相关 | 定义:每个 LSP 在被从链路状态数据库中删除前可以保留的最长时间。 标准值:ISO 10589 中定义为 1200s(20 分钟)。 操作流程:路由器生成 LSP 时,将剩余时间设置为最大生存时间,然后泛洪到邻接路由器并在本区域扩散,剩余时间随时间推移减少。 | 定义:无明确类似单独概念表述,但 LSA 老化时间(age-time)相关。 标准值:无对应准确值,LSA 老化时间默认情况下为 3600s(可理解为类似某种最大有效时间概念)。 操作流程:无类似从生成就设置最大生存时间并随时间减少剩余时间的操作,LSA 在链路状态数据库中随着时间增加而累积老化时间,一旦超过默认的 3600s,就会被从链路状态数据库中清除。 |
| 刷新间隔定时器相关 | 作用:当路由器生成一个 LSP 后启动,到期后路由器重新生成(刷新)LSP 并泛洪到本区域内所有路由器。 标准值:ISO 10589 中定义为 900s(15 分钟)。 与剩余时间关系:每当路由器重新生成新的 LSP 后,将 LSP 的剩余时间重置为最大生存时间。若某条 LSP 剩余时间达到 0 时还未收到生成该 LSP 的路由器的刷新 LSP,此 LSP 将被清除。 | 触发条件:当 LSA 中的链路状态信息发生变化(如链路开销改变、链路状态改变等)或者达到一定的刷新周期时,路由器会重新生成并泛洪新的 LSA(可理解有类似刷新概念但触发条件表述不同)。 与老化时间关系:新的 LSA 会重新开始计算老化时间(与 IS-IS 中 LSP 剩余时间和刷新的关系有差异)。 |
| 影响 | 更大的 LSP 生存时间意味着路由器在链路状态数据库中将保留 LSP 更长时间,但可能导致陈旧路由选择信息保留时间过长。 刷新间隔过长,会增加其他路由器保留陈旧路由信息的时间,但可减少网络资源开销;刷新间隔过短,会增大网络资源利用率和路由器系统资源开销。 | 如果老化时间过长,可能会导致网络收敛缓慢,因为过时的链路状态信息可能会在数据库中停留较长时间,影响路由决策。 频繁刷新 LSA 会增加网络带宽消耗和路由器的处理负担;刷新间隔过长可能导致网络中不同路由器的链路状态数据库不一致,影响路由计算的准确性。 |
| 调整原则 | 调整 LSP 的最大生存时间时,要根据实际情况相应调整 LSP 刷新间隔。 要保证 LSP 最大生存时间大于 LSP 刷新间隔,以便路由器在清除 LSP 前有足够时间接收其他路由器重新生成的 LSP。 | 在调整 LSA 老化时间和刷新间隔时,需要考虑网络的稳定性、收敛速度和资源消耗。 一般情况下,尽量使用默认值,除非网络环境有特殊要求。同时,调整老化时间和刷新间隔时,也要确保两者的平衡,避免出现信息更新不及时或网络资源过度消耗的情况。 |
LSA and LSP
vishalpatil86
06-16-2013 11:05 PM - edited 03-07-2019 01:55 PM
Dear all,
is there any difference between LSA and LSP in OSPF or these are the terms used interchangeably?
OSPF 中的 LSA 和 LSP 之间是否有任何区别,或者这些术语可以互换使用?
Regards,
Vishal
InayathUlla Sharieff
06-16-2013 11:48 PM
Vishal,
Easy way of saying is;
简单的说法是;
Lsa come under ospf and lsp’s come under Is-Is link state pdu’s.
Lsa 属于 ospf,lsp 属于 Is-Is 链路状态 pdu。
link-state advertisement 链路状态通告
(LSA) is a basic communication means of the OSPF routing protocol for the Internet Protocol (IP). It communicates the router’s local routing topology to all other local routers in the same OSPF area. OSPF is designed for scalability, so some LSAs are not flooded out on all interfaces, but only on those that belong to the appropriate area. In this way detailed information can be kept localized, while summary information is flooded to the rest of the network
(LSA) 是 Internet 协议 (IP) 的 OSPF 路由协议的基本通信方式。它将路由器的本地路由拓扑传达给同一 OSPF 区域中的所有其他本地路由器。OSPF 专为可扩展性而设计,因此某些 LSA 不会在所有接口上泛洪,而只会在属于相应区域的接口上泛洪。通过这种方式,详细信息可以保持本地化,而摘要信息则被泛洪到网络的其余部分
Link State Packet 链路状态数据包
(LSP) is a packet of information generated by a network router in a link state routing protocol that lists the router’s neighbors. Link state packet can also be further defined as special datagrams that determine the names of and the cost or distance to any neighboring routers and associated networks. They are used to efficiently determine what the new neighbor is, if a link failure occurs, and the cost of changing a link if the need arises. LSPs are queued for transmission, and must time out at about the same time. They must be acknowledged, and can be distributed throughout the network, but cannot use the routing database.
( LSP )是网络路由器在链路状态路由协议中生成的信息包,其中列出了路由器的邻居。链路状态数据包也可以进一步定义为特殊数据报,用于确定任何相邻路由器和相关网络的名称以及到任何相邻路由器和关联网络的成本或距离。它们用于有效地确定新邻居是什么、是否发生链路故障以及在需要时更改链路的成本。LSP 排队等待传输,并且必须大约在同一时间超时。它们必须得到确认,并且可以在整个网络中分发,但不能使用 routing 数据库。
LSA’s are encapsulated behind an OPSF packet and then an ip packet,
LSA 封装在 OPSF 数据包后面,然后是 ip 数据包。
whereas an LSP is a packet itself.
而 LSP 本身就是一个数据包。
I guess that’s the most significant difference between these too.
我想这是它们之间的最显著的区别。
OSPF vs. ISIS
ylmva1 March 19, 2020
Long ago, when I didn’t know much about ISIS, and I mostly worked with customers running OSPF, I used to think of ISIS as a strange routing protocol, that nobody really cared much about. But I was sooo wrong!
很久以前,当我对 ISIS 知之甚少,主要与运行 OSPF 的客户合作时,我曾经认为 ISIS 是一种奇怪的路由协议,没有人真正关心它。但我大错特错了!
I started studying ISIS in depth as I progressed in the service provider certification tracks, and obviously when I got to the E-level I had to know ISIS very well. Then, I had the chance to work for a major Service Provider in the US, and discovered that not many people actually knew much about OSPF, but were well versed in ISIS.
随着我在服务提供商认证轨道上的进步,我开始深入研究 ISIS,显然,当我达到 E 级时,我必须非常了解 ISIS。然后,我有机会在美国的一家大型服务提供商工作,发现实际上并不多人对 OSPF 了解很多,但精通 ISIS。
The more I learned about it, and the more I worked with it supporting my customer, the more I liked it. I came to realize that ISIS is actually a pretty awesome routing protocol. And I would like people to understand it better, and embrace it. I am sure that anyone who’s being in the Service Provider world, is already on board.
我对它了解得越多,我使用它支持客户的次数越多,我就越喜欢它。我开始意识到 ISIS 实际上是一个非常棒的路由协议。我希望人们能更好地理解它,并接受它。我敢肯定,任何在服务提供商领域工作的人都已经参与其中。
Students have always asked me: “If I am familiar with OSPF, would that help me understand ISIS? Do the concepts in OSPF, apply to ISIS? or are they way different?”
学生们总是问我:“如果我熟悉 OSPF,那会帮助我了解 ISIS 吗?OSPF 中的概念是否适用于 ISIS?还是他们大不相同?
I guess I will answer those questions with YES! YES! and YES!
我想我会用 YES 来回答这些问题!是的!是的!
In some ways, the two protocols are very similar, and the concepts you already know in OSPF apply very closely, but at the same time, they are very different.
在某些方面,这两种协议非常相似,您在 OSPF 中已经了解的概念非常适用,但同时,它们也非常不同。
So, let me try to summarize the similarities and differences for you:
那么,让我试着为你总结一下异同:
SIMILARITIES: 相似之处:
Both routing protocols are IGP (Internal Gateway Protocols) and Link State Protocols, which means they both advertise link information and build a Link State Database. The exchange of information is reliable, and the routers will make sure that the databases are synchronized.
两种路由协议都是 IGP(内部网关协议)和链路状态协议,这意味着它们都通告链路信息并构建链路状态数据库。信息交换是可靠的,路由器将确保数据库同步。
They both run the SPF (Shortest Path First) algorithm to calculate the best path to each destination network, and to make that determination they add the metrics of the different links.
它们都运行 SPF(最短路径优先)算法来计算到每个目标网络的最佳路径,并做出该决定,并添加不同链路的度量。
Also, before routers can exchange actual link information they form an adjacency, or formal neighbor relationship, which is built using hello packets. Both OSPF, and ISIS use hello packets for discovering neighbors and maintaining the relationship with those neighbors.
此外,在路由器可以交换实际链路信息之前,它们会形成邻接关系或正式邻居关系,这是使用你好数据包构建的。OSPF 和 ISIS 都使用你好数据包来发现邻居并维护与这些邻居的关系。
Also, when you implement OSPF or ISIS, you do so following a 2-level hierarchical model (backbone/non-backbone areas in OSPF, and LEVEL 1/LEVEL 2 in ISIS)
此外,在实施 OSPF 或 ISIS 时,应遵循 2 级分层模型(OSPF 中的主干/非主干区域,以及 ISIS 中的级别 1/级别 2)
They also have many common features and options, just implemented in different ways.
它们也有许多常见的功能和选项,只是以不同的方式实现。
To summarize, both protocols: 总而言之,这两种协议都:
-
Are IGP Link State routing protocols and build a Link State Database
是 IGP 链路状态路由协议并构建链路状态数据库
-
Have reliable updates
拥有可靠的更新
-
Run SPF to calculate best routes.
-
运行 SPF 以计算最佳路由。
-
Use hello packets to create adjacencies
-
使用你好数据包创建邻接关系
-
Have a two level hierarchical model
具有两级分层模型
-
Support authentication and route summarization
支持身份验证和路由汇总
-
Use multicast addresses
使用多播地址
-
Elect a designated device on multiaccess networks.
在多路访问网络上选择指定的设备。
-
Can differentiate internal and external routes and tag routes
可以区分内部和外部路由和标记路由
-
Support features like graceful restart, GRES/NSR, Traffic Engineering, IPv6, and so on.
-
支持正常重启、GRES/NSR、流量工程、IPv6 等功能。
Thus, yes, there are a lot of similarities! But, as I said: they are also very different. Let’s take a look at that now:
因此,是的,有很多相似之处!但是,正如我所说:它们也非常不同。现在让我们来看看它:
DIFFERENCES:
| OSPF | ISIS |
|---|---|
| ROUTER TYPES: * Internal router: A router with all its interfaces within the same area * Backbone router: A router with at least one interface connected to the backbone area. * Internal Backbone router: A router that with all its interface within the backbone area. * Internal Non-backbone router: A router with all its interfaces within an area other than the backbone * ABR (Area Border Router): A router connected to more than one area (commonly one of those areas is the backbone area) * ASBR (Autonomous System Boundary Router): Any router injecting routes into the OSPF domain via redistribution. | ROUTER TYPES: * L1 router: A routers that can only form adjacencies with other routers in the same area. Similar to an internal router. * L2 router: A router that can form adjacencies with routers in the same area & with router in other areas. Similar in concept to a internal backbone router. * L1/L2 router: A routers that can form adjacencies with L1 routers and also with L2 routes. Similar in concept to an ABR. NOTE: refer to the adjacency formation section for more details. |
| INTERFACE TYPES: * p2p * broadcast (LAN) – default for ethernet * NBMA * p2mp | INTERFACE TYPES: * p2p * broadcast (LAN) – default for ethernet |
| BROADCAST NETWORK: | BROADCAST NETWORK: |
| * A Designated (DR) and a Backup Designated Router (BDR) are elected | * A Designated Intermediate System (DIS) is elected. |
| * Routers establish adjacencies (Full State) only with the DR & BDR in the broadcast network * DR and BDR have adjacencies with all routers in the network | * Routers establish adjacencies with ALL other routers in the broadcast network. |
| * There is a BDR | * There is NO Backup (DIS) |
| * There is a DR/BDR per segment | * DIS per level, per segment |
| * Default priority for DR election = 128 (range 1-255) * Router with highest priority is elected. * If priority is the same, then router with highest router-id is elected * Priority of 0 means ineligible | * Default priority for DR election = 64 (range 0-127). * Router with highest priority is elected. * If priority is the same, then router with highest MAC address is elected. * Priority of 0 does NOT mean ineligible |
| * There is no preemption for the DR | * There is preemption for the DIS |
| PROTOCOLS SUPPORT: * V2 only supports IPv4. * V3 supports IPv4 and IPv6 | PROTOCOLS SUPPORT: * IPv4, IPv6 & CNLS |
| ADJACENCY FORMATION REQUIREMENTS/RULES: * Same Area ID * Same timers (hello and dead intervals) * Same Area type (options bits) * Authentication type, and key * Unique RID * Matching MTU * Matching IP subnet and subnet mask | ADJACENCY FORMATION REQUIREMENTS/RULES: * For LEVEL 1 adjacencies: routers must be in the same area * For LEVEL 2 adjacencies: routers can be in the same area or in different areas. * By default, a Juniper router is configured as an L1/L2 router. => By default, between two Juniper router running ISIS, two adjacencies will be formed (L1 and L2) * Minimum MTU of 1492 is required * NET configured under lo0.0 must be configured 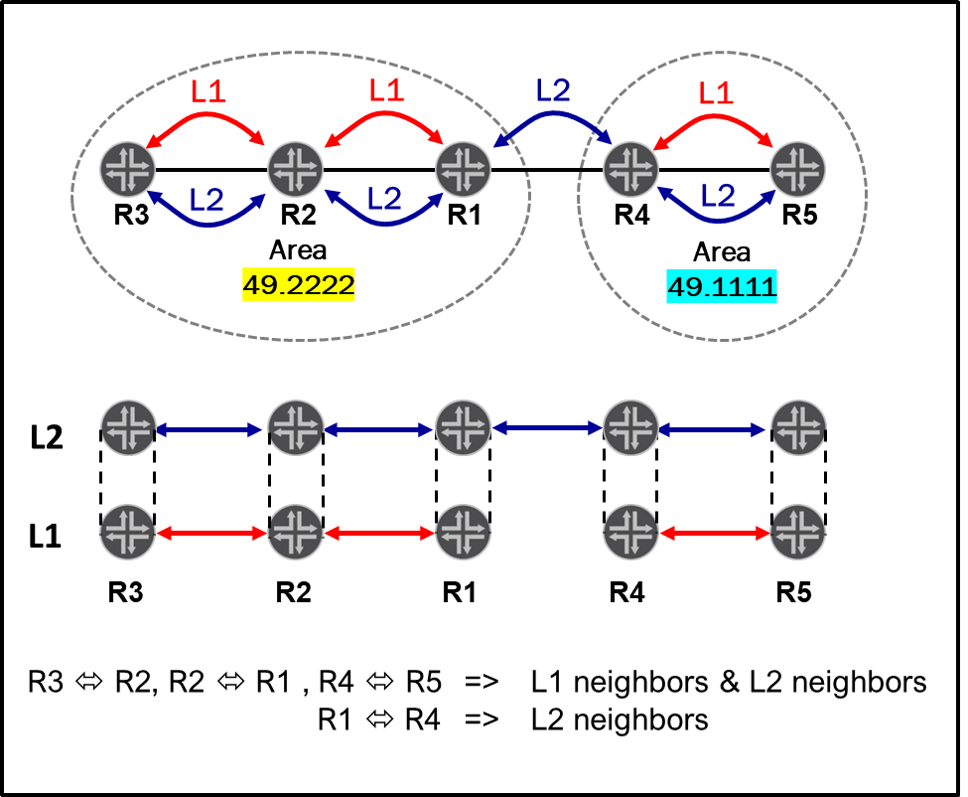 In the example, all routers are L1/L2 but an L1 adjacency between R1 and R4 cannot form because they are in different areas. In the example, all routers are L1/L2 but an L1 adjacency between R1 and R4 cannot form because they are in different areas. |
| AREAS: | AREAS: |
| * Area assignment: – An internal router has all interfaces within an area. – An ABR has interfaces in the backbone area, and interfaces on one or more non-backbone areas. – Boundary between areas is on the ABR. 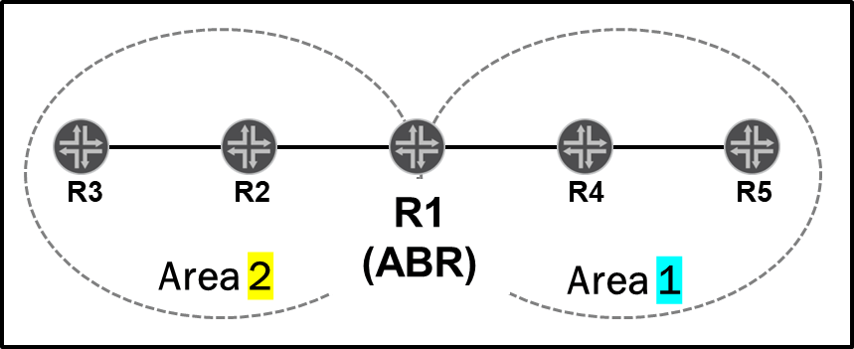 | * Area assignment: – A router is completely within an area. – All interfaces in the same area (always). – Boundary between areas is on the links. 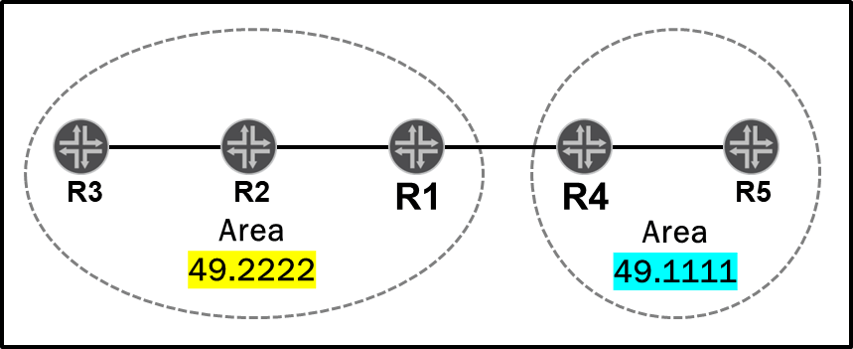 |
| * Area ID: – Associated with the interfaces – An interface belongs to only one are (a secondary area is possible with multiarea adjacencies)  | * Area ID: – Associated with the router not the interfaces – A router can belong to multiple areas  |
| * Inter-area information: – ABRs advertise inter-area routing information to internal routers using LSAs type 3 – If an area is configured as a stubby no-summary (totally stubby area), these LSAs are replaced with a default route, if configured NOTE: refer to the DEFAULT ROUTE section. – Policies can be applied to control which LSA3 are created by the ABR. | * Inter-level information: – L1/L2 routers do NOT advertise L2 routes to L1 routers by default (Behavior is equivalent to NSSA no summaries). > A policy can be configured to leak routes from LEVEL 2 into LEVEL 1 – L1/L2 routers advertise internal L1 routes to L2 neighbors by default. – L1/L2 routers do NOT advertise external L1 routes to L2 neighbors by default. > A policy can be configured to stop routes from LEVEL 1 into LEVEL 2 or to leak external routes. NOTE: with wide-metrics-only there is no difference between internal and external routes.  |
| *** Area Types:** – Regular Area: LSAs type 1, 2,3,4, & 5 – Stub Area: LSAs type 1, 2, & 3 – Stub Area no-summary (totally stubby area): LSAs type 1, 2, & 3 (only 0/0) – Not So Stubby Area (NSSA): LSAs type 1, 2, 3, & 7 – NSSA no-summary: LSAs type 1, 2, 7, & 3 (only 0/0). 0/0 can be changed to 7. | N/A |
| HIERARCHICAL DESIGN: | HIERARCHICAL DESIGN: |
| * Area 0 required * Backbone – > Non Backbone area * Boundary = ABR 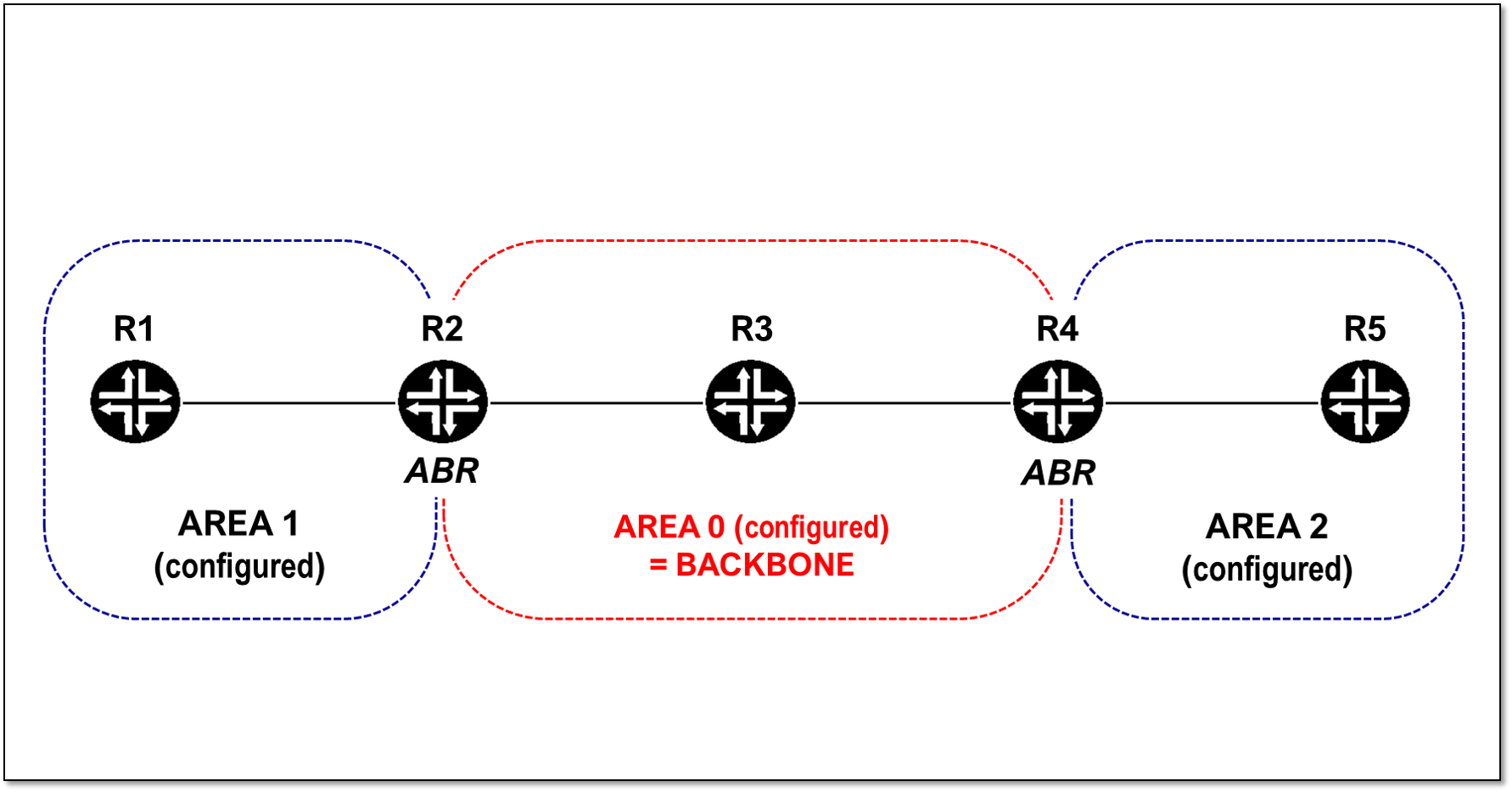 | * Area 0 NOT required * LEVEL 2 -> LEVEL 1 * There is no backbone or area 0 configured * Boundary = L1/L2 router. 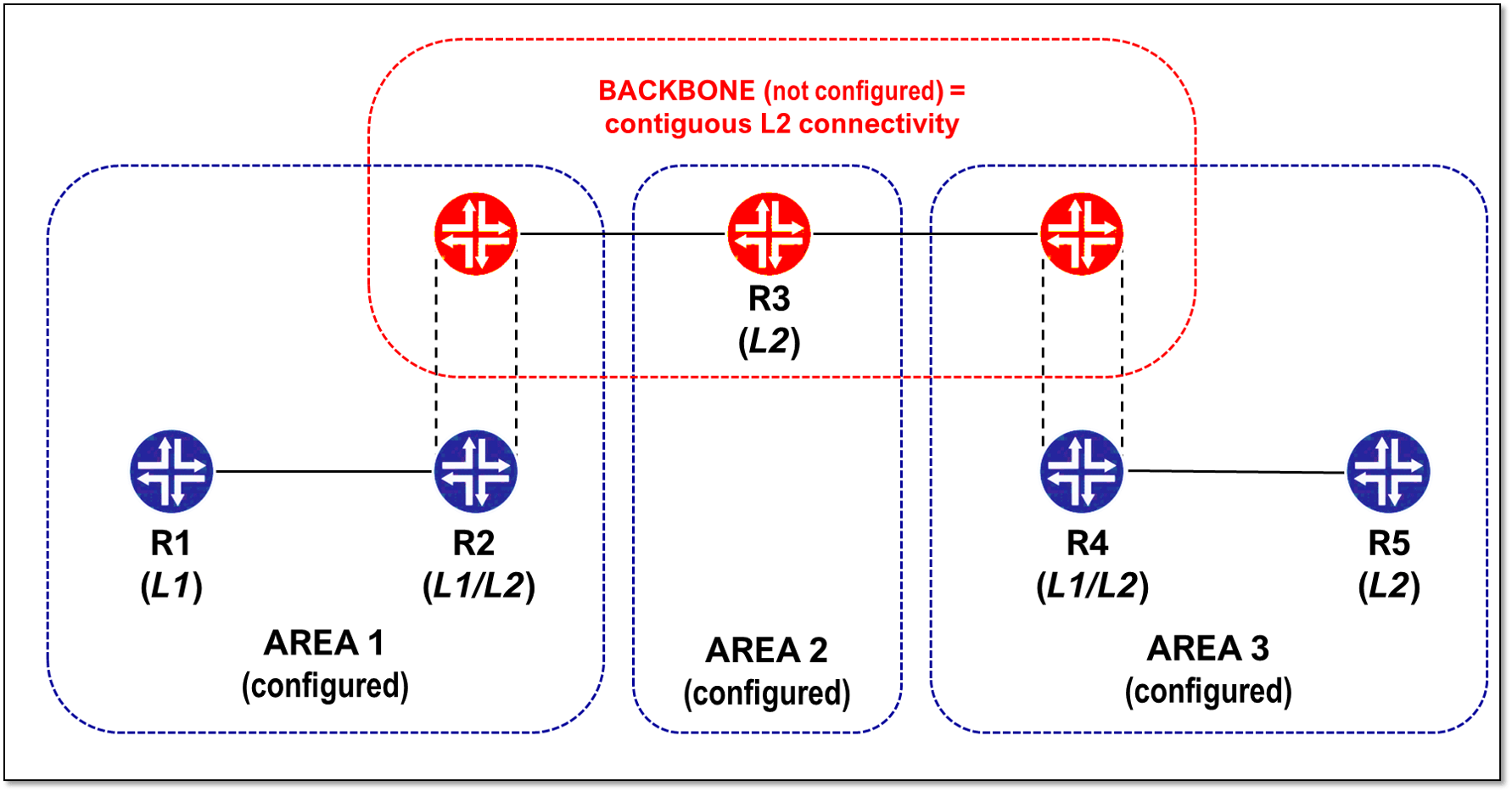 |
| TIMERS: | TIMERS: |
| * Hello interval: – 10 sec (broadcast and p2p) – 30 sec (NBMA) Configurable | * Hello interval: – 3 seconds (for DIS routers) – 9 seconds (for non-DIS routers) Configurable |
| * Dead interval (3 x hello interval): – 40 sec (broadcast and p2p) – 120 sec (NBMA) Configurable | * Hold time (3 x hello interval): – 9 seconds (for DIS routers) – 27 seconds (for non-DIS routers) Configurable |
| * Age starts at 0 and increments up to maxage. | * Age is set to max. age and gets decremented up to 0 |
| * Maximum Age = 3600 sec (60 min) Configurable | * LSP Lifetime = 1200 sec (20 min) Configurable |
| * Default LSA Refresh Interval = 3000 sec (50 min) Configurable | * Default LSP Refresh Interval= 883 sec (lifetime minus 317) |
| N/A | *** CSNP Interval:** – on broadcast interfaces = 10 sec – on point-to-point interface = 5 sec |
| ROUTE PREFERENCES: * Internal = 10 * External = 150 Configurable | ROUTE PREFERENCES: * Level 1 internal = 15 * Level 2 internal = 18 * Level 1 external = 160 * Level 2 external = 165 Configurable |
| OVERLOAD: indicated with metric = 65535 | OVERLOAD: Indicated with overload bit |
| METRICS: * Not specified by standard * Referred as cost. * Most vendors use cost = 10^8/Bandwidth (by default), where 10^8 is the reference bandwidth. * Default metric for lo0 interface = 0 * You can configure the metric of the interface, the reference bandwidth, or the bandwidth of the interface. | METRICS: * Specified by standard ISO 10589 * 4 types of metrics defined: –Default: Mandatory. Default for ALL interfaces = 10 (configurable value) – Delay: not used – Expense: not used – Error: not used * You can also configure the metric to be calculated automatically as 10^8/Bandwidth * Metrics can be configured on a per level basis. |
| * Maximum metric = 65,535 | * Maximum Total Metric on a path = 1023 * Maximum metric on an interface = 63 Limit technically removed with wide-metric-only (~16 million maximum value) |
| DESTINATION ADDRESS/PROTOCOL: * Encapsulated within IP PACKETS using: – Protocol = 89 – Multicast DA = 224.0.0.6 (DR/BDRs) – Multicast DA = 224.0.0.5 (All OSPF routers) | DESTINATION ADDRESS/PROTOCOL: * Encapsulated within Layer 2 frames using: – DSAP/SSAP= 0xFE – Multicast DA = 0180.c200.0014 (LEVEL 1) – Multicast DA = 0180.c200.0015 (LEVEL 2) * Requires GRE encapsulation to run on connections such as IPSEC tunnels. |
| DEFAULT ROUTE: * When configured, an ABR can inject a default route into a stub area or a NSSA, – For Stub Area => LSA type 3 – For NSSA => LSA type 7 – For NSSA no-summary => LSA type 3 | DEFAULT ROUTE: * An L1 router installs a default route in its routing table when it receives an update from an L1/L2 router with the attached bit set. * Can be disabled with the ignored-attached-bit command |
| ROUTER ID: * primary address of lo0.0 interface OR * router-id configured under routing-options. | ROUTER ID: * iso address (NET) of lo0.0 interface 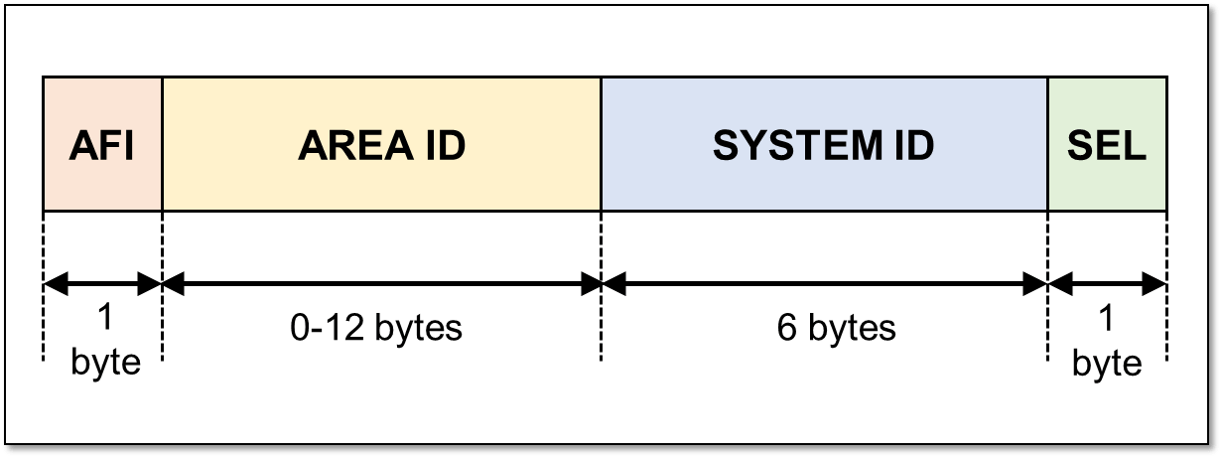 |
| TRAFFIC ENGINEERING: * Supported, but needs to be configured. * Use LSA Type 10. | TRAFFIC ENGINEERING: * Supported by default. * Use TE Sub-TLV within the Extended IS Reachability (TLV 22) and the Extended IP Reachability (TLV 135) |
| ROUTING POLICIES: | ROUTING POLICIES: |
| *** Default Export Policy:** – ALL routes are rejected = NO redistribution by default – An export policy would enable redistribution and create LSAs type 5/7 – LSAs are still created for interfaces running OSPF, and sent out (cannot modified by policies). – Writing and applying a policy that rejects everything:  does NOT stop the advertisement of interfaces running OSPF | *** Default Export Policy:** - ALL routes (except direct routes for interfaces running ISIS) are rejected = NO redistribution by default – LSPs are created for interfaces running ISIS, and sent out (can be affected by policy). – An export policy can control which prefixes are actually advertised (even for interfaces running ISIS), configures redistribution and creates external routes – w/ narrow metrics) – Writing and applying a policy that rejects everything:  stops the advertisement of interfaces running OSPF |
| *** Default import policy:** – All routes from SPF calculations are accepted and imported into the routing table. – LSAs sent by neighbors are accepted and placed in the LSDB, and SPF calculates routes (not affected by policies). – Import policies can be configured, but only for external routes. | *** Default import policy:** – All routes from SPF calculations are accepted and imported into the routing table. – LSPs sent by neighbors are accepted and placed in the LSDB, and SPF calculates routes, routes. (not affected by policies). – Import policies could NOT be configured for ISIS until Junos 17.1 |
| AUTHENTICATION: * Simple test OR MD5 OR IPSEC * Per area OR per interface (all router in an area must have same authentication configured) * Applies to ALL packets | AUTHENTICATION: * Simple test OR MD5 * Per level or per interface: – Per level applies LSPs, CNPs and Hello messages (can be disable for a specific type of packet) – Per interface applies only for hello messages |
| ROUTE AGGREGATION: * area-range under the area configuration level  Summarizes the prefixes injected into other areas by the ABR (LSAs type 3). ABR learns about these prefixes from LSAs type 1 and type 2. * area-range under the nssa area configuration level  Summarizes the prefixes injected into an area, by the ABR, when translating from LSAs type 7 into LSAs type 5. * NO other LSAs can be summarized! * ONLY the ABR can summarize! * Specific prefixes within the range automatically suppressed. * The restrict option can be used with the area range to stop any updates for prefixes within the range. | ROUTE AGGREGATION: * NO specific command for route summarization. * To summarize prefixes 1) Create an aggregate and redistribute with policy 2) Redistribute the aggregate into ISIS using a policy:  |
| ROUTING INFORMATION: | ROUTING INFORMATION: |
| * Packet Types: – Type 1 = Hello – Type 2 = Database Description – Type 3 = Link State Request – Type 4 = Link State Update – Type 5 = Link State Acknowledge | * Packet Types (PDU: Packet Data Units): – Hello broadcast network: For L1 and L2 – Hello point-to-point network – LSPs (Link State Packets): Like OSPF LSAs For L1 and L2 Include reachability TLVs. – PSNP (Partial Sequence Number PDU): Like OSPF Request/Update/Ack – CSNP (Complete Seq. Number PDU): Like OSPF DBD Only sent by DIS on broadcast net. Periodic For L1 and L2 |
| * LSA Types: – Type 1 = Router LSA (all routers) – Type 2 = Network LSA (DR) – Type 3 = Network Summary LSA (ABR) – Type 4 = ASBR Summary LSA (ABR) – Type 5 = External LSA (ASBR) – Type 7 = NSSA LSA (ASBR NSSA) | *** LSP Types:** – Level 1 – Level 2 |
| * Database on boundary router: An ABR has links state databases for all the areas it is connected to. | * Database on boundary router: A L1/L2 router has a database for L1 and a database for L2. |
| * SPF calculation on a per area basis | * SPF calculations on a per level basis |
via:
-
OSPF VS ISIS - huawei
https://forum.huawei.com/enterprise/en/ospf-vs-isis/thread/667230417431969792-667213852955258880 -
OSPF vs ISIS: Detailed Comparison
https://ipwithease.com/ospf-vs-isis/ -
OSPF Vs ISIS
https://www.networkurge.com/2019/12/ospf-isis-brief-comparison.html -
IS-IS versus OSPF
https://ipcisco.com/lesson/is-is-versus-ospf/ -
Difference between OSPF and IS-IS - GeeksforGeeks
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/difference-between-ospf-and-is-is/ -
OSPF vs. ISIS – Mom, Network Engineer, Juniper Ambassador
https://momcanfixanything.com/ospf-vs-isis/ -
LSA and LSP - Cisco Community
https://community.cisco.com/t5/switching/lsa-and-lsp/td-p/2225006 -
LSA/LSP Flooding in OSPF and IS-IS « ipSpace.net blog
https://blog.ipspace.net/2021/09/ospf-is-is-flooding/ -
ISIS vs OSPF - huaei
https://forum.huawei.com/enterprise/en/isis-vs-ospf/thread/667224320662978560-667213852955258880 -
OSPF 与 ISIS 路由优选问题??
https://forum.huawei.com/enterprise/zh/thread/blog/658657167521234944 -
ISIS 与 OSPF 双向充分发
https://forum.huawei.com/enterprise/zh/thread/blog/580905928302149632 -
ISIS 与 OSPF 之差异比较 beloved818414 2016-10-18 21:01:17
https://forum.huawei.com/enterprise/zh/thread/blog/580906996658487296 -
OSPF 与 IS-IS – Routing Freak!
https://routingfreak.wordpress.com/category/ospf-vs-is-is/ -
IS-IS Packet Types ⋆ | IHH | LSP | PSNP | CSNP | IPCisco.com
https://ipcisco.com/lesson/is-is-packet-types/
























 6231
6231

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








