背景
Dropout原文:Dropout: A Simple Way to Prevent Neural Networks from Overfi tting 发表于2014年。
提出Dropout的目的是为了解决深度神经网络中的如下问题:
- 参数过多,训练速度慢
- 过拟合
Dropout关键思想:在训练过程中从神经网络中随机删除单元(及其连接),这样可以防止单元之间的相互适应过多。
原理
训练阶段:
假设神经元被保留的概率为
p
p
p,则在前向传播中,神经元以
1
−
p
1-p
1−p概率被删除,并同时删除它的所有连接,包括income和outcome。
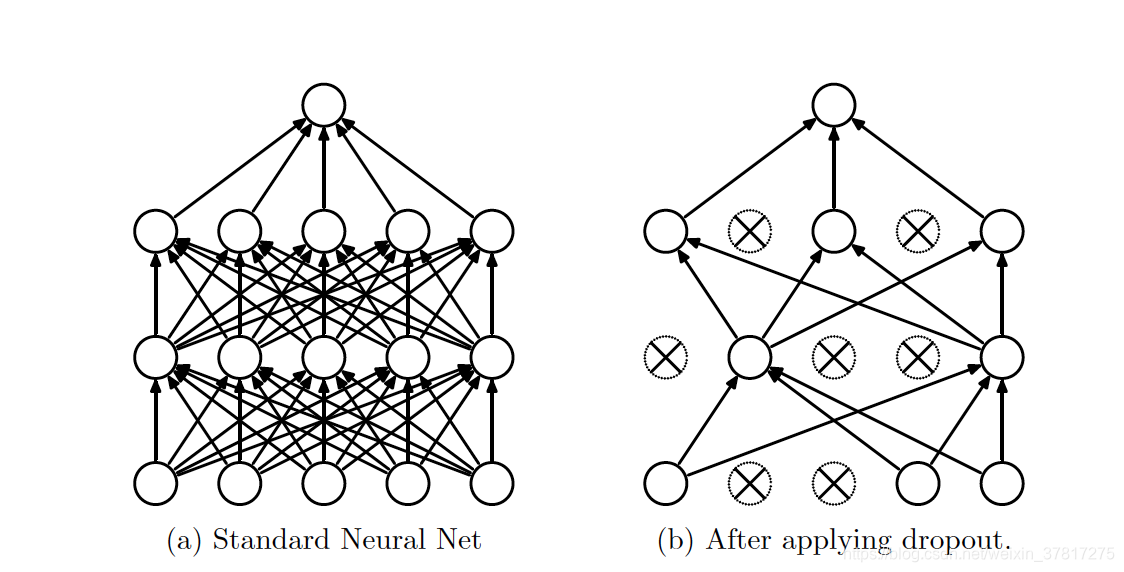
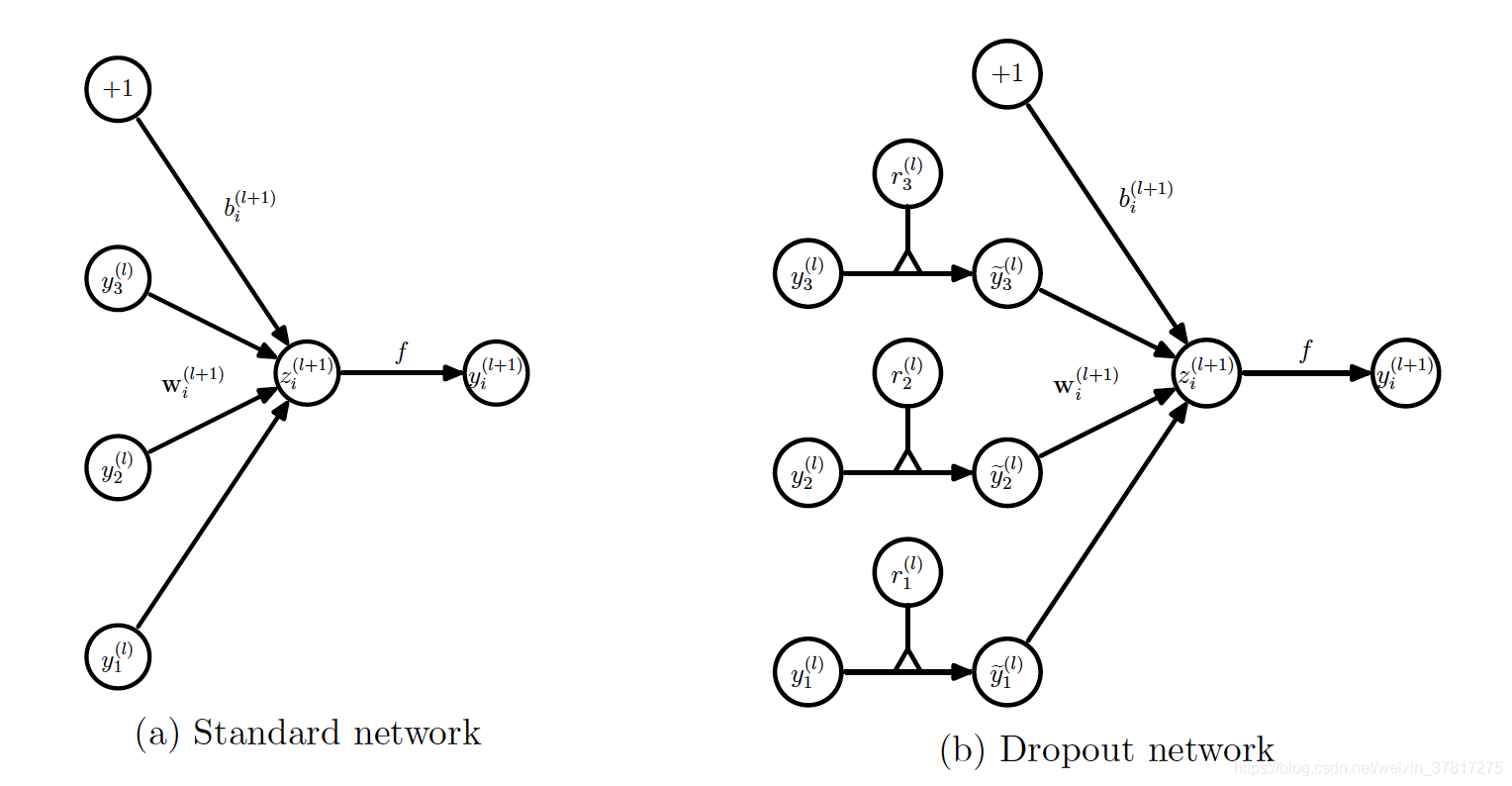
假设神经网络有L个隐藏层
l
∈
{
1
,
2
,
.
.
.
,
L
}
l \in \{1, 2, ..., L\}
l∈{1,2,...,L}代表隐藏层的下标,
z
(
l
)
z^{(l)}
z(l)表示第
l
l
l层输入,
y
(
l
)
y^{(l)}
y(l)表示第
l
l
l层输出,
W
(
l
)
,
b
(
l
)
W^{(l)}, b^{(l)}
W(l),b(l)表示第
l
l
l层参数。则标准神经网络前向传播过程如下:
z
i
(
l
+
1
)
=
w
i
(
l
+
1
)
y
(
l
)
+
b
i
(
l
+
1
)
y
(
l
+
1
)
=
f
(
z
i
(
l
+
1
)
)
z_i^{(l+1)}=w_i^{(l+1)}y^{(l)}+b_i^{(l+1)}\\ y^{(l+1)}=f(z_i^{(l+1)})
zi(l+1)=wi(l+1)y(l)+bi(l+1)y(l+1)=f(zi(l+1))
其中f代表激活函数
添加Dropout后,前向传播过程如下:
r
j
(
l
)
=
B
e
r
n
o
u
l
l
i
(
p
)
y
~
(
l
)
=
r
j
(
l
)
∗
y
(
l
)
z
i
(
l
+
1
)
=
w
i
(
l
+
1
)
y
~
(
l
)
+
b
i
(
l
+
1
)
y
(
l
+
1
)
=
f
(
z
i
(
l
+
1
)
)
r_j^{(l)}=Bernoulli(p)\\ \widetilde{y}^{(l)}=r_j^{(l)}*y^{(l)}\\ z_i^{(l+1)}=w_i^{(l+1)}\widetilde{y}^{(l)}+b_i^{(l+1)}\\ y^{(l+1)}=f(z_i^{(l+1)})
rj(l)=Bernoulli(p)y
(l)=rj(l)∗y(l)zi(l+1)=wi(l+1)y
(l)+bi(l+1)y(l+1)=f(zi(l+1))
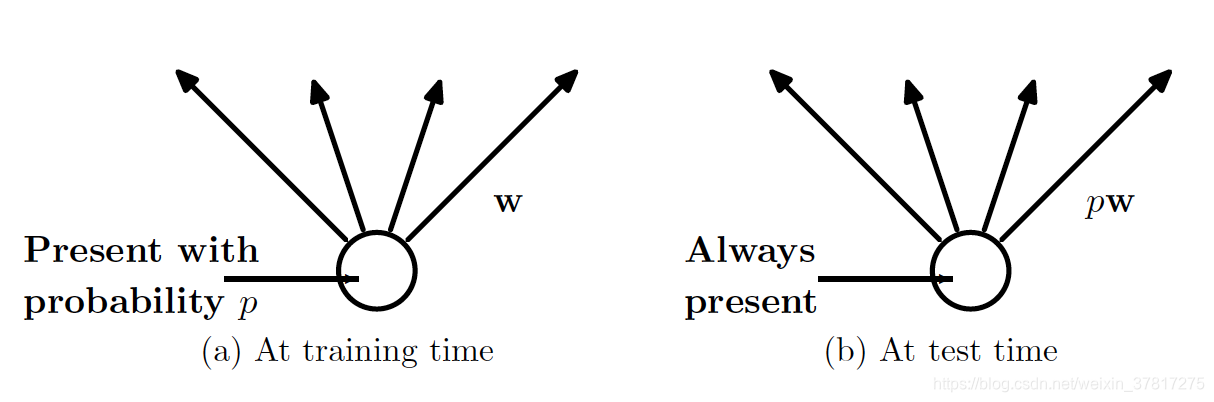
测试阶段:
如果在训练期间以概率p保留一个单位,则在测试时将该单位的输出权重乘以p,如图所示。
模型的使用
- 通过MBGD (Mini-Batch Gradient Descent) 训练Dropout神经网络。和传统MBGD的区别是,对于Mini-Batch中的每个train案例,我们都通过剔除神经元来对网络进行采样,也就是每个Batch,都对神经网络进行一次Dropout。
- 最后每个神经元参数的梯度在所有Mini-Batch的训练案例中取平均值。 任何不使用参数的训练案例都会为该参数贡献零梯度。
模型改善
- 使用Momentum梯度下降法
- 使用退火的学习速率
- L2权重衰减





















 346
346











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








