Introduction to Client/Server Architecture
In the Oracle database system environment, the database application and the database are separated into two parts: afront-end or client portion, and a back-end or server portion--hence the term client/server architecture. The client runs the database application that accesses database information and interacts with a user through the keyboard, screen, and pointing device, such as a mouse. The server runs the Oracle software and handles the functions required for concurrent, shared data access to an Oracle database.
Although the client application and Oracle can be run on the same computer, greater efficiency can often be achieved when the client portions and server portion are run by different computers connected through a network.
Distributed processing is the use of more than one processor, located in different systems, to perform the processing for an individual task.
Overview of Multitier Architecture
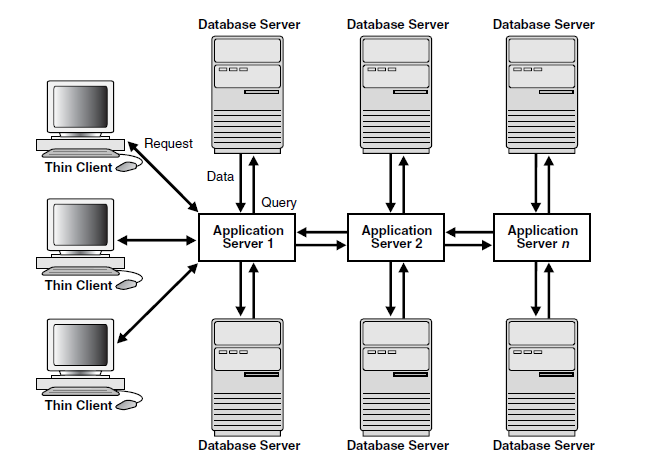
In a multitier architecture environment, an application server provides data for clients and serves as an interface between clients and database servers. This architecture is particularly important because of the prevalence of Internet use.
This architecture enables use of an application server to:
- validate the credentials of a client, such as a web browser.
- Connect to a database server
- Perform the requested operation
Clients
A client initiates a request for an operation to be performed on the database server. The client can be a Web browser or other end-user process. In a multitier architecture, the client connects to the database server through on or more application severs.
Application Servers
An application server provides access to the data for the client. It serves as an interface between the client and one or more database servers, which provides an additional level of security. It can also perform some of the query processing for the client, thus removing some of the load from the database server.
The application server assumes the identity of the client when it is performing operations on the database server for that client. The application server's privileges are restricted to prevent it from performing unneeded and unwanted operations during a client operation.
Database Servers
A database server provides the data requested by an application server on behalf of a client. The database server does all of the remaining query processing.
The Oracle database server can audit operations performed by the application server on behalf of individual clients as well as operations performed by the application server on its own behalf.
Overview of Oracle Net Services
Oracle Net Services provides enterprise-wide connectivity solutions in distributed, heterogeneous computing environments. Oracle Net Services enables a network session from a client application to an Oracle database.
Oracle Net Services uses the communication protocols or application programmatic interfaces (APIs) supported by a wide range of networks to provide a distributed database and distributed processing for Oracle.
- A communication protocol is a set of rules that determine how applications access the network and how data is subdivided into packets for transmission across the network.
- An API is a set of subroutines that provide, in the case of networks, a means to establish remote process-to-proces communication through a communication protocol.
After a network session is established, Oracle Net services acts as a data courier for the client application and the database server. It is responsible for establishing and maintaining the connection between the client application and database server, as well as exchanging mesages between them. Oracle Net Services is able to perform these jobs because it is located on each computer in the network.
Oracle Net Services provides location transparency, centralized configuration and management, and quick out-of-the-box installation and configuration. It also lets you maximize system resources and improve performance. Oracle's shared server architecture increases the scalability of applications and the number of clients simultaneously connected to the dtaabase. The Virtual Interface (VI) protocol places most of the messaging burden on high-speed network hardware, freeing the CPU for more important tasks.
How Oracle Net Services Works
Oracle's support of industry network protocols provides an interface between Oracle processes running on the database server and the user processes of Oracle applications running on other computers of the network.
The Oracle protocols take SQL statements from the interface of the Oracle applications and package them for transmission to Oracle through one of the supported industry-standard higher level protocols or programmatic interfaces. The protocols also take replies from Oracle and package them for transmission to the applications through the same higher level communications mechanism. This is all done independently of the network operating system.
Dependently on the operation system that runs Oracle, the Oracle Net Services software of the database server could include the driver software and start an additional Oracle background process.





















 2854
2854











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








