在笔者的上一篇博客中,解析了Faster R-CNN中的RPN代码,在本篇博客中,笔者详细地解析一下ROI-Pooling代码。为大家讲解2015年Fast R-CNN的核心贡献(ROI Pooling被Faster R-CNN沿用)ROI Pooling的实现原理。(笔者其实一年半之前就看过这个代码,只是当时没有写到博客上,感慨.jpg)
在代码解析正式开始之前,笔者声明几点:
1. 本篇博客解析的ROI-Pooling代码分为两个框架下实现的,第一个当然是Ross Girshick实现的py-faster-rcnn中使用的ROI-Pooling代码,工程代码链接地址https://github.com/rbgirshick/py-faster-rcnn,ROI-Pooling代码链接地址https://github.com/rbgirshick/caffe-fast-rcnn/tree/0dcd397b29507b8314e252e850518c5695efbb83,后者打开是一个包含ROI-Pooling的caffe源码包,关于ROI-Pooling代码详见include/caffe/fast_rcnn_layers.hpp,src/caffe/proto/caffe.proto和src/caffe/layers/roi_pooling_layers.cpp以及src/caffe/layers/roi_pooling_layers.cu等四个文件。第二个是tensorflow实现的Faster R-CNN,工程链接地址https://github.com/kevinjliang/tf-Faster-RCNN,ROI-Pooling代码在Lib/roi_pool.py文件中。
2. 在大家看代码解析之前请大家完全明了ROI-Pooling的原理,有以下几个途径:
1) 直接进行Fast R-CNN论文阅读,链接https://arxiv.org/abs/1504.08083
2) 可以参考一下笔者的博客,里面对ROI-Pooling做出了解析,详询以下链接:
实例分割模型Mask R-CNN详解:从R-CNN,Fast R-CNN,Faster R-CNN再到Mask R-CNN
3) Region of interest pooling explained
下面开始正文:
首先是原版的ROI-Pooling的实现,是用c++语言实现的,在caffe框架下运行,代码分成四个部分。
第一个部分是caffe.proto文件中的定义:
-
// Message that stores parameters used by ROIPoolingLayer
-
message ROIPoolingParameter {
-
// Pad, kernel size, and stride are all given as a single value for equal
-
// dimensions in height and width or as Y, X pairs.
-
optional uint32 pooled_h =
1 [
default =
0];
//The pooled output height: roi pool过后的特征的高
-
optional uint32 pooled_w =
2 [
default =
0];
//The pooled output width: roi pool过后的特征的宽
-
// Multiplicative spatial scale factor to translate ROI coords from their
-
// input scale to the scale used when pooling
-
optional
float spatial_scale =
3 [
default =
1];
//共享卷积层输出的Feature Map相较于原图缩小的尺度(1/16)
-
}
上面的proto文件定义了三个参数,roi_pool输出特征的高,输出特征的宽和共享卷积层输出的特征相较于原图长宽缩小的尺度,如共享卷积层使用的是ResNet50,那么该值就是1/16。
第二个部分是fast_rcnn_layers.hpp中的定义:
-
/* ROIPoolingLayer - Region of Interest Pooling Layer
-
*/
-
template <
typename Dtype>
-
class
ROIPoolingLayer :
public Layer<Dtype> {
-
public:
-
explicit ROIPoolingLayer(const LayerParameter& param)
-
: Layer<Dtype>(param) {}
//空的构造函数继承父类
-
virtual void LayerSetUp(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
-
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top);
//Layer初始化函数,实现详见cpp文件
-
virtual void Reshape(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
-
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top);
//Reshape函数,实现详见cpp文件
-
-
virtual inline const char* type() const {
return
"ROIPooling"; }
-
-
//bottom blob最小和最大数量都为2,第一个bottom blob是共享卷积层输出的特征,第二个是roi的信息
-
virtual inline int MinBottomBlobs() const {
return
2; }
-
virtual inline int MaxBottomBlobs() const {
return
2; }
-
//top blob最小和最大数量都为1,表示pool过后的roi特征
-
virtual inline int MinTopBlobs() const {
return
1; }
-
virtual inline int MaxTopBlobs() const {
return
1; }
-
-
protected:
-
virtual void Forward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
-
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top);
//cpu前传
-
virtual void Forward_gpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
-
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top);
//cpu反传
-
virtual void Backward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
-
const vector<
bool>& propagate_down,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom);
//gpu前传
-
virtual void Backward_gpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
-
const vector<
bool>& propagate_down,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom);
//gpu反传
-
-
int channels_;
//记录共享卷积层输出的特征的channels
-
int height_;
//记录共享卷积层输出的特征的高
-
int width_;
//记录共享卷积层输出的特征的宽
-
int pooled_height_;
//记录pool过后的特征的高
-
int pooled_width_;
//记录pool过后的特征的宽
-
Dtype spatial_scale_;
//记录共享特征图相比于原图缩小的尺度,如果共享卷积层的使用的是ResNet50,那么就为1/16
-
Blob<
int> max_idx_;
//记录roi_pool过后得到的特征中的每个值在共享卷积层输出的特征图中的位置索引
-
};
在头文件定义中,除了caffe的四个标配LayerSetUp,Reshape,Forward和Backward四个模块定义之外,还有一些别的定义,详见上面的代码片最下方。其中有一个不显眼的Blob<int> 类型的变量max_idx_,先告诉大家这是ROI_Pooling中非常重要的变量之一,记录了roi pool过后的特征中的各个值在共享卷积层输出的特征图上的位置,这在反传过程中会起到核心作用。
第三个部分是roi_pooling_layer.cpp中的LayerSetUp,Reshape和Forward_cpu部分:
-
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
-
// Fast R-CNN
-
// Copyright (c) 2015 Microsoft
-
// Licensed under The MIT License [see fast-rcnn/LICENSE for details]
-
// Written by Ross Girshick
-
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-
#include <cfloat>
-
-
#include "caffe/fast_rcnn_layers.hpp"
-
-
using std::max;
-
using std::min;
-
using std::floor;
-
using std::ceil;
-
-
namespace caffe {
-
-
template <
typename Dtype>
-
void ROIPoolingLayer<Dtype>::
LayerSetUp(
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
-
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
-
ROIPoolingParameter roi_pool_param =
this->layer_param_.
roi_pooling_param();
-
CHECK_GT(roi_pool_param.
pooled_h(),
0)
-
<<
"pooled_h must be > 0";
-
CHECK_GT(roi_pool_param.
pooled_w(),
0)
-
<<
"pooled_w must be > 0";
-
//LayerSetUp函数,主要做了一件事,就是给三个变量赋值,这三个变量在caffe.proto文件里面指定:
-
pooled_height_ = roi_pool_param.
pooled_h();
//第一个是roi pool过后的高
-
pooled_width_ = roi_pool_param.
pooled_w();
//第二个是roi pool过后的宽
-
spatial_scale_ = roi_pool_param.
spatial_scale();
//第三个是共享卷积层输出的Feature Map相较于原图缩小的尺度
-
LOG(INFO) <<
"Spatial scale: " << spatial_scale_;
-
}
-
-
template <
typename Dtype>
-
void ROIPoolingLayer<Dtype>::
Reshape(
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
-
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
-
channels_ = bottom[
0]->
channels();
//得到共享卷积的层输出的特征图的channel数量
-
height_ = bottom[
0]->
height();
//得到共享卷积的层输出的特征图的高
-
width_ = bottom[
0]->
width();
//得到共享卷积的层输出的特征图的宽
-
top[
0]->
Reshape(bottom[
1]->
num(), channels_, pooled_height_,
-
pooled_width_);
//top[0]表示pool过后的特征,第一维为roi的数量(即bottom[1]->num())
-
max_idx_.
Reshape(bottom[
1]->
num(), channels_, pooled_height_,
-
pooled_width_);
//max_idx_表示pool过后的特征中的每一个值在原共享特征图上的索引,第一维亦为roi的数量(即bottom[1]->num())
-
}
-
-
//cpu前传函数
-
template <
typename Dtype>
-
void ROIPoolingLayer<Dtype>::
Forward_cpu(
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
-
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
-
const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[
0]->
cpu_data();
//bottom_data表示共享卷积层输出的特征图
-
const Dtype* bottom_rois = bottom[
1]->
cpu_data();
//bottom_rois表示rois的信息,一共5维,第一维表示rois在训练batch中的图片索引,后四维表示rois的坐标信息
-
// Number of ROIs
-
int num_rois = bottom[
1]->
num();
//roi的总数
-
int batch_size = bottom[
0]->
num();
//batch_size表示一次训练中输入的图片数量,因为roi并不是都存在于同一张图片上
-
int top_count = top[
0]->
count();
//top_count表示top[0]的全部容量(N*C*H*W)
-
Dtype* top_data = top[
0]->
mutable_cpu_data();
//使用top_data指针索引top[0]
-
caffe_set(top_count,
Dtype(-FLT_MAX), top_data);
//初始化top_data(即top[0]),将其初始值(共top_count个)置为最小值(-FLT_MAX)
-
int* argmax_data = max_idx_.
mutable_cpu_data();
//使用argmax_data指针索引max_idx_
-
caffe_set(top_count,
-1, argmax_data);
//初始化argmax_data(即max_idx_),将其初始值(共top_count个)置为-1
-
-
// For each ROI R = [batch_index x1 y1 x2 y2]: max pool over R (rois的五维数据的说明)
-
for (
int n =
0; n < num_rois; ++n) {
//第一个for循环,遍历rois
-
int roi_batch_ind = bottom_rois[
0];
//找到该roi对应的训练图片在训练batch中的索引
-
int roi_start_w =
round(bottom_rois[
1] * spatial_scale_);
//得到该roi的x1(左上角x坐标)在共享卷积层输出的特征图上面的位置(注意使用了round取整)
-
int roi_start_h =
round(bottom_rois[
2] * spatial_scale_);
//得到该roi的y1(左上角y坐标)在共享卷积层输出的特征图上面的位置(注意使用了round取整)
-
int roi_end_w =
round(bottom_rois[
3] * spatial_scale_);
//得到该roi的x2(右下角x坐标)在共享卷积层输出的特征图上面的位置(注意使用了round取整)
-
int roi_end_h =
round(bottom_rois[
4] * spatial_scale_);
//得到该roi的y2(右下角x坐标)在共享卷积层输出的特征图上面的位置(注意使用了round取整)
-
//下面两行代码核验该roi必须要出现在训练batch的某一张图片中
-
CHECK_GE(roi_batch_ind,
0);
//核验roi_batch_ind是否大于等于零
-
CHECK_LT(roi_batch_ind, batch_size);
//核验roi_batch_ind是否小于batch_size
-
-
int roi_height =
max(roi_end_h - roi_start_h +
1,
1);
//得到该roi在共享卷积层输出的特征图上面的高
-
int roi_width =
max(roi_end_w - roi_start_w +
1,
1);
//得到该roi在共享卷积层输出的特征图上面的宽
-
const Dtype bin_size_h =
static_cast<Dtype>(roi_height)
-
/
static_cast<Dtype>(pooled_height_);
//得到roi_pool的时候该roi在高方向上被划分的段数
-
const Dtype bin_size_w =
static_cast<Dtype>(roi_width)
-
/
static_cast<Dtype>(pooled_width_);
//得到roi_pool的时候该roi在宽方向上被划分的段数
-
-
const Dtype* batch_data = bottom_data + bottom[
0]->
offset(roi_batch_ind);
//找到该roi对应的batch中的那张图片
-
-
for (
int c =
0; c < channels_; ++c) {
//第二个for循环,遍历channels
-
for (
int ph =
0; ph < pooled_height_; ++ph) {
//第三个for循环,遍历pooled_height_,即pool过后的roi的高
-
for (
int pw =
0; pw < pooled_width_; ++pw) {
//第四个for循环,遍历pooled_width_,即pool过后的roi的宽
-
// Compute pooling region for this output unit:
-
// start (included) = floor(ph * roi_height / pooled_height_)
-
// end (excluded) = ceil((ph + 1) * roi_height / pooled_height_)
-
//hstart,wstart,hend,wend构成了在得到roi_pool输出中每一个值的过程中在共享卷积层输出的特征图上面的检索区域的坐标,下称"该值"
-
int hstart =
static_cast<
int>(
floor(
static_cast<Dtype>(ph)
-
* bin_size_h));
//找到该值对应的检索区域在共享卷积层输出的特征图上面的高开始的偏移坐标
-
int wstart =
static_cast<
int>(
floor(
static_cast<Dtype>(pw)
-
* bin_size_w));
//找到该值对应的检索区域在共享卷积层输出的特征图上面的宽开始的偏移坐标
-
int hend =
static_cast<
int>(
ceil(
static_cast<Dtype>(ph +
1)
-
* bin_size_h));
//找到该值对应的检索区域在共享卷积层输出的特征图上面的高结束的偏移坐标
-
int wend =
static_cast<
int>(
ceil(
static_cast<Dtype>(pw +
1)
-
* bin_size_w));
//找到该值对应的检索区域在共享卷积层输出的特征图上面的宽结束的偏移坐标
-
-
hstart =
min(
max(hstart + roi_start_h,
0), height_);
//找到该值对应的检索区域在共享卷积层输出的特征图上面的高开始坐标
-
hend =
min(
max(hend + roi_start_h,
0), height_);
//找到该值对应的检索区域在共享卷积层输出的特征图上面的宽开始坐标
-
wstart =
min(
max(wstart + roi_start_w,
0), width_);
//找到该值对应的检索区域在共享卷积层输出的特征图上面的高结束坐标
-
wend =
min(
max(wend + roi_start_w,
0), width_);
//找到该值对应的检索区域在共享卷积层输出的特征图上面的宽结束坐标
-
-
bool is_empty = (hend <= hstart) || (wend <= wstart);
//如果说该roi的尺寸非法,即(hend <= hstart)或者(wend <= wstart),is_empty就为true
-
-
const
int pool_index = ph * pooled_width_ + pw;
//找到该值对应的pool_index
-
if (is_empty) {
-
top_data[pool_index] =
0;
//如果is_empty为true,那么该值就为0
-
argmax_data[pool_index] =
-1;
//如果is_empty为true,那么该值对应的max_idx_为-1
-
}
-
-
for (
int h = hstart; h < hend; ++h) {
//第五个for循环,遍历该值对应的检索区域的高
-
for (
int w = wstart; w < wend; ++w) {
//第六个for循环,遍历该值对应的检索区域的宽
-
const
int index = h * width_ + w;
//找到检索区域中正被比较的值在共享卷积层输出的特征图上面的位置索引
-
if (batch_data[index] > top_data[pool_index]) {
-
top_data[pool_index] = batch_data[index];
//该值对应检索区域中的最大值
-
argmax_data[pool_index] = index;
//记录该值对应的共享特征图上面的位置
-
}
-
}
-
}
-
}
-
}
//结束第三至第六个for循环
-
// Increment all data pointers by one channel
-
batch_data += bottom[
0]->
offset(
0,
1);
//做完了一个channel,将batch_data索引指针移动到下一个channel继续pool
-
top_data += top[
0]->
offset(
0,
1);
//做完了一个channel,将输出索引指针移动到下一个channel继续接收pool的输出
-
argmax_data += max_idx_.
offset(
0,
1);
//做完了一个channel,将max_idx_索引指针移动到下一个channel继续接收坐标记录
-
}
//结束第二个for循环
-
// Increment ROI data pointer
-
bottom_rois += bottom[
1]->
offset(
1);
//处理完了一个roi,接着处理下一个roi
-
}
//结束第一个for循环
-
}
-
-
//Backward_cpu没有实现,在.cu文件上实现的gpu版本
-
template <
typename Dtype>
-
void ROIPoolingLayer<Dtype>::
Backward_cpu(
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
-
const vector<
bool>& propagate_down,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom) {
-
NOT_IMPLEMENTED;
-
}
-
-
-
#ifdef CPU_ONLY
-
STUB_GPU(ROIPoolingLayer);
-
#endif
-
-
INSTANTIATE_CLASS(ROIPoolingLayer);
-
REGISTER_LAYER_CLASS(ROIPooling);
-
-
}
// namespace caffe
在上面的代码中,我们可以看到,Forward_cpu函数核心是使用六个for循环实现。大家可以看到,ROI_Pooling是依次对每一个ROI实现的(第一个for循环),在得到一个ROI的信息之后,首先要找到该ROI对应的训练batch中的图片的特征在bottom[0]中的位置,即batch_data。然后,对于逐个通道(第二个for循环),将每一个通道上的ROI区域划分成pooled_height_×pooled_width_份(第三个和第四个for循环),将每一份中(hstart, hend, wstart和wend规定的区域)的最大值填入该通道roi_pool的输出区域(第五个和第六个for循环找最大值)。请大家注意,在做上述操作的同时,前传函数还记录了ROI Pooling的输出中的每一个值在共享卷积层输出的FeatureMap上面的位置,通过argmax_data指针记录,并保存在max_idx_里面。记录输出值的位置这个操作相当关键相当关键相当关键,因为在反传的时候,梯度只会反传到相应位置的值上面。最后,对于反传的cpu版本,作者并没有实现,而是实现在gpu版本上。
第四个部分是roi_pooling_layer.cu中的Forward_gpu和Backward_gpu部分:
-
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
-
// Fast R-CNN
-
// Copyright (c) 2015 Microsoft
-
// Licensed under The MIT License [see fast-rcnn/LICENSE for details]
-
// Written by Ross Girshick
-
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-
#include <cfloat>
-
-
#include "caffe/fast_rcnn_layers.hpp"
-
-
using std::max;
-
using std::min;
-
-
namespace caffe {
-
-
//以下是roi_pooling前传的gpu版本,和cpu版本差别不大,主要在gpu上变成了多线程实现。原理请详见roi_pooling_layer.cpp文件。
-
template <
typename Dtype>
-
__global__ void ROIPoolForward(const int nthreads, const Dtype* bottom_data,
-
const Dtype spatial_scale,
const
int channels,
const
int height,
-
const
int width,
const
int pooled_height,
const
int pooled_width,
-
const Dtype* bottom_rois, Dtype* top_data,
int* argmax_data) {
-
CUDA_KERNEL_LOOP(index, nthreads) {
-
// (n, c, ph, pw) is an element in the pooled output
-
int pw = index % pooled_width;
-
int ph = (index / pooled_width) % pooled_height;
-
int c = (index / pooled_width / pooled_height) % channels;
-
int n = index / pooled_width / pooled_height / channels;
-
-
bottom_rois += n *
5;
-
int roi_batch_ind = bottom_rois[
0];
-
int roi_start_w =
round(bottom_rois[
1] * spatial_scale);
-
int roi_start_h =
round(bottom_rois[
2] * spatial_scale);
-
int roi_end_w =
round(bottom_rois[
3] * spatial_scale);
-
int roi_end_h =
round(bottom_rois[
4] * spatial_scale);
-
-
// Force malformed ROIs to be 1x1
-
int roi_width =
max(roi_end_w - roi_start_w +
1,
1);
-
int roi_height =
max(roi_end_h - roi_start_h +
1,
1);
-
Dtype bin_size_h =
static_cast<Dtype>(roi_height)
-
/
static_cast<Dtype>(pooled_height);
-
Dtype bin_size_w =
static_cast<Dtype>(roi_width)
-
/
static_cast<Dtype>(pooled_width);
-
-
int hstart =
static_cast<
int>(
floor(
static_cast<Dtype>(ph)
-
* bin_size_h));
-
int wstart =
static_cast<
int>(
floor(
static_cast<Dtype>(pw)
-
* bin_size_w));
-
int hend =
static_cast<
int>(
ceil(
static_cast<Dtype>(ph +
1)
-
* bin_size_h));
-
int wend =
static_cast<
int>(
ceil(
static_cast<Dtype>(pw +
1)
-
* bin_size_w));
-
-
// Add roi offsets and clip to input boundaries
-
hstart =
min(
max(hstart + roi_start_h,
0), height);
-
hend =
min(
max(hend + roi_start_h,
0), height);
-
wstart =
min(
max(wstart + roi_start_w,
0), width);
-
wend =
min(
max(wend + roi_start_w,
0), width);
-
bool is_empty = (hend <= hstart) || (wend <= wstart);
-
-
// Define an empty pooling region to be zero
-
Dtype maxval = is_empty ?
0 : -FLT_MAX;
-
// If nothing is pooled, argmax = -1 causes nothing to be backprop'd
-
int maxidx =
-1;
-
bottom_data += (roi_batch_ind * channels + c) * height * width;
-
for (
int h = hstart; h < hend; ++h) {
-
for (
int w = wstart; w < wend; ++w) {
-
int bottom_index = h * width + w;
-
if (bottom_data[bottom_index] > maxval) {
-
maxval = bottom_data[bottom_index];
-
maxidx = bottom_index;
-
}
-
}
-
}
-
top_data[index] = maxval;
-
argmax_data[index] = maxidx;
-
}
-
}
-
-
template <
typename Dtype>
-
void ROIPoolingLayer<Dtype>::
Forward_gpu(
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
-
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
-
const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[
0]->
gpu_data();
-
const Dtype* bottom_rois = bottom[
1]->
gpu_data();
-
Dtype* top_data = top[
0]->
mutable_gpu_data();
-
int* argmax_data = max_idx_.
mutable_gpu_data();
-
int count = top[
0]->
count();
-
// NOLINT_NEXT_LINE(whitespace/operators)
-
ROIPoolForward<Dtype><<<
CAFFE_GET_BLOCKS(count), CAFFE_CUDA_NUM_THREADS>>>(
-
count, bottom_data, spatial_scale_, channels_, height_, width_,
-
pooled_height_, pooled_width_, bottom_rois, top_data, argmax_data);
-
CUDA_POST_KERNEL_CHECK;
-
}
-
-
-
-
//以上是roi_pooling前传的gpu版本,和cpu版本差别不大,主要在gpu上变成了多线程实现。原理请详见roi_pooling_layer.cpp文件。
-
//——————————————————————————————————分割线——————————————————————————————————————————
-
//..................................分割线..........................................
-
//----------------------------------分割线------------------------------------------
-
-
-
//以下是roi_pooling反传的gpu版本。
-
template <
typename Dtype>
-
__global__ void ROIPoolBackward(const int nthreads, const Dtype* top_diff,
-
const
int* argmax_data,
const
int num_rois,
const Dtype spatial_scale,
-
const
int channels,
const
int height,
const
int width,
-
const
int pooled_height,
const
int pooled_width, Dtype* bottom_diff,
-
const Dtype* bottom_rois) {
-
CUDA_KERNEL_LOOP(index, nthreads) {
//第一个LOOP
-
// (n, c, h, w) coords in bottom data
-
//对于共享卷积层输出的每一个值,找到对应的w,h,c,n坐标
-
int w = index % width;
-
int h = (index / width) % height;
-
int c = (index / width / height) % channels;
-
int n = index / width / height / channels;
-
-
Dtype gradient =
0;
-
// Accumulate gradient over all ROIs that pooled this element
-
//下面开始累积梯度
-
for (
int roi_n =
0; roi_n < num_rois; ++roi_n) {
//第一个for循环,遍历所有roi
-
const Dtype* offset_bottom_rois = bottom_rois + roi_n *
5;
//得到一个roi的信息
-
int roi_batch_ind = offset_bottom_rois[
0];
//得到这个roi对应的训练batch的图片索引
-
// Skip if ROI's batch index doesn't match n
-
if (n != roi_batch_ind) {
//如果这个roi对应的图片不是目前累积梯度的特征值所在的图片,直接continue
-
continue;
-
}
-
-
int roi_start_w =
round(offset_bottom_rois[
1] * spatial_scale);
//得到该roi的x1(左上角x坐标)在共享卷积层输出的特征图上面的位置
-
int roi_start_h =
round(offset_bottom_rois[
2] * spatial_scale);
//得到该roi的y1(左上角y坐标)在共享卷积层输出的特征图上面的位置
-
int roi_end_w =
round(offset_bottom_rois[
3] * spatial_scale);
//得到该roi的x2(右下角x坐标)在共享卷积层输出的特征图上面的位置
-
int roi_end_h =
round(offset_bottom_rois[
4] * spatial_scale);
//得到该roi的y2(右下角x坐标)在共享卷积层输出的特征图上面的位置
-
-
// Skip if ROI doesn't include (h, w)
-
const
bool in_roi = (w >= roi_start_w && w <= roi_end_w &&
-
h >= roi_start_h && h <= roi_end_h);
-
if (!in_roi) {
-
continue;
-
}
//判断一下roi的坐标是否合法,如果不合法直接continue
-
-
int offset = (roi_n * channels + c) * pooled_height * pooled_width;
//找到这个roi对应的顶层梯度blob的偏移量
-
const Dtype* offset_top_diff = top_diff + offset;
//找到这个roi对应的顶层梯度blob中的位置
-
const
int* offset_argmax_data = argmax_data + offset;
//找到这个roi对应的pooled_feature在共享卷积层输出的特征里面的位置,梯度反传的时候非常重要
-
-
// Compute feasible set of pooled units that could have pooled
-
// this bottom unit
-
-
// Force malformed ROIs to be 1x1
-
int roi_width =
max(roi_end_w - roi_start_w +
1,
1);
//得到这个roi在共享卷积层输出的特征图上面的宽
-
int roi_height =
max(roi_end_h - roi_start_h +
1,
1);
//得到这个roi在共享卷积层输出的特征图上面的高
-
-
Dtype bin_size_h =
static_cast<Dtype>(roi_height)
-
/
static_cast<Dtype>(pooled_height);
//得到roi_pool的时候这个roi在高方向上被划分的段数
-
Dtype bin_size_w =
static_cast<Dtype>(roi_width)
-
/
static_cast<Dtype>(pooled_width);
//得到roi_pool的时候这个roi在宽方向上被划分的段数
-
-
int phstart =
floor(
static_cast<Dtype>(h - roi_start_h) / bin_size_h);
//得到共享特征图上的某个值对应的在roi_pool的输出上的高起始坐标
-
int phend =
ceil(
static_cast<Dtype>(h - roi_start_h +
1) / bin_size_h);
//得到共享特征图上的某个值对应的在roi_pool的输出上的高结束坐标
-
int pwstart =
floor(
static_cast<Dtype>(w - roi_start_w) / bin_size_w);
//得到共享特征图上的某个值对应的在roi_pool的输出上的宽起始坐标
-
int pwend =
ceil(
static_cast<Dtype>(w - roi_start_w +
1) / bin_size_w);
//得到共享特征图上的某个值对应的在roi_pool的输出上的宽结束坐标
-
-
phstart =
min(
max(phstart,
0), pooled_height);
//得到共享特征图上的某个值对应的在roi_pool的输出上的最终的高起始坐标,对上面求出的坐标做判断,必须要大于0,和小于pooled_height,意思是该点在这个roi之内,下同
-
phend =
min(
max(phend,
0), pooled_height);
//得到共享特征图上的某个值对应的在roi_pool的输出上的最终的高结束坐标
-
pwstart =
min(
max(pwstart,
0), pooled_width);
//得到共享特征图上的某个值对应的在roi_pool的输出上的最终的宽起始坐标
-
pwend =
min(
max(pwend,
0), pooled_width);
//得到共享特征图上的某个值对应的在roi_pool的输出上的最终的宽结束坐标
-
-
for (
int ph = phstart; ph < phend; ++ph) {
//第二个for循环,遍历共享特征图上的某个值对应的对应的roi_pool输出区域的高的范围
-
for (
int pw = pwstart; pw < pwend; ++pw) {
//第三个for循环,遍历共享特征图上的某个值对应的对应的roi_pool输出区域的宽的范围
-
if (offset_argmax_data[ph * pooled_width + pw] == (h * width + w)) {
-
gradient += offset_top_diff[ph * pooled_width + pw];
-
}
//一旦发现记录的roi_pool输出得到的特征上对应的共享特征图上的位置等同于目前被累积梯度的共享特征图上的位置,就在目前的共享特征图上的位置累积top传下来的该点对应的梯度
-
}
//结束第三个for循环
-
}
//结束第二个for循环
-
}
//结束第一个for循环
-
bottom_diff[index] = gradient;
//最终得到共享特征图上某一点对应的总的梯度
-
}
//结束LOOP
-
}
-
-
template <
typename Dtype>
-
void ROIPoolingLayer<Dtype>::
Backward_gpu(
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top,
-
const vector<
bool>& propagate_down,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom) {
-
if (!propagate_down[
0]) {
-
return;
-
}
//如果不需反传,直接return
-
const Dtype* bottom_rois = bottom[
1]->
gpu_data();
//bottom_rois对应rois的信息
-
const Dtype* top_diff = top[
0]->
gpu_diff();
//top_diff对应顶层的梯度
-
Dtype* bottom_diff = bottom[
0]->
mutable_gpu_diff();
//bottom_diff对应需要传到共享卷积层的梯度
-
const
int count = bottom[
0]->
count();
//count对应bottom[0]的容量(即共享卷积层输出的特征的容量)
-
caffe_gpu_set(count,
Dtype(
0.), bottom_diff);
//将bottom[0]的梯度全部初始化为零
-
const
int* argmax_data = max_idx_.
gpu_data();
//argmax_data对应roi_pool输出得到的特征上每一个值对应的共享卷积层输出的特征图上的位置
-
// NOLINT_NEXT_LINE(whitespace/operators)
-
//下面是具体的反传函数
-
ROIPoolBackward<Dtype><<<
CAFFE_GET_BLOCKS(count), CAFFE_CUDA_NUM_THREADS>>>(
-
count, top_diff, argmax_data, top[
0]->
num(), spatial_scale_, channels_,
-
height_, width_, pooled_height_, pooled_width_, bottom_diff, bottom_rois);
-
CUDA_POST_KERNEL_CHECK;
-
}
-
-
INSTANTIATE_LAYER_GPU_FUNCS(ROIPoolingLayer);
-
-
}
// namespace caffe
大家可以看到,上述代码中,ROI Pooling的反传主要是通过一个CUDA_KERNEL_LOOP和三个for循环实现。最外层的CUDA_KERNEL_LOOP遍历了共享卷积层输出的特征图上面的每一个位置的梯度。然后,第一个for循环表示是逐ROI进行,第二个和第三个for循环表示的是从高和宽方向遍历ROI_Pooling的输出blob。在这里有个问题,channel哪去了?大家可以看到channel已经被融合在第一个CUDA_KERNEL_LOOP中了,也就是说反传中的梯度累积是对共享卷积层输出的特征图中的每一个位置进行的。对于共享卷积层输出的特征图中的每一个位置的梯度,找到其可能出现在ROI_Pool输出的特征图上的位置并进行位置匹配,一旦发现共享卷积层输出的特征图中这个值的位置和在前传的过程中记录的位置相同,则将该ROI_Pool输出的特征图上的位置对应的梯度累积到共享卷积层输出的特征图中的那个位置上。
总的来说,既然ROI Pooling的输出是从共享卷积层输出的特征图上面选择的,那么,在反传的时候,梯度也自然反传到相应的被选择的位置上面。
以上四个部分,就是Ross Girshick的py-faster-rcnn工程里面使用的ROI Pooling代码,总的来说还是相当复杂的,代码确实让人眼花缭乱。不过,在理解透彻了ROI Pooling的原理之后再看这个代码,就比较轻松了。
下面,我们来看一下tensorflow中实现的ROI Pooling的代码:
-
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
-
"""
-
Created on Wed Jan 11 14:29:57 2017
-
-
@author: Kevin Liang
-
-
ROI pooling layer: Using tensorflow's crop_and_resize function as replacement.
-
crop_and_resize expects box indices in normalized coordinates.
-
-
Convolutional feature maps are cropped to a constant size of (14,14) and then
-
maxpooled to (7x7)
-
"""
-
-
import tensorflow
as tf
-
-
#featureMaps指的是共享卷积层输出的特征图
-
#rois指的是需要被pool的框的坐标,shape[M, 5],后一维中5个值中的第一个值指的是该框在某一个训练batch中的图片索引
-
#im_dims指的是图片的尺度,shape[N, 2],N指的是batch_size,这里固定为1
-
def
roi_pool(
featureMaps,rois,im_dims):
-
'''
-
Regions of Interest (ROIs) from the Region Proposal Network (RPN) are
-
formatted as:
-
(image_id, x1, y1, x2, y2)
-
-
Note: Since mini-batches are sampled from a single image, image_id = 0s
-
'''
-
with tf.variable_scope(
'roi_pool'):
-
# Image that the ROI is taken from (minibatch of 1 means these will all be 0)
-
box_ind = tf.cast(rois[:,
0],dtype=tf.int32)
#在这里取到所有需要pool的框在训练batch中的对应图片序号,由于batch_size为1,因此box_ind里面的值都为0
-
-
# ROI box coordinates. Must be normalized and ordered to [y1, x1, y2, x2]
-
boxes = rois[:,
1:]
#在这里取到所有的需要pool的框 shape[N, 4]
-
normalization = tf.cast(tf.stack([im_dims[:,
1],im_dims[:,
0],im_dims[:,
1],im_dims[:,
0]],axis=
1),dtype=tf.float32)
#在这里取到归一化框的坐标时需要的图片尺度
-
boxes = tf.div(boxes,normalization)
#在这里归一化框的坐标
-
boxes = tf.stack([boxes[:,
1],boxes[:,
0],boxes[:,
3],boxes[:,
2]],axis=
1)
# y1, x1, y2, x2 在这里交换框的坐标(x1, y1, x2, y2)->(y1, x1, y2, x2)
-
-
# ROI pool output size
-
crop_size = tf.constant([
14,
14])
#在这里规定初始pool过后输出的尺度
-
-
# ROI pool
-
#进行ROI pool,之所以需要归一化框的坐标是因为tf接口的要求
-
pooledFeatures = tf.image.crop_and_resize(image=featureMaps, boxes=boxes, box_ind=box_ind, crop_size=crop_size)
-
-
# Max pool to (7x7)
-
#用2×2的滑动窗口进行最大池化操作,输出的尺度是7×7
-
pooledFeatures = tf.nn.max_pool(pooledFeatures, ksize=[
1,
2,
2,
1], strides=[
1,
2,
2,
1], padding=
'SAME')
-
-
return pooledFeatures
非常意外,ROI Pooling在tensorflow中已经被规范在了框架里面,使用tf.image.crop_and_resize函数实现。
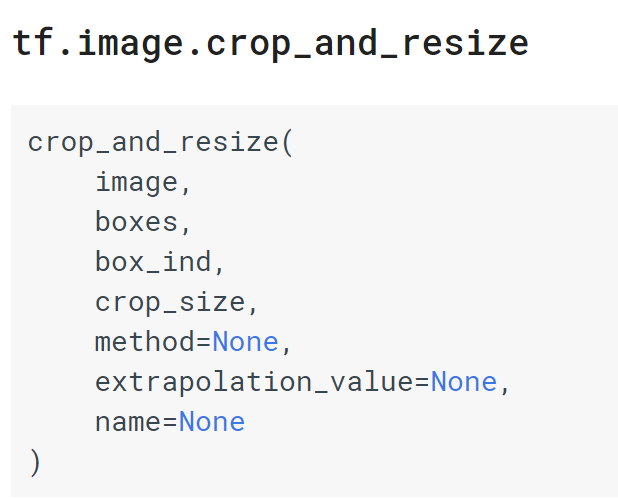
在tf.image.crop_and_resize函数中,image就是共享卷积层输出的特征图。
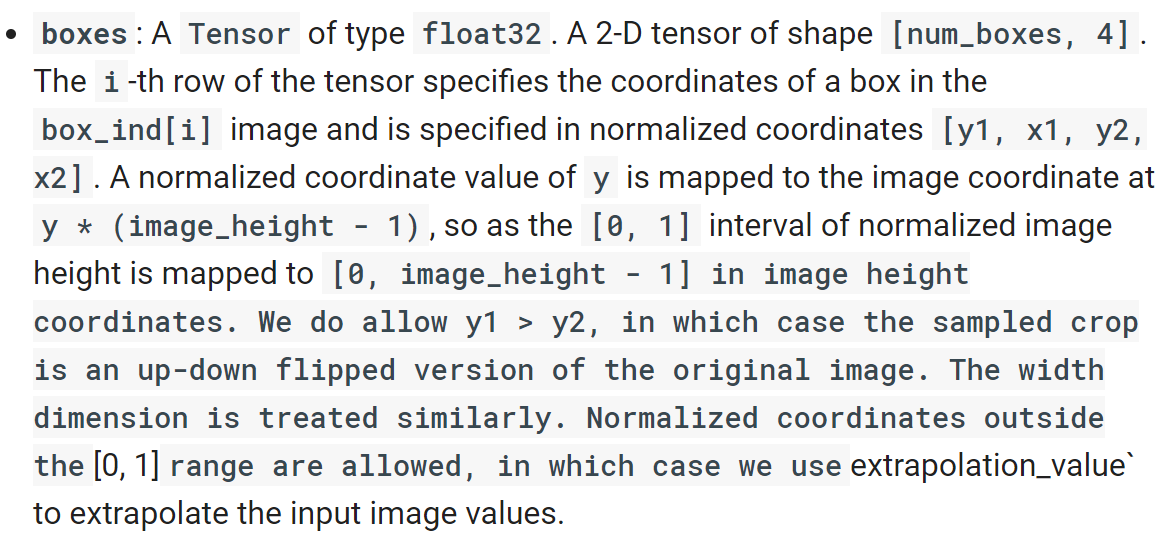
boxes指的就是ROI的坐标,不过需要换成[y1, x1, y2, x2]的顺序,并且要归一化。可见在代码中做出了交换并使用tf.div进行了归一化。
box_ind就是rois在训练batch中的图片索引数组。
crop_size指的是ROI Pooling后输出的特征图的大小,上面的代码中是14×14。
最后则是一些resize的方式等参数,默认是采用双线性插值方式进行resize。
在上面的代码中,是先将ROI pool成了14×14的大小,再使用tf.nn.max_pool将其转化成了7×7的大小。
不得不说,tf的实现方式还是和caffe原版的不太一样,主要体现在caffe原版实现的时候,是将特征图的逐通道上面的ROI区域划成了若干份,并从每一份中选取了最大值,也就是说,每一个通道的选值情况是不一样的!而tensorflow实现的ROI Pooling是先直接将ROI区域对应的特征割出来,并按照某一尺度(14×14)进行双线性插值resize,再使用tf.nn.max_pool将特征转化为更小的维度(7×7)。
到这里,ROI Pooling代码解析就接近尾声了,笔者想说的是,第一,Caffe代码虽然复杂,但是笔者坚持认为Caffe这框架确实是深入理解深度学习的好法宝,因为有很多机会能看到许多模块的底层实现代码。第二,R-CNN,Fast R-CNN和Faster R-CNN作为深度学习计算机视觉领域中的革命性成果,其代码是相当值得学习吸收的,在最开始阅读的时候不可避免也会有一些挑战,但是,还是要静下心来仔细分析。只要了解了算法原理,再仔细阅读分析算法代码,就能对原理更加深理解,最终达到完全理解算法的目的。
最后,对于ROI Pooling代码的分析,如果各位读者朋友们认为存在疏漏,欢迎在评论区指出与讨论,笔者不胜感激。
欢迎阅读笔者后续博客,各位读者朋友的支持与鼓励是我最大的动力!
written by jiong
空谈误国,实干兴邦!


























 458
458











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








