题目描述(中等难度)
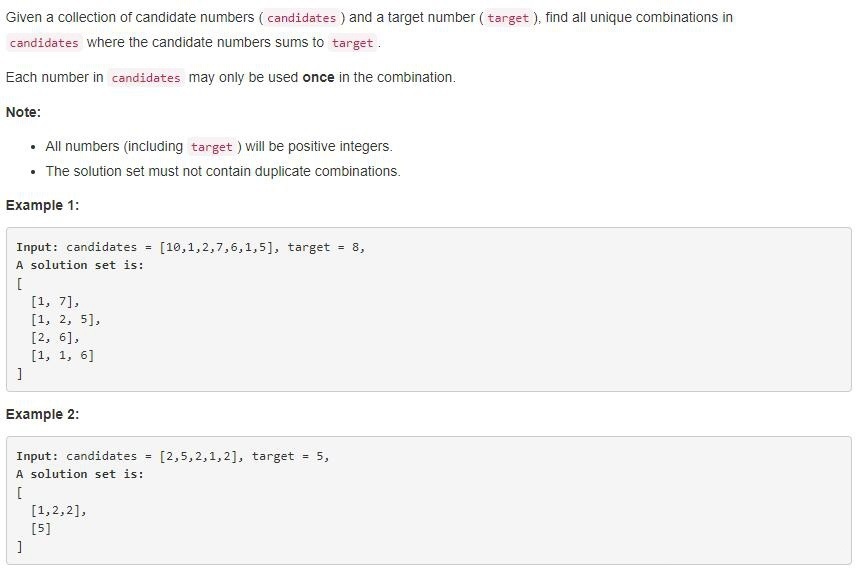
给定一个数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。
candidates 中的每个数字在每个组合中只能使用一次。
说明:
- 所有数字(包括目标数)都是正整数。
- 解集不能包含重复的组合。
和上一道题非常像了,区别在于这里给的数组中有重复的数字,每个数字只能使用一次,然后同样是给出所有和等于 target 的情况。
解法一 回溯法
只需要在上题的基础上改一下就行了。直接看代码吧。
Java
public class Combination_Sum_II {
public static List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<>();
getAnswer(ans, temp, candidates, target, 0);
/*************修改的地方*******************/
// 如果是 Input: candidates = [2,5,2,1,2], target = 5,
// 输出会出现 [2 2 1] [2 1 2] 这样的情况,所以要去重
return removeDuplicate(ans);
}
private static void getAnswer(List<List<Integer>> ans, ArrayList<Integer> temp, int[] candidates, int target, int start) {
if (target == 0) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(temp));
} else if (target < 0) {
return;
} else {
for (int i = start; i < candidates.length; i++) {
temp.add(candidates[i]);
/*************修改的地方*******************/
//i -> i + 1 ,因为每个数字只能用一次,所以下次遍历的时候不从自己开始
getAnswer(ans, temp, candidates, target - candidates[i], i + 1);
/****************************************/
temp.remove(temp.size() - 1);
}
}
}
private static List<List<Integer>> removeDuplicate(List<List<Integer>> list) {
Map<String, String> ans = new HashMap<String, String>();
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
List<Integer> l = list.get(i);
Collections.sort(l);
String key = "";
for (int j = 0; j < l.size() - 1; j++) {
key = key + l.get(j) + ",";
}
key = key + l.get(l.size() - 1);
ans.put(key, "");
}
List<List<Integer>> ans_list = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
for (String k : ans.keySet()) {
String[] l = k.split(",");
List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < l.length; i++) {
int c = Integer.parseInt(l[i]);
temp.add(c);
}
ans_list.add(temp);
}
return ans_list;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int[] nums= {10,1,2,7,6,1,5};
int target=8;
List<List<Integer>> ans=combinationSum2(nums,target);
System.out.println(ans);
}
}

这里我们使用手写函数判断数组是否重复比较麻烦,可以直接在后面加入如下语句,判断是否有重复数组
Arrays.sort(candidates);
while(i<candidates.length-1 && candidates[i] == candidates[i+1]) i++;
完整代码如下:
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<>();
Arrays.sort(candidates);
getAns(ans,temp,candidates,target,0);
return ans;
}
public void getAns(List<List<Integer>> ans,ArrayList<Integer> temp,int[] candidates,int target,int start){
if(target < 0){
return;
}else if(target == 0){
ans.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(temp));
}else{
for(int i = start;i<candidates.length;i++){
temp.add(candidates[i]);
//因为每个数字只能用一次,所以下次遍历的饿时候不从自己开始
getAns(ans,temp,candidates,target-candidates[i],i+1);
temp.remove(temp.size()-1);
while(i<candidates.length-1 && candidates[i] == candidates[i+1]){
i++;
}
}
}
}
}

Python
class Solution(object):
def combinationSum2(self, candidates, target):
ans = []
temp = []
self.getAnswer(ans, temp, candidates, target, 0)
return self.removeDuplicate(ans)
def getAnswer(self,ans, temp, candidates, target, start):
if (target == 0):
ans.append(list(temp))
elif (target < 0):
return
else:
for i in range(start, len(candidates)):
temp.append(candidates[i])
self.getAnswer(ans, temp, candidates, target - candidates[i], i + 1)
del temp[len(temp) - 1]
def removeDuplicate (self,ans):
new_list = []
for i in range(len(ans)):
id = sorted(ans[i])
if id not in new_list:
new_list.append(id)
return new_list

调整之后的代码:
class Solution(object):
def combinationSum2(self, candidates, target):
ans = []
temp = []
candidates = sorted(candidates)
self.getAnswer(ans, temp, candidates, target, 0)
return ans
def getAnswer(self,ans, temp, candidates, target, start):
if (target == 0):
ans.append(list(temp))
elif (target < 0):
return
else:
i = start
while i < len(candidates):
# for i in range(start,len(candidates)):
temp.append(candidates[i])
self.getAnswer(ans, temp, candidates, target - candidates[i], i + 1)
del temp[len(temp) - 1]
if (i < len(candidates) - 1 and candidates[i] == candidates[i + 1]):
while (i < len(candidates) - 1 and candidates[i] == candidates[i + 1]):
i += 1
i+=1
else:
i += 1

在由Java改写成Python的工程中,有一个大坑需要避免,那就是Java和Python中对for循环的不同,来看下例子。
一般,Java中or循环这样写:
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i ++){
if (i == 3){
i = i + 3;
}
System.out.println("i:" + i);
}
输出如下:
i:0
i:1
i:2
i:6
i:7
i:8
i:9
改写成对应的Python语句:
for i in range(10):
if i == 3:
i = i + 3
print ('i:', i)
输出如下:
i: 0
i: 1
i: 2
i: 6
i: 4
i: 5
i: 6
i: 7
i: 8
i: 9
从结果中可以看到Java中当i=3时,i重新赋值,后续循环会跳过4、5的循环,而在Python中,只是修改了当前循环的i值,后续循环不会产生变化,因为Python中的循环遍历的是一个序列,或者可以认为是一个list,所以如果需要处理此情况最好使用while做循环操作判断。 面试过程中会出现这样的坑。























 226
226











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










