优先队列式分支限界法
基本思想:为了加速搜索的进程,应采用有效地方式选择活结点进行扩展。按照优先队列中规定的优先级选取优先级最高的结点成为当前扩展结点。
搜索策略:对每一活结点计算一个优先级(某些信息的函数值),并根据这些优先级;从当前活结点表中优先选择一个优先级最高(最有利)的结点作为扩展结点,使搜索朝着解空间树上有最优解的分支推进,以便尽快地找出一个最优解。再从活结点表中下一个优先级别最高的结点为当前扩展结点,……,直到找到一个解或活结点队列为空为止。
--转自http://blog.csdn.net/liufeng_king/article/details/8900872
这种搜索策略生成的仅仅是解空间树(理论),即包含着问题解的树。并不等同实际搜索过程中生成的解空间树,因为在实际中,会在理论上的解空间树上进行剪枝,得出最简的解空间树。
例如:
问题描述
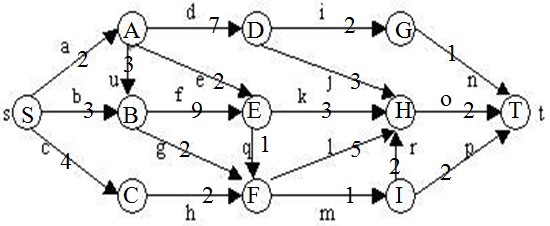
在下图所给的有向图G中,每一边都有一个非负边权。要求图G的从源顶点s到目标顶点t之间的最短路径。
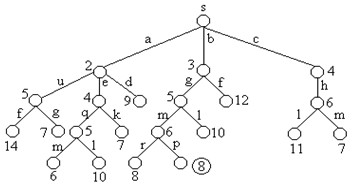
下图是用优先队列式分支限界法解有向图G的单源最短路径问题产生的解空间树。其中,每一个结点旁边的数字表示该结点所对应的当前路长。
--转自http://blog.csdn.net/liufeng_king/article/details/8900872
但是实际运行中,得出最终解的问题解空间树如下:
由此得到的解空间树一定是最简的,因为存在剪枝函数,所以不会重复的搜索解空间。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include "MinHeap.h"
#define INF 10000
template<class Type>
class Graph
{
private:
int n, //the number of Graph's node
*prev; //array of previous node
Type **c, // adjcent matrix of Graph G
*dist; //array of shortest distance
public:
Graph(const int m);
void setAdjMartix(int **cAdj); //interface
void ShortestPath(const int v);
~Graph();
friend void main(); //可以通过Graph类的实例访问其私有和保护成员和方法
};
template<class Type>
class MinHeapNode
{
private:
int i; //the number code of node
Type length; //current length of road
public:
int operator<=(MinHeapNode a)
{
return (length <= a.length);
}
int operator < (MinHeapNode a)
{
return (length<a.length);
}
int operator >(MinHeapNode a)
{
return (length > a.length);
}
int operator >=(MinHeapNode a)
{
return (length >= a.length);
}
friend class Graph<Type>;
};
template<class Type>
Graph<Type>::Graph(const int m)
{
n = m; //the number of Graph's node
dist = new int[m + 1]; //array of shortest distance
prev = new int[m + 1]; //array of previous node
}
template<class Type>
Graph<Type>::~Graph()
{
delete[] dist;
delete[] prev;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
{
delete[] c[i]; //delete everything the Array's pointer has pointed
}
delete[] c; //delete the pointer arrays
}
template<class Type>
void Graph<Type>::setAdjMartix(int **cAdj)
{
c = cAdj;
}
template<class Type>
void Graph<Type>::ShortestPath(const int v)
{
//定义堆的最小容量为1000
MinHeap<MinHeapNode<Type> > H(1000); //主要问题是“>> ”不要写在一起
//定义源为扩展节点
MinHeapNode<Type> E;
for (int k = 1; k <= n; k++){
dist[k] = INF;
prev[k] = -1;
}
//初始化源点
E.i = v;
E.length = 0;
dist[v] = 0;
//搜索问题的解空间
while (true)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
if ((c[E.i][j]<INF) && (E.length + c[E.i][j]<dist[j]))
{
//顶点i到顶点j可达,且满足控制约束
dist[j] = E.length + c[E.i][j];
prev[j] = E.i;
//加入活结点优先队列
MinHeapNode<Type> N;
N.i = j;
N.length = dist[j];
H.Insert(N);
}
try
{
E = H.RemoveMin();
}
catch (int)
{
break;
}
}
}
int** CreatGraph_AdjMatrix(int &n)
{
int i, j, k, e;
int weight;
int **c;
printf("please input graph's vexnum and arcnum:\n");
cin >> n >> e;
c = new int *[n + 1];
for (i = 0; i <= n; i++)
c[i] = new int[n+1];
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++)
c[i][j] = INF;
for (k = 1; k <= e; k++)
{
printf("please input NO.%d edge's start,end and weight:\n", k);
cin >> i >> j >> weight;
c[i][j] = weight;
}
return c;
}
void main()
{
int **c=NULL, n;
c=CreatGraph_AdjMatrix(n);
Graph<int> G(n);
G.setAdjMartix(c);
G.ShortestPath(1);
cout << "previous\t" << "i\t"<<"current" << endl;
for (int i = 1; i <= G.n; i++)
cout << G.prev[i] << "\t" << i <<"\t"<<G.dist[i]<< endl;
cout << endl;
}MinHeap.h:
#ifndef MYMINHEAP_H
#define MYMINHEAP_H
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
class MinHeap
{
private:
T *heap; //元素数组,0号位置也储存元素
int CurrentSize; //目前元素个数
int MaxSize; //可容纳的最多元素个数
void FilterDown(const int start,const int end); //自上往下调整,使关键字小的节点在上
void FilterUp(int start); //自下往上调整
public:
MinHeap(int n=1000);
~MinHeap();
bool Insert(const T &x); //插入元素
T RemoveMin(); //删除最小元素
T GetMin(); //取最小元素
bool IsEmpty() const;
bool IsFull() const;
void Clear();
};
template<class T>
MinHeap<T>::MinHeap(int n)
{
MaxSize=n;
heap=new T[MaxSize]; //动态开辟内存
CurrentSize=0;
}
template<class T>
MinHeap<T>::~MinHeap()
{
delete []heap;
}
template<class T>
void MinHeap<T>::FilterUp(int start) //自下往上调整
{
int j=start,i=(j-1)/2; //i指向j的双亲节点
T temp=heap[j];
while(j>0)
{
if(heap[i]<=temp)
break;
else
{
heap[j]=heap[i];
j=i;
i=(i-1)/2;
}
}
heap[j]=temp;
}
template<class T>
void MinHeap<T>::FilterDown(const int start,const int end) //自上往下调整,使关键字小的节点在上
{
int i=start,j=2*i+1;
T temp=heap[i];
while(j<=end)
{
if( (j<end) && (heap[j]>heap[j+1]) )
j++;
if(temp<=heap[j])
break;
else
{
heap[i]=heap[j];
i=j;
j=2*j+1;
}
}
heap[i]=temp;
}
template<class T>
bool MinHeap<T>::Insert(const T &x)
{
if(CurrentSize==MaxSize)
return false;
heap[CurrentSize]=x;
FilterUp(CurrentSize);
CurrentSize++;
return true;
}
template<class T>
T MinHeap<T>::RemoveMin( )
{
if(CurrentSize<0)
throw -1;
T x=heap[0];
heap[0]=heap[CurrentSize-1];
CurrentSize--;
FilterDown(0,CurrentSize-1); //调整新的根节点
return x;
}
template<class T>
T MinHeap<T>::GetMin()
{
return heap[0];
}
template<class T>
bool MinHeap<T>::IsEmpty() const
{
return CurrentSize==0;
}
template<class T>
bool MinHeap<T>::IsFull() const
{
return CurrentSize==MaxSize;
}
template<class T>
void MinHeap<T>::Clear()
{
CurrentSize=0;
}
#endif























 1998
1998

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








