Hibernate 缓存详解
session 一级缓存
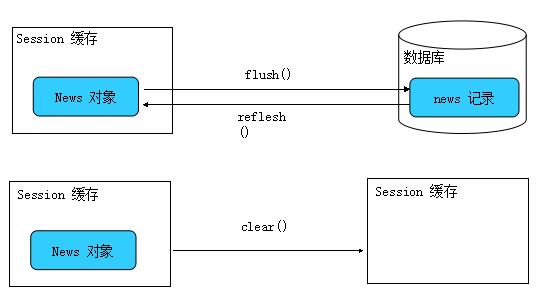
1、session 一级缓存所持有的方法特征如下图:
详解:
flush:Session 按照缓存中对象的属性变化来同步更新数据库
默认情况下 Session 在以下时间点刷新缓存:
显式调用 Session 的 flush() 方法
当应用程序调用 Transaction 的 commit()方法的时, 该方法先 flush ,然后在向数据库提交事务
当应用程序执行一些查询(HQL, Criteria)操作时,如果缓存中持久化对象的属性已经发生了变化,会先 flush 缓存,以保证查询结果能够反映持久化对象的最新状态
flush 缓存的例外情况: 如果对象使用 native 生成器生成 OID, 那么当调用 Session 的 save() 方法保存对象时, 会立即执行向数据库插入该实体的 insert 语句.
commit() 和 flush() 方法的区别:flush 执行一系列 sql 语句,但不提交事务;commit 方法先调用flush() 方法,然后提交事务. 意味着提交事务意味着对数据库操作永久保存下来。
程序设计
隐式 flush() 方法
/**
* 1.就算没有flush()方法,如果执行了下面的程序方法,同样发送了 update 语句
* 2.只要在session的生命周期中,如果发现对象属性改变,就会隐士调用flush()方法
* 3.session的所有方法包括 get query 都符合这种session缓存机制
*/
@Test
public void testHiberneteSecondCache(){
News news = (News) session.get(News.class, 1);
news.setAuthor("AUTHOR");
System.out.println(news.toString());
}
@Test
public void testHQLSecondCache(){
Query query = session.createQuery("from News where id = 1");
News news = (News) query.uniqueResult();
news.setAuthor("AUTHOR2");
System.out.println(news.getAuthor());
}
flush() 方法
/**
* flush: 使数据表中的记录和 Session 缓存中的对象的状态保持一致. 为了保持一致, 则可能会发送对应的 SQL 语句.
* 1. 在 Transaction 的 commit() 方法中: 先调用 session 的 flush 方法, 再提交事务
* 2. flush() 方法会可能会发送 SQL 语句, 但不会提交事务.
* 3. 注意: 在未提交事务或显式的调用 session.flush() 方法之前, 也有可能会进行 flush() 操作.
* 1). 执行 HQL 或 QBC 查询, 会先进行 flush() 操作, 以得到数据表的最新的记录 -- 先查询了一次,然后再HQL,隐身的调用了flush
* 2). 若记录的 ID 是由底层数据库使用自增的方式生成的, 则在调用 save() 方法时, 就会立即发送 INSERT 语句.
* 因为 save 方法后, 必须保证对象的 ID 是存在的!
*/
@Test
public void testSessionFlush2(){
News news = new News("Java", "SUN", new Date());
session.save(news);
}
@Test
public void testSessionFlush(){
News news = (News) session.get(News.class, 1);
news.setAuthor("Oracle");
session.flush();
//在外部一定要commit();这样就会将java中的改变,以及session中的缓存存入oracle中,看到效果
News news2 = (News) session.createCriteria(News.class).uniqueResult();
System.out.println(news2);
}
@Test
public void testSessionCache(){
News news = (News) session.get(News.class, 1);
System.out.println(news);
News news2 = (News) session.get(News.class, 1);
System.out.println(news2);
}
reflush()方法
/**
* refresh(): 会强制发送 SELECT 语句, 以使 Session 缓存中对象的状态和数据表中对应的记录保持一致!
*/
@Test
public void testRefresh(){
News news = (News) session.get(News.class, 1);
System.out.println(news);
session.refresh(news);
System.out.println(news);
}
clear()方法
/**
* clear(): 清理缓存
*/
@Test
public void testClear(){
News news1 = (News) session.get(News.class, 1);
session.clear();
News news2 = (News) session.get(News.class, 1);
}
session 二级缓存
解析:
1. 使用 Hibernate 二级缓存的步骤:
1). 加入二级缓存插件的 jar 包及配置文件:
I. 复制 \hibernate-release-4.2.4.Final\lib\optional\ehcache\*.jar 到当前 Hibrenate 应用的类路径下.
II. 复制 hibernate-release-4.2.4.Final\project\etc\ehcachexml 到当前 WEB 应用的类路径下
2). 配置 hibernate.cfg.xml
I. 配置启用 hibernate 的二级缓存
<property name="cache.use_second_level_cache">true</property>
II. 配置hibernate二级缓存使用的产品
<property name="hibernate.cache.region.factory_class">org.hibernate.cache.ehcache.EhCacheRegionFactory</property>
III. 配置对哪些类使用 hibernate 的二级缓存
<class-cache usage="read-write" class="com.atguigu.hibernate.entities.Employee"/>
实际上也可以在 .hbm.xml 文件中配置对哪些类使用二级缓存, 及二级缓存的策略是什么.
2). 集合级别的二级缓存的配置
I. 配置对集合使用二级缓存
<collection-cache usage="read-write" collection="com.atguigu.hibernate.entities.Department.emps"/>
也可以在 .hbm.xml 文件中进行配置
<set name="emps" table="GG_EMPLOYEE" inverse="true" lazy="true">
<cache usage="read-write"/>
<key>
<column name="DEPT_ID" />
</key>
<one-to-many class="com.atguigu.hibernate.entities.Employee" />
</set>
II. 注意: 还需要配置集合中的元素对应的持久化类也使用二级缓存! 否则将会多出 n 条 SQL 语句.
3). ehcache 的 配置文件: ehcache.xml
4). 查询缓存: 默认情况下, 设置的缓存对 HQL 及 QBC 查询时无效的, 但可以通过以下方式使其是有效的
I. 在 hibernate 配置文件中声明开启查询缓存
<property name="cache.use_query_cache">true</property>
II. 调用 Query 或 Criteria 的 setCacheable(true) 方法
III. 查询缓存依赖于二级缓存
项目试验
项目清单
项目源码及分析
1、package com.atguigu.hibernate.helloworld
package com.atguigu.hibernate.helloworld;
import java.sql.Blob;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Set;
public class News {
private Integer id; //field
private String title;
private String author;
private Date date;
private Set<People> peoples;
public Set<People> getPeoples() {
return peoples;
}
public void setPeoples(Set<People> peoples) {
this.peoples = peoples;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author = author;
}
public Date getDate() {
return date;
}
public void setDate(Date date) {
this.date = date;
}
public News(String title, String author, Date date,Set<People> peoples) {
this.title = title;
this.author = author;
this.date = date;
this.peoples = peoples;
}
public News() {
}
}
package com.atguigu.hibernate.helloworld;
/**
* 发送News人员
*/
public class People {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private News news;
public News getNews() {
return news;
}
public void setNews(News news) {
this.news = news;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public People() {
}
public People(Integer id, String name,News news) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.news = news;
}
}
package com.atguigu.hibernate.helloworld;
import java.util.Set;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
import org.hibernate.service.ServiceRegistry;
import org.hibernate.service.ServiceRegistryBuilder;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
public class SessionSecondCache {
private SessionFactory sessionFactory;
private Session session;
private Transaction transaction;
@Before
public void init(){
Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure();
ServiceRegistry serviceRegistry =
new ServiceRegistryBuilder().applySettings(configuration.getProperties())
.buildServiceRegistry();
sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory(serviceRegistry);
session = sessionFactory.openSession();
transaction = session.beginTransaction();
}
@After
public void destroy(){
sessionFactory.close();
}
@Test
public void testHiberneteSecondCache(){
News news = (News) session.get(News.class, 1);
Set<People> peoples = news.getPeoples();
System.out.println(peoples.size());
transaction.commit();
session.close();
Session session2 = sessionFactory.openSession();
transaction = session2.beginTransaction();
News news2 = (News) session2.get(News.class, 1);
Set<People> peoples2 = news2.getPeoples();
System.out.println(peoples2.size());
}
}
2、ehcache.xml
<ehcache>
<!-- Sets the path to the directory where cache .data files are created.
If the path is a Java System Property it is replaced by
its value in the running VM.
The following properties are translated:
user.home - User's home directory
user.dir - User's current working directory
java.io.tmpdir - Default temp file path -->
<!--
指定一个目录:当 EHCache 把数据写到硬盘上时, 将把数据写到这个目录下.
-->
<diskStore path="d:\\tempDirectory"/>
<!--Default Cache configuration. These will applied to caches programmatically created through
the CacheManager.
The following attributes are required for defaultCache:
maxInMemory - Sets the maximum number of objects that will be created in memory
eternal - Sets whether elements are eternal. If eternal, timeouts are ignored and the element
is never expired.
timeToIdleSeconds - Sets the time to idle for an element before it expires. Is only used
if the element is not eternal. Idle time is now - last accessed time
timeToLiveSeconds - Sets the time to live for an element before it expires. Is only used
if the element is not eternal. TTL is now - creation time
overflowToDisk - Sets whether elements can overflow to disk when the in-memory cache
has reached the maxInMemory limit.
-->
<!--
设置缓存的默认数据过期策略
-->
<defaultCache
maxElementsInMemory="10000"
eternal="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="120"
timeToLiveSeconds="120"
overflowToDisk="true"
/>
<!--
设定具体的命名缓存的数据过期策略。每个命名缓存代表一个缓存区域
缓存区域(region):一个具有名称的缓存块,可以给每一个缓存块设置不同的缓存策略。
如果没有设置任何的缓存区域,则所有被缓存的对象,都将使用默认的缓存策略。即:<defaultCache.../>
Hibernate 在不同的缓存区域保存不同的类/集合。
对于类而言,区域的名称是类名。如:com.atguigu.domain.Customer
对于集合而言,区域的名称是类名加属性名。如com.atguigu.domain.Customer.orders
-->
<!--
name: 设置缓存的名字,它的取值为类的全限定名或类的集合的名字
maxElementsInMemory: 设置基于内存的缓存中可存放的对象最大数目
eternal: 设置对象是否为永久的, true表示永不过期,
此时将忽略timeToIdleSeconds 和 timeToLiveSeconds属性; 默认值是false
timeToIdleSeconds:设置对象空闲最长时间,以秒为单位, 超过这个时间,对象过期。
当对象过期时,EHCache会把它从缓存中清除。如果此值为0,表示对象可以无限期地处于空闲状态。
timeToLiveSeconds:设置对象生存最长时间,超过这个时间,对象过期。
如果此值为0,表示对象可以无限期地存在于缓存中. 该属性值必须大于或等于 timeToIdleSeconds 属性值
overflowToDisk:设置基于内存的缓存中的对象数目达到上限后,是否把溢出的对象写到基于硬盘的缓存中
-->
</ehcache>
3、hibernate.cfg.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<!-- 配置连接数据库的基本信息 -->
<property name="connection.username">root</property>
<property name="connection.password">123456</property>
<property name="connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="connection.url">jdbc:mysql:///hibernate5</property>
<!-- 配置 hibernate 的基本信息 -->
<!-- hibernate 所使用的数据库方言 -->
<property name="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLInnoDBDialect</property>
<!-- 执行操作时是否在控制台打印 SQL -->
<property name="show_sql">true</property>
<!-- 是否对 SQL 进行格式化 -->
<property name="format_sql">true</property>
<!-- 指定自动生成数据表的策略 -->
<property name="hbm2ddl.auto">update</property>
<!-- 启用二级缓存 -->
<property name="cache.use_second_level_cache">true</property>
<!-- 配置使用的二级缓存的产品 -->
<property name="hibernate.cache.region.factory_class">org.hibernate.cache.ehcache.EhCacheRegionFactory</property>
<!-- 配置启用查询缓存 -->
<property name="cache.use_query_cache">true</property>
<!-- 指定关联的 .hbm.xml 文件 -->
<mapping resource="com/atguigu/hibernate/helloworld/News.hbm.xml"/>
<mapping resource="com/atguigu/hibernate/helloworld/People.hbm.xml"/>
<class-cache usage="read-write" class="com.atguigu.hibernate.helloworld.News"/>
<class-cache usage="read-write" class="com.atguigu.hibernate.helloworld.People"/>
<collection-cache usage="read-write" collection="com.atguigu.hibernate.helloworld.News.peoples"/>
<!--
1.缓存在此配置也行,或者在各个xml中配置<cache/>
2.涉及到集合,比如多对一这样的情况,也需要对此配置缓存,或者在<set>下配置<cache/>
-->
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>
4、sql 脚本
CREATE TABLE NEWS (
ID INTEGER NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
TITLE VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
AUTHOR VARCHAR(255),
DATE DATE,
PRIMARY KEY (ID)
)
CREATE TABLE People (
ID INTEGER NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
NAME VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
n_id INTEGER,
PRIMARY KEY (ID)
)
ALTER TABLE NEWS
ADD CONSTRAINT UK_duq2gjdo5k53otrakypw0888b UNIQUE (TITLE)
ALTER TABLE People
ADD CONSTRAINT UK_24fes2jfmnlqa29qtgceqvjoc UNIQUE (NAME)
ALTER TABLE People
ADD INDEX FK_4ldntgu2n6tr9rlcq23ouvytd (n_id),
ADD CONSTRAINT FK_4ldntgu2n6tr9rlcq23ouvytd
FOREIGN KEY (n_id)
REFERENCES NEWS (ID)






















 936
936

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








