Advisory lock vs Mandatory lock
建议锁和强制锁。
- Advisory lock
- 建议性锁并不从内核限制程序访问文件,而是依赖各个合作进程(cooperating process)之间遵循相应的规则。
- 这意味着进程可以自由地忽略 fcntl()(或flock())的使用,而只需对文件执行 I/O。
- Mandatory lock
- 强制内核检查每次open, read, 和 write操作,保证调用进程没有违反对正在访问的文件的锁。
Advisory mode locking is sometimes referred to as discretionary locking, while mandatory locking is sometimes referred to as enforcement-mode locking. SUSv3 doesn’t specify mandatory locking, but it is available (with some variation in the details) on most modern UNIX implementations.
本文介绍flock(),fcntl()。
flock(), which places locks on entire files; and
fcntl(), which places locks on regions of a file.
flock和fcntl在内核中都用struct file_lock实现。其主要差别就在于owner的不同。
如果lock的owner相同,conflict的检测就会跳过,即相同owner的lock可以递归申请。
flock锁的粒度为整个文件。fcntl提供了字节范围粒度的lock,即 byte-range locking。
Flock
- Values for operation:
operation表明锁的类型,需要指明LOCK_SH,LOCK_EX, 和LOCK_UN中的其中一个。
并且如果|LOCK_NB,那么 flock() 不会被阻塞,而是返回error:EWOULDBLOCK。
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| LOCK_SH | 对 fd 引用的文件加共享锁 shared lock |
| LOCK_EX | 对 fd 引用的文件加排他锁 exclusive lock |
| LOCK_UN | 对 fd 引用的文件解锁 |
| LOCK_NB | 非阻塞的锁请求 |
- Capability of flock() locking types :

多个进程可以同时对一个文件持有shared lock,只有一个进程可以对一个文件持有exclusive lock(其他进程不能再持有shared lock或是exclusive lock)。
注意,无论文件的访问模式(read, write, or read-write)如何,进程都可以放置共享或排他锁。
通过再次调用flock() ,可以将现有的共享锁转换为排他锁(反之亦然)。如果另一个进程持有文件上的共享锁,则将共享锁转换为排他锁将阻塞,除非还指定了 LOCK_NB。
Semantics
flock对整个文件上锁。flock的owner是内核态open fd,而不是用户态fd或者inode。
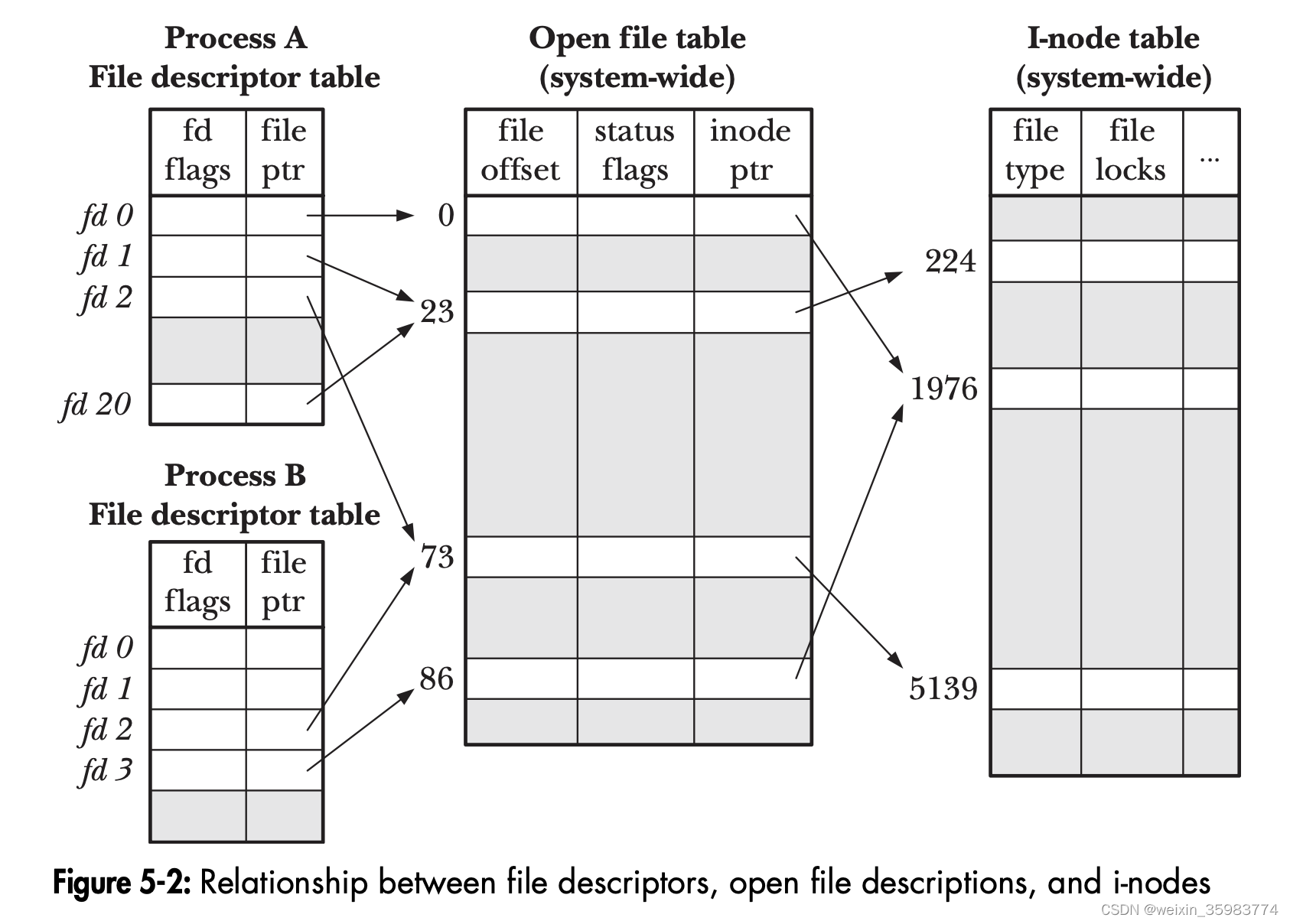
A file lock obtained via flock() is associated with the open file
description , rather than the file descriptor or the file (i-node)
itself.
- 若调用
dup(),dup2(), orfcntl() F_DUPFD复制fd,新的fd指向同一个内核态中的open fd,故指向同一个的file lock。 (以下以go语言做示例)
fd, _ := syscall.Open("lockfile", syscall.O_RDWR, 0644)
newfd, _ := syscall.Dup(fd)
if err = unix.Flock(fd, unix.LOCK_EX|unix.LOCK_NB); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
if err = unix.Flock(newfd, unix.LOCK_EX|unix.LOCK_NB); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
fd和newfd指向同一个open fd,对fd上锁,并不影响通过newfd上锁。
- 若调用
open()获取相同文件的新fd,fd1,fd2对应内核态中不同的open fd。
fd1, _ := syscall.Open("lockfile", syscall.O_RDWR, 0644)
fd2, _ := syscall.Open("lockfile", syscall.O_RDWR, 0644)
if err = unix.Flock(fd1, unix.LOCK_EX|unix.LOCK_NB); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
if err = unix.Flock(fd2, unix.LOCK_UN|unix.LOCK_NB); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err) /*return: resource temporarily unavailable, Locked out by lock on 'fd1'*/
}
对fd2上锁被阻塞。
Limitation
- 锁的粒度为整个文件。
- 只能为advisory locks
- Many NFS implementations don’t recognize locks granted by flock().
Fcntl
flock structure
struct flock {
short l_type; /* Lock type: F_RDLCK, F_WRLCK, F_UNLCK */
short l_whence; /* How to interpret 'l_start': SEEK_SET, SEEK_CUR, SEEK_END */
off_t l_start;/* Offset where the lock begins */
off_t l_len;/* Number of bytes to lock; 0 means "until EOF" */
pid_t l_pid; /* Process preventing our lock (F_GETLK only) */
};
锁的类型
l_type表明想要加的锁的类型, 可以为下表的其中之一。F_RDLCK,F_WRLCK分别对应 flock() 中的LOCK_SH和LOCK_EX,F_UNLCK可以类比LOCK_UN。
| Lock type | Description |
|---|---|
| F_RDLCK | 加写锁 |
| F_WRLCK | 加读锁 |
| F_UNLCK | 移除已有的锁 |
注意,如果要加读锁,那么文件必须以读权限打开。同样,加写锁,需要以写权限打开。如果加锁但权限不够,返回EBADF。
锁的范围
l_whence, l_start, 和 l_len规定了锁作用的字节范围,锁的开始位置由l_start,l_whence共同决定。
- l_start: 开始位置的偏移量
- l_whence:开始的位置。
当l_whence为SEEK_CUR或SEEK_END时,l_start可以为负数。
| l_whence可选参数 | Description |
|---|---|
| SEEK_SET | the start of the file |
| SEEK_CUR | the current file offset |
| SEEK_END | the end of the file |
-
l_len : 锁定文件的长度
l_len设为0有特殊的含义:锁定从 l_start 和 l_whence 指定的点到文件末尾的所有字节,无论文件增长多大。
若锁定整个文件,通常将
l_whence设为SEEK_SET,l_start设为0,l_len设为0.
cmd
- F_SETLK: 给当前文件上锁 (
l_type为 F_RDLCK 或 F_WRLCK) 或 释放锁 (l_type为 F_UNLCK) - F_SETLKW :阻塞状态的 F_SETLK,当前文件正在被锁住,该函数一直阻塞。
- F_GETLK: 获取当前锁的状态(
l_type必须为 F_RDLCK 或 F_WRLCK)
将不同模式的锁放在我们已经持有的锁中间会产生三个锁:在新锁的两侧创建两个先前模式中的较小锁。
Splitting of an existing read lock by a write lock by the same process:

record lock与进程和inode关联。当一个进程终止时,它的所有record lock都被释放。每当一个进程关闭一个文件描述符时,该进程在相应文件上持有的所有锁都会被释放,而不管获得锁的文件描述符是什么。
Reference
- The Linux Programming Interface Chapter 55.
- Advanced Programming in the UNIX Environment 14.3








 本文对比了Advisorylock的建议性模型与Mandatorylock的强制内核检查机制,讨论了flock和fcntl在Linux中的应用,包括锁的类型、粒度、并发控制和局限性。特别关注了flock对整个文件的锁定以及fcntl的字节范围锁定。
本文对比了Advisorylock的建议性模型与Mandatorylock的强制内核检查机制,讨论了flock和fcntl在Linux中的应用,包括锁的类型、粒度、并发控制和局限性。特别关注了flock对整个文件的锁定以及fcntl的字节范围锁定。


















 9881
9881

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








