1、Hibernate之生成SessionFactory源码追踪
Hibernate的所有session都是由sessionFactory来生成的,那么,sessionFactory是怎么得来的呢?它与我们配置的xxx.cfg.xml文件以及xxx.hbm.xml文件之间又有着怎么样的联系呢?
先看一小段生成sessionFactory的代码:
code_1:
public class HibernateTest {
@Test
public void test() {
System.out.println("test...");
//1. 创建一个 SessionFactory 对象
SessionFactory sessionFactory = null;
//1). 创建 Configuration 对象: 对应 hibernate 的基本配置信息和 对象关系映射信息
Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure();
//4.0 之前这样创建
//sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory();
//2). 创建一个 ServiceRegistry 对象: hibernate 4.x 新添加的对象
//hibernate 的任何配置和服务都需要在该对象中注册后才能有效.
ServiceRegistry serviceRegistry =
new ServiceRegistryBuilder().applySettings(configuration.getProperties())
.buildServiceRegistry();
//3). 利用serviceRegistry来创建sessionFactory实例
sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory(serviceRegistry);
//2. 创建一个 Session 对象
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
//3. 开启事务
Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
//4. 执行保存操作
News news = new News("Java12345", "ATGUIGU", new Date(new java.util.Date().getTime()));
session.save(news);
//5. 提交事务
transaction.commit();
//6. 关闭 Session
session.close();
//7. 关闭 SessionFactory 对象
sessionFactory.close();
}
}
从上面的代码很清晰的可以看见,这一切的源头都在 Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure() 这条语句上:创建ServiceRegistry 需要用到configuration,生成sessionFactory同样需要用到configuration。
Configuration的生成过程
从源代码中可以看到,Configuration的configure()方法共有5中重载方式:
code_2:
public Configuration configure(); //无参
public Configuration configure(String resource)
public Configuration configure(URL url)
public Configuration configure(File configFile)
public Configuration configure(org.w3c.dom.Document document)
现在从无参的configure()方法开始分析,它代表了一种默认的行为,默认读取类路径下的hibernate.cfg.xml文件作为hibernate的配置文件:
code_3:
public Configuration configure() throws HibernateException {
configure( "/hibernate.cfg.xml" ); //默认读取classpath路径下的hibernate.cfg.xml文件
return this;
}
继续追踪configure( “/hibernate.cfg.xml” )方法:
code_4:
1 public Configuration configure(String resource) throws HibernateException {
2 InputStream stream = getConfigurationInputStream( resource ); //通过传入的资源路径获取一个输入流
3 return doConfigure( stream, resource ); //这个方法会完成解析的第一步:将输入流转换成Document对象
4 }
继续追踪 return doConfigure( stream, resource ) 语句,可以发现底层会通过SAX解析工具将输入流转换成Document对象。然后调用然后调用doConfigure(Document doc)来继续解析这个文档:
code_5:
1 protected Configuration doConfigure(InputStream stream, String resourceName) throws HibernateException {
2
3 ErrorLogger errorLogger = new ErrorLogger( resourceName ); //将输入流转换成Document对象
5 Document document = xmlHelper.createSAXReader( errorLogger, entityResolver )
6 .read( new InputSource( stream ) );
7 //具体解析document树,并将结果以键值对的形式存放到properties中
8 doConfigure( document );
9
10 return this;
11 }
doConfigure(Document doc)是实际解析文档的方法,前面configure()的5种重载方法最后都要调用这个方法来完成实际的解析。我们看看它的解析思路:
code_6:
1 protected Configuration doConfigure(Document doc) throws HibernateException {
2 Element sfNode = doc.getRootElement().element( "session-factory" );
3 String name = sfNode.attributeValue( "name" );
4 if ( name != null ) { //session-factory根节点是可以有name属性值的
5 properties.setProperty( Environment.SESSION_FACTORY_NAME, name );
6 }
7 //遍历文档中所有的property节点,读取器name属性值以及节点的文本,
8 //以name-value的形式放入到properties中
9 addProperties( sfNode );
10 //解析除了property之外的节点:mapping、class-cache、collection-cache
11 parseSessionFactory( sfNode, name );
12
13 Element secNode = doc.getRootElement().element( "security" );
14 if ( secNode != null ) {
15 parseSecurity( secNode );
16 }
17
18 LOG.configuredSessionFactory( name );
19 LOG.debugf( "Properties: %s", properties );
20
21 return this;
22 }
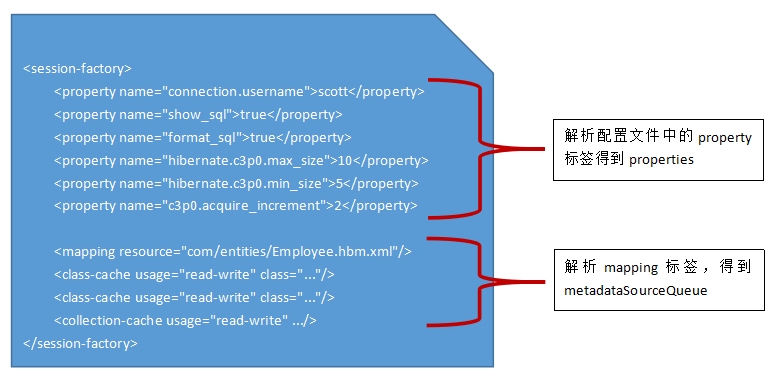
doConfigure(Document doc)方法中对Document的解析主要分为两个步骤进行:
①解析xxx.cfg.xml配置文档中所有的property节点;
②解析xxx.cfg.xml配置文档中除了property节点之外的其它5种节点。
先来看看第
①步,它在addProperties(…)方法中完成(code_6代码段的第9行)思路很清晰,用一个迭代器来遍历文档中所有的property节点,并将name-value存放到Configuration的properties属性中:
code_7:
1 private void addProperties(Element parent) {
2 //指定,只会遍历property节点
3 Iterator itr = parent.elementIterator( "property" );
4 while ( itr.hasNext() ) {//循环遍历
5 Element node = (Element) itr.next();
6 //读取节点的name属性值
7 String name = node.attributeValue( "name" );
8 //读取节点的文本值
9 String value = node.getText().trim();
10 LOG.debugf( "%s=%s", name, value );
11 //将name-value值存放如properties中
12 properties.setProperty( name, value );
13 //待研究...
14 if ( !name.startsWith( "hibernate" ) ) {
15 properties.setProperty( "hibernate." + name, value );
16 }
17 }
18 Environment.verifyProperties( properties );
19 }
再来看看第②步,它在parseSessionFactory( …)方法中进行(code_6代码段的第10行),它主要解析3类标签:mapping、class-cache、collection-cache:
code_8:
1 private void parseSessionFactory(Element sfNode, String name) {
2 Iterator elements = sfNode.elementIterator();
3 while ( elements.hasNext() ) {
4 Element subelement = (Element) elements.next();
5 String subelementName = subelement.getName();
6 //解析mapping节点,mapping可以指定hibernate的映射文件位置
7 if ( "mapping".equals( subelementName ) ) {
8 //具体解析mapping节点
9 parseMappingElement( subelement, name );
10 }
11 //下面两个是和hibernate的二级缓存相关的配置,不做深入探讨
12 else if ( "class-cache".equals( subelementName ) ) {
13 String className = subelement.attributeValue( "class" );
14 Attribute regionNode = subelement.attribute( "region" );
15 final String region = ( regionNode == null ) ? className : regionNode.getValue();
16 boolean includeLazy = !"non-lazy".equals( subelement.attributeValue( "include" ) );
17 setCacheConcurrencyStrategy( className, subelement.attributeValue( "usage" ), region, includeLazy );
18 }
19 else if ( "collection-cache".equals( subelementName ) ) {
20 String role = subelement.attributeValue( "collection" );
21 Attribute regionNode = subelement.attribute( "region" );
22 final String region = ( regionNode == null ) ? role : regionNode.getValue();
23 setCollectionCacheConcurrencyStrategy( role, subelement.attributeValue( "usage" ), region );
24 }
25 }
26 }
后面两个标签class-cache和collection-cache是和hibernate的二级缓存相关,不作深入探讨。主要看看解析mapping的方法:
code_9:
1 private void parseMappingElement(Element mappingElement, String name) {
2 // 从源代码可以看出,mapping节点支持的属性值有5个
3 final Attribute resourceAttribute = mappingElement.attribute( "resource" );
4 final Attribute fileAttribute = mappingElement.attribute( "file" );
5 final Attribute jarAttribute = mappingElement.attribute( "jar" );
6 final Attribute packageAttribute = mappingElement.attribute( "package" );
7 final Attribute classAttribute = mappingElement.attribute( "class" );
8
9 if ( resourceAttribute != null ) {
10 final String resourceName = resourceAttribute.getValue();
11 LOG.debugf( "Session-factory config [%s] named resource [%s] for mapping", name, resourceName );
12 //将hibernate的映射文件作进一步的解析
13 addResource( resourceName );
14 }
15 else if ( fileAttribute != null ) {
16 final String fileName = fileAttribute.getValue();
17 LOG.debugf( "Session-factory config [%s] named file [%s] for mapping", name, fileName );
18 addFile( fileName );
19 }
20 else if ( jarAttribute != null ) {
21 final String jarFileName = jarAttribute.getValue();
22 LOG.debugf( "Session-factory config [%s] named jar file [%s] for mapping", name, jarFileName );
23 addJar( new File( jarFileName ) );
24 }
25 else if ( packageAttribute != null ) {
26 final String packageName = packageAttribute.getValue();
27 LOG.debugf( "Session-factory config [%s] named package [%s] for mapping", name, packageName );
28 addPackage( packageName );
29 }
30 else if ( classAttribute != null ) {
31 final String className = classAttribute.getValue();
32 LOG.debugf( "Session-factory config [%s] named class [%s] for mapping", name, className );
33 try {
34 addAnnotatedClass( ReflectHelper.classForName( className ) );
35 }
36 catch ( Exception e ) {
37 throw new MappingException(
38 "Unable to load class [ " + className
+ "] declared in Hibernate configuration <mapping/> entry",e);
41 }
42 }
43 else {
44 throw new MappingException( "<mapping> element in configuration specifies no known attributes" );
45 }
46 }
addResource( resourceName )是如何解析的呢?那么它是如何工作的呢?这里不再一步一步追踪源代码,因为嵌套太深,直接给出一个感性的认识即可:
在Configuration中定义了一个名为MetadataSourceQueue的内部内,同时Configuration中还有一个该队列的属性值:metadataSourceQueue。
addResource( resourceName )方法嵌套到最后会调用metadataSourceQueue.add(…)方法来将映射的元数据存储到metadataSourceQueue队列中。要使用的时候,从该队列中取就可以了。
metadataSourceQueue的底层存储是一个Map类型…
到现在为止,Configuration对象就得到了,总结一下,其重要的几个点:
1、configure()方法默认读取/hibernate.cfg.xml作为hibernate的配置文件。当然,configure()方法还有其它重载形式可用。
2、doConfigure(Document document)方法会调用两个重要的方法:addProperties( sfNode )和parseSessionFactory( sfNode, name );
3、addProperties( sfNode )方法会解析配置文件中的property节点,并将解析到的name-value放入到properties中
4、parseSessionFactory( sfNode, name )方法会解析配置文件中除了property节点外的其它3个类型的节点(4.2版本):mapping、class-cache和collection-cache
5、mapping配置是和映射相关的,class-cache和collection-cache是与二级缓存相关的。
6、mapping解析的结果会存放到metadataSourceQueue对象中。
7、所以,整个过程得到Configuration中两个重要的属性值:properties和metadataSourceQueue。
2、Spring的LocalSessionFactoryBean创建过程源码分析
spring的LocalSessionFactoryBean生成过程与hibernate的SessionFactory生成过程是高度吻合的。
为了后面源码分析,首先讲解一个接口,一个类的功能:
①、接口InitializingBean
接口的功能:这个接口专门为bean设计的,它只有一个方法。我们知道所有的bean都是由beanFactory来生成的,如果一个bean实现了该接口,在beanFactory为该bean装配好了所有的属性以后,在返回实际bean之前还会调用一次该接口的afterPropertiesSet(…)方法。其设计目的是为了实现个性化,或者是为了检查bean属性值的完整性等。
public interface InitializingBean {
void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception;
}
②、类LocalSessionFactoryBuilder
显然,LocalSessionFactoryBuilder继承自org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration,那么Configuration拥有的属性,LocalSessionFactoryBuilder也具有
public class LocalSessionFactoryBuilder extends Configuration{
//...
}
从LocalSessionFactoryBean源码中分析出其于hibernate的sessionFactory和configuration之间的关系:
public interface InitializingBean {
void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception;
}
//②、类LocalSessionFactoryBuilder
//显然,LocalSessionFactoryBuilder继承自org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration,那么Configuration拥有的属性,LocalSessionFactoryBuilder也具有
public class LocalSessionFactoryBuilder extends Configuration{
//...
}
//现在主要分析LocalSessionFactoryBean
//1、看一下几个非常重要的属性值定义
public class LocalSessionFactoryBean extends... implements InitializingBean, ...{
//数据源
private DataSource dataSource;
//hibernate的配置文件Xxx.cfg.xml所在的
//位置多个可以用","隔开
private Resource[] configLocations;
private String[] mappingResources;
//hibernate的映射文件位置
private Resource[] mappingLocations;
//hibernate的properties属性,存放了配置
//文件中解析property标签的结果
private Properties hibernateProperties;
//hibernate的configuration属性
private Configuration configuration;
//这个sessionfactory是hibernate的sessionFactory
private SessionFactory sessionFactory;
//省略其它的属性以及setter方法...
//注意这个set方法,说明当只有一个配置文件
//的时候可以使用configLocation属性来配置,
//最终也会被转换成configLocations
public void setConfigLocation(Resource configLocation) {
this.configLocations = new Resource[] {configLocation};
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws IOException {
LocalSessionFactoryBuilder sfb = new LocalSessionFactoryBuilder(this.dataSource, this.resourcePatternResolver);
if (this.configLocations != null) {
for (Resource resource : this.configLocations) {
//sfb.configure(...)实际上也就是调用其父类
//org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration的configure(...)方法
//这里完成xxx.cfg.xml文件中property节点
//的解析,得到一个properties
sfb.configure(resource.getURL());
}
}
//mappingResources和mappingLocations效果是一样的,
//都会将资源转换成输入流,并调用sfb.addInputStream(...)方法
//sfb.addInputStream(...)最终会完成xxx.cfg.xml文件的
//非property节点解析(主要有3类:mapping、class-cache和collection-cache)
//将解析结果放入到metadataSourceQueue中
if (this.mappingResources != null) {
for (String mapping : this.mappingResources) {
Resource mr = new ClassPathResource(mapping.trim(), this.resourcePatternResolver.getClassLoader());
sfb.addInputStream(mr.getInputStream());
}
}
if (this.mappingLocations != null) {
for (Resource resource : this.mappingLocations) {
sfb.addInputStream(resource.getInputStream());
}
}
//sfb.addProperties(...)方法会调用properties.putAll( extraProperties )方法
//说明我们可以配置一个properties对象来达到配置xxx.cfg.xml相同的效果!!
//两方面的配置最终都会放入到properties对象中
if (this.hibernateProperties != null) {
sfb.addProperties(this.hibernateProperties);
}
//省略若干其它方法...
// 将sfb向上转型,LocalSessionFactoryBean中的configuration属性实际上
// 就是org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration
this.configuration = sfb;
//在得到configuration以后,通过它来创建一个sessionFactory,
//并赋值给sessionFactory属性(LocalSessionFactoryBean的属性)
//在底层会调用return super.buildSessionFactory()来的到一个
//sessionFactory,由于其父类是org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration
//所以,相当于调用了configuration.buildSessionFactory()来生成
//sessionFactory,这是hibernate4.0版本之前的做法,新版本已经
//被buildSessionFactory(ServiceRegistry)所取代。
this.sessionFactory = buildSessionFactory(sfb);
}
}
总结:
spring的LocalSessionFactoryBean实际完成的工作有:
1、通过解析bean中的configLocation和mappingLocations等属性,得到一个hibernate的原生态的org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration属性
2、通过org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration生成一个hibernate原生态的org.hibernate.SessionFactory属性
3、可以在外部配置一个Properties对象,并将其配置为properties属性,可以达到与xxx.cfg.xml相同的配置效果
3、Spring整合Hibernate
我们可以得到这样一个结论,spring的LocalSessionFactoryBean具体是调用Hibernate的Configuration中configure(…)方法来读取并解析xxx.cfg.xml文件的,同样也会得到一个原生态的org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration 和 org.hibernate.SessionFactory属性。
所以,我们可以看见LocalSessionFactoryBean中保存有hibernate的configuration、sessionFactory、properties 以及 metadataSourceQueue。
从前面两节分析中我们知道,LocalSessionFactoryBean会读取并解析xxx.cfg.xml和xxx.hbm.xml文件,所以在配置LocalSessionFactoryBean的时候需要明确指定这两个文件的位置。当然,连接数据库的dataSource也要配置在spring的bean中:
下面是一个spring整合hibernate的实例:
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
4 xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
5 xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
6 xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
7 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
8 http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.1.xsd
9 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.1.xsd
10 http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.1.xsd">
11
12 <!-- 配置自动扫描的包 -->
13 <!-- 实体和dao -->
14 <context:component-scan base-package="comentity,com.dao.impl"></context:component-scan>
15 <!-- service -->
16 <context:component-scan base-package="com.service.impl"></context:component-scan>
17
18 <!-- 导入数据库资源文件 -->
19 <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties"/>
20
21 <!-- 配置c3p0数据源 -->
22 <bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
23 <property name="user" value="${jdbc.user}"></property>
24 <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
25 <property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}"></property>
26 <property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.jdbcUrl}"></property>
27
28 <property name="initialPoolSize" value="${jdbc.initialPoolSize}"></property>
29 <property name="minPoolSize" value="${jdbc.minPoolSize}"></property>
30 <property name="maxPoolSize" value="${jdbc.maxPoolSize}"></property>
31 <property name="acquireIncrement" value="${jdbc.acquireIncrement}"></property>
32 </bean>
33
34 <!-- 配置sessionFacory -->
35 <bean id="sessionFactory" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate4.LocalSessionFactoryBean">
36 <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
37 <!-- 如果有多个配置文件,可以使用属性configLocations来配置,多个配置文件之间用逗号“,”来分割,
38 如:classpath:hibernate.cfg.xml,classpath:extension.cfg.xml -->
39 <property name="configLocation" value="classpath:hibernate.cfg.xml"></property>
40 <!-- ORM映射关系配置文件 -->
41 <property name="mappingLocations" value="classpath:com/gzpp123/web/entity/*.hbm.xml"></property>
42 </bean>
43
44 <!-- 配置spring的声明式事物 -->
45 <!-- 1、配置hibernate的事物管理器 -->
46 <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate4.HibernateTransactionManager">
47 <property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory"></property>
48 </bean>
49
50 <!-- 2、配置事物属性 -->
51 <tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
52 <tx:attributes>
53 <tx:method name="get*" read-only="true"/>
54 <tx:method name="*"/>
55 </tx:attributes>
56 </tx:advice>
57
58 <!-- 3、配置事物切入点,再把事物属性和事务切入点关联起来 -->
59 <aop:config>
60 <aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.service.*.*(..))" id="txPointcut"/>
61 <aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="txPointcut"/>
62 </aop:config>
63
64 <aop:config>
65 <aop:pointcut expression="execution (* com.service.CoreService.*(..))" id="txPointcut1"/>
66 <aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="txPointcut1"/>
67 </aop:config>
68
69 </beans>
再看看类路径下的db.properties文件:
jdbc.user=root
jdbc.password=tiger123
jdbc.driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.jdbcUrl=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/gzpp
jdbc.initialPoolSize=2
jdbc.maxPoolSize=10
jdbc.minPoolSize=1
jdbc.acquireIncrement=5
#...
#appSecret: 62e5c0141c2fc9a3bc9d2ae73fb7cd12
#appid: wx15fc2152e1406d02
由于mapping以及dataSource都在spring中配置完成了,所以hibernate.cfg.xml文件则相对简单:
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
2 <!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
3 "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
4 "http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
5 <hibernate-configuration>
6 <session-factory>
7
8 <!-- 配置 hibernate 的基本属性 -->
9
10 <!-- 方言 -->
11 <property name="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect</property>
12
13 <!-- 是否显示及格式化 SQL -->
14 <property name="hibernate.show_sql">true</property>
15 <property name="hibernate.format_sql">true</property>
16
17 <!-- 生成数据表的策略 -->
18 <property name="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto">update</property>
19
20 <!-- 二级缓存相关 -->
21
22 </session-factory>
23 </hibernate-configuration>





















 5835
5835











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








