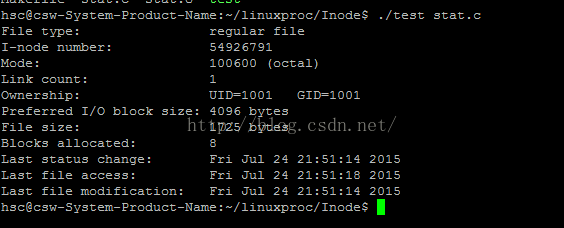
1.stat既有命令也有同名函数,用来获取文件Inode里主要信息(即文件类型、文件权限、创建/修改/访问时间等就是ls -l看到的相关的信息),stat 跟踪符号链接,lstat不跟踪符号链接。可以通过man 2 stat查看相关的信息。
#include
#include
#include
int stat(const char *path, struct stat *buf);
int fstat(int fd, struct stat *buf);
int lstat(const char *path, struct stat *buf);
struct stat {
dev_t st_dev; /* ID of device containing file */
ino_t st_ino; /* inode number */
mode_t st_mode; /* protection */
nlink_t st_nlink; /* number of hard links */
uid_t st_uid; /* user ID of owner */
gid_t st_gid; /* group ID of owner */
dev_t st_rdev; /* device ID (if special file) */
off_t st_size; /* total size, in bytes */
blksize_t st_blksize; /* blocksize for filesystem I/O */
blkcnt_t st_blocks; /* number of 512B blocks allocated */
time_t st_atime; /* time of last access */
time_t st_mtime; /* time of last modification */ //指的是修改文件内容
time_t st_ctime; /* time of last status change */ //指的是修改inode属性
};
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
struct stat filestat;
if (argc < 2)
{
printf("Usage: %s \n", argv[0]);
return 0;
}
if (stat(argv[1], &filestat) == -1)
{
perror("stat error:");
return 0;
}
printf("File type: ");
switch (filestat.st_mode & S_IFMT)// 0170000 bit mask for the file type bit fields
{
case S_IFBLK:
printf("block device\n");
break;
case S_IFCHR:
printf("character device\n");
break;
case S_IFDIR:
printf("directory\n");
break;
case S_IFIFO:
printf("FIFO/pipe\n");
break;
case S_IFLNK:
printf("symlink\n");
break;
case S_IFREG:
printf("regular file\n");
break;
case S_IFSOCK:
printf("socket\n");
break;
default:
printf("unknown?\n");
break;
}
printf("I-node number: %ld\n", (long) filestat.st_ino);
printf("Mode: %lo (octal)\n",
(unsigned long) filestat.st_mode);
printf("Link count: %ld\n", (long) filestat.st_nlink);
printf("Ownership: UID=%ld GID=%ld\n", (long) filestat.st_uid,
(long) filestat.st_gid);
printf("Preferred I/O block size: %ld bytes\n", (long) filestat.st_blksize);
printf("File size: %lld bytes\n", (long long) filestat.st_size);
printf("Blocks allocated: %lld\n", (long long) filestat.st_blocks);
printf("Last status change: %s", ctime(&filestat.st_ctime));
printf("Last file access: %s", ctime(&filestat.st_atime));
printf("Last file modification: %s", ctime(&filestat.st_mtime));
return 0;
}
2.access函数
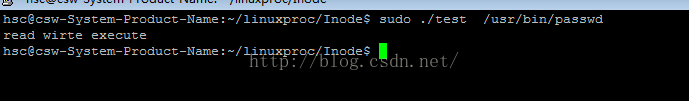
功 能: 确定文件或文件夹的访问权限。即,检查某个文件的存取方式,比如说是只读方式、只写方式等。如果指定的存取方式有效,则函数返回0,否则函数返回-1。
#include
int access(const char *pathname, int mode);按实际用户ID和实际组ID测试,跟踪符号链接
参数mode
R_OK 是否有读权限
W_OK 是否有写权限
X_OK 是否有执行权限
F_OK 测试一个文件是否存在
#include
#include
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc < 2)
{
printf("Usage: %s \n", argv[0]);
return 0;
}
if(access(argv[1],R_OK|X_OK|W_OK)==0)
{
printf("read wirte execute \n");
}
return 0;
}
版权声明:欢迎转载,如有不足之处,恳请斧正。
原文:http://blog.csdn.net/huangshanchun/article/details/47045523





















 6634
6634











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








