SpringBoot
-
为什么要使用 Spring Boot
因为Spring, SpringMVC 需要使用的大量的配置文件 (xml文件)
还需要配置各种对象,把使用的对象放入到spring容器中才能使用对象
需要了解其他框架配置规则。
-
SpringBoot 就相当于 不需要配置文件的Spring+SpringMVC。 常用的框架和第三方库都已经配置好了。拿来就可以使用了。
-
SpringBoot开发效率高,使用方便多了
1.1 第一章 Xml 和 JavaConfig
Spring 使用 Xml 作为容器配置文件, 在 3.0 以后加入了 JavaConfig. 使用 java 类做配置文件使用。
1.1.1 什么是 JavaConfig
JavaConfig: 是 Spring 提供的使用 java 类配置容器。 配置 Spring IOC 容器的纯 Java 方法。
优点:
1.可以使用面像对象的方式, 一个配置类可以继承配置类,可以重写方法
2.避免繁琐的 xml 配置
JavaConfig: 使用java类作为xml配置文件的替代, 是配置spring容器的纯java的方式。 在这个java类这可以创建java对象,把对象放入spring容器中(注入到容器)。
使用两个注解:1)@Configuration : 放在一个类的上面,表示这个类是作为配置文件使用的。
2)@Bean:声明对象,把对象注入到容器中。
1.1.2 Xml 配置容器的方式
pom文件
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<!-- 编译插件 -->
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<!-- 插件的版本 -->
<version>3.1</version>
<!-- 编译级别 -->
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
<!-- 编码格式 -->
<encoding>UTF-8</encoding>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
创建数据类 Student
public class Student {
String name;
Integer age;
String sex;
resources 目录下创建 Spring 的配置文件 applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<bean id="myCat" class="com.link.vo.Cat">
<property name="name" value="tom猫"/>
<property name="age" value="2" />
<property name="cardId" value="uw532423422"/>
</bean>
<!-- <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:config.properties" />-->
<!-- <context:component-scan base-package="com.link.vo" />-->
<!-- <import resource="classpath:beans.xml" />-->
</beans>
单元测试:
/**
* 使用xml作为容器配置文件
*/
@Test
public void test01(){
String config="beans.xml";
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(config);
Student myStudent = context.getBean("myStudent", Student.class);
System.out.println("容器中的对象:"+myStudent);
}
1.1.3 JavaConfig 配置容器的方式
JavaConfig 主要使用的注解
@Configuration:放在类的上面, 这个类相当于 xml 配置文件,可以在其中声明 bean
@Bean:放在方法的上面, 方法的返回值是对象类型, 这个对象注入到 spring ioc 容器
创建配置类(等同于 xml 配置文件)
/**
* Configuration:表示当前类是作为配置文件使用的。 就是用来配置容器的
* 位置:在类的上面
*
* SpringConfig这个类就相当于beans.xml
*/
@Configuration
@ImportResource(value = {"classpath:applicationContext.xml","classpath:beans.xml"})
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:config.properties")
@ComponentScan(value = "com.link.vo")
public class SpringConfig {
/**
/**
/**
/**
* 创建方法,方法的返回值是对象。 在方法的上面加入@Bean
* 方法的返回值对象就注入到容器中。
*
* @Bean: 把对象注入到spring容器中。 作用相当于<bean>
* 位置:方法的上面
* 说明:@Bean,不指定对象的名称,默认是方法名是 id
*/
@Bean
public Student createStudent()
{
Student s1 = new Student();
s1.setName("张三");
s1.setAge(20);
s1.setSex("男");
return s1;
}
/***
* 指定对象在容器中的名称(指定<bean>的id属性)
* @Bean的name属性,指定对象的名称(id)
*/
@Bean(name="lisiStudent")
public Student makeStudent(){
Student s2 = new Student();
s2.setName("李四");
s2.setAge(25);
s2.setSex("男");
return s2;
}
}
测试方法:
/**
* 使用JavaConfig
*/
@Test
public void test02(){
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
Student student = ctx.getBean("createStudent", Student.class);
System.out.println("使用JavaConfig创建的bean对象:"+student);
}
@Test
public void test03(){
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
Student student = (Student) ctx.getBean("lisiStudent");
System.out.println("使用JavaConfig创建的bean对象:"+student);
}
1.1.4 @ImportResource
@ImportResource 作用导入其他的xml配置文件, 等同于 xml 文件的 resources
<import resources="其他配置文件"/>
创建数据类:
public class Cat {
private String cardId;
private String name;
private Integer age;
创建配置文件 applicationContext.xml
<bean id="myCat" class="com.link.vo.Cat">
<property name="name" value="tom猫"/>
<property name="age" value="2" />
<property name="cardId" value="uw532423422"/>
</bean>
创建配置类:
/**
* Configuration:表示当前类是作为配置文件使用的。 就是用来配置容器的
* 位置:在类的上面
*
* SpringConfig这个类就相当于beans.xml
*/
@Configuration
@ImportResource(value = {"classpath:applicationContext.xml","classpath:beans.xml"})
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:config.properties")
@ComponentScan(value = "com.link.vo")
public class SpringConfig {
/**
/**
/**
/**
* 创建方法,方法的返回值是对象。 在方法的上面加入@Bean
* 方法的返回值对象就注入到容器中。
*
* @Bean: 把对象注入到spring容器中。 作用相当于<bean>
* 位置:方法的上面
* 说明:@Bean,不指定对象的名称,默认是方法名是 id
*/
@Bean
public Student createStudent()
{
Student s1 = new Student();
s1.setName("张三");
s1.setAge(20);
s1.setSex("男");
return s1;
}
/***
* 指定对象在容器中的名称(指定<bean>的id属性)
* @Bean的name属性,指定对象的名称(id)
*/
@Bean(name="lisiStudent")
public Student makeStudent(){
Student s2 = new Student();
s2.setName("李四");
s2.setAge(25);
s2.setSex("男");
return s2;
}
}
创建测试方法:
@Test
public void test04()
{
ApplicationContext ctx=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
Cat myCat = ctx.getBean("myCat", Cat.class);
System.out.println("容器中使用ImportResource从xml文件导入的对象:"+myCat);
Student student = ctx.getBean("myStudent", Student.class);
System.out.println("容器中使用ImportResource从xml文件导入的对象:"+student);
}
1.1.5 @PropertyResource
@PropertyResource: 读取properties属性配置文件。 使用属性配置文件可以实现外部化配置 .
步骤:
- 在resources目录下,创建properties文件, 使用k=v的格式提供数据
- 在PropertyResource 指定properties文件的位置
- 使用@Value(value="${key}")
1.在resources目录下,创建properties文件, 使用k=v的格式提供数据
tiger.name="大老虎"
tiger.age=3
创建数据类 Tiger
@Component("tiger")
public class Tiger {
@Value("${tiger.name}")
private String name;
@Value("${tiger.age}")
private Integer age;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Tiger{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
2.在PropertyResource 指定properties文件的位置
/**
* Configuration:表示当前类是作为配置文件使用的。 就是用来配置容器的
* 位置:在类的上面
*
* SpringConfig这个类就相当于beans.xml
*/
@Configuration
@ImportResource(value = {"classpath:applicationContext.xml","classpath:beans.xml"})
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:config.properties")
@ComponentScan(value = "com.link.vo")
public class SpringConfig {
/**
/**
/**
/**
* 创建方法,方法的返回值是对象。 在方法的上面加入@Bean
* 方法的返回值对象就注入到容器中。
*
* @Bean: 把对象注入到spring容器中。 作用相当于<bean>
* 位置:方法的上面
* 说明:@Bean,不指定对象的名称,默认是方法名是 id
*/
@Bean
public Student createStudent()
{
Student s1 = new Student();
s1.setName("张三");
s1.setAge(20);
s1.setSex("男");
return s1;
}
/***
* 指定对象在容器中的名称(指定<bean>的id属性)
* @Bean的name属性,指定对象的名称(id)
*/
@Bean(name="lisiStudent")
public Student makeStudent(){
Student s2 = new Student();
s2.setName("李四");
s2.setAge(25);
s2.setSex("男");
return s2;
}
}
测试
@Test
public void test05(){
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
Tiger tiger = (Tiger) ctx.getBean("tiger");
System.out.println("tiger=="+tiger);
}
注解的方式和xml的方式对比
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:config.properties")读取配置文件,
@Component("tiger") 使用注解的方式创建javabean
@ComponentScan(value = "com.link.vo") 扫描vo下所有使用注解方式创建的javabean
@ImportResource(value = {"classpath:applicationContext.xml","classpath:beans.xml"}) 导入其他xml文件
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:config.properties" />
<context:component-scan base-package="com.link.vo" />
<import resource="classpath:beans.xml" />
1.2 第二章 Spring Boot 入门
1.2.1 第一种方式:https://start.spring.io
第一种方式, 使用Spring提供的初始化器, 就是向导创建SpringBoot应用
使用 spring boot 提供的初始化器。 向导的方式,完成 spring boot 项目的创建: 使用方便。
1.2.1.1 创建项目步骤
step 1: 新建项目

step 2

step 3 选择依赖

step 4 : 最后创建项目,设置项目的目录位置
step 5: Spring Boot 项目目录结构

1.2.1.2 起步依赖

1.2.2 第二种方式,使用 springboot 提供的初始化器, 使用的国内的地址
国内地址: https://start.springboot.io
创建项目的步骤同上

1.2.3 第三种方式 使用 maven 向导创建项目
创建一个普通 maven 项目


点击 finish 创建,完成项目创建。

添加 Spring Boot 依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
创建启动类:加入@SpringBootApplication 注解
package com.bjpowernode;
@SpringBootApplication
public class MySpringBootMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MySpringBootMain.class,args);
}
}
1.2.3.1 重要注解
@SpringBootApplication : @SpringBootApplication 是 一 个 复 合 注 解 , 是 由@SpringBootConfiguration,@EnableAutoConfiguration ,@ComponentScan 联合在一起组成的。
@SpringBootConfiguration : 就 是 @Configuration 这 个 注 解 的 功 能 , 使 用@SpringBootConfiguration 这个注解的类就是配置文件的作用。
@EnableAutoConfiguration:开启自动配置, 把一些对象加入到 spring 容器中。
@ComponentScan:组件扫描器, 扫描注解,根据注解的功能,创建 java bean,给属性赋值等等。组件扫描器默认扫描的是 @ComponentScan 注解所在的类, 类所在的包和子包。
1.2.4 Spring Boot 核心配置文件
Spring Boot 的核心配置文件用于配置 Spring Boot 程序,名字必须以 application 开始
配置文件名称: application
扩展名有: properties( k=v) ; yml ( k: v)
使用application.properties, application.yml
1.2.4.1 .properties 文件(默认采用该文件)
通过修改 application.properties 配置文件,在修改默认 tomcat 端口号及项目上下文件根键值对的 properties 属性文件配置方式
#设置端口号
server.port=8082
#设置访问应用的上下文路径 context
server.servlet.context-path=/myboot
启动应用, 在浏览器访问 http://localhost:8082/myboot/
1.2.4.2 .yml 文件
yml 是一种 yaml 格式的配置文件,主要采用一定的空格、换行等格式排版进行配置。
yaml 是一种直观的能够被计算机识别的的数据序列化格式,容易被人类阅读,yaml 类似于 xml,但是语法比 xml 简洁很多,值与前面的冒号配置项必须要有一个空格, yml 缀也可以使用 yaml 后缀
server:
port: 8083
servlet:
context-path: /myboot
注意 : 当两种格式配置文件同时存在 ,在 SpringBoot2.4 开始, 使用的是 yml 配置文件.修改配置名称都为 application。
当properties、yaml和yml三种文件路径相同时,三个文件中的配置信息都会生效,但是当三个文件中有配置信息冲突时,加载顺序是:yml > yaml > properties
yml的优先级会大于properties,所以如果同时存在这两种配置,因为properties是后加载的,所以此时yml就没有生效。由里向外加载,所以最外层的最后被加载,会覆盖里层的属性,最后被加载。所以最后生效的是properties 。
推荐使用 yml 格式配置文件
1.2.4.3 多环境配置
在实际开发的过程中,我们的项目会经历很多的阶段(开发->测试->上线),每个阶段的配置也会不同,例如:端口、上下文根、数据库等,那么这个时候为了方便在不同的环境之间切换,SpringBoot 提供了多环境配置,具体步骤如下
为每个环境创建一个配置文件,命名必须以 application-环境标识.properties|yml

application.properties
#激活使用哪个配置文件
#使用dev
#spring.profiles.active=dev
#使用test
spring.profiles.active=test
application-dev.yml
server:
port: 8081
servlet:
context-path: /mydev
application-online.yml
server:
port: 9002
servlet:
context-path: /myonline
application-test.yml
server:
port: 9001
servlet:
context-path: /mytest
1.2.4.4 Spring Boot 自定义配置
SpringBoot 的核心配置文件中,除了使用内置的配置项之外,我们还可以在自定义配置,然后采用如下注解去读取配置的属性值
1.2.4.4.1 @Value 注解
@Value("${key}") , key 来自 application.properties(yml)
application.properties:添加两个自定义配置项 school.name 和 school.website。
server.port=8082
server.servlet.context-path=/myboot
#自定义k-v
school.name=linkacademy
school.website=www.linkacademy.com
school.address=成都市
site=www.baidu.com
读取配置文件数据


启动应用 Application , 访问浏览器
1.2.4.4.2 @ConfigurationProperties
@ConfigurationProperties: 把配置文件的数据映射为java对象。
属性:prefix 配置文件中的某些key的开头的内容。
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "school")
public class Academy {
private String name;
private String website;
private String address;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getWebsite() {
return website;
}
public void setWebsite(String website) {
this.website = website;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Academy{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", website='" + website + '\'' +
", address='" + address + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@Value("${server.port}")
private Integer port;
@Value("${server.servlet.context-path}")
private String contextPath;
@Value("${site}")
private String site;
@Resource
private Academy academy;
@RequestMapping(value = "/data")
@ResponseBody
public String QueryDate()
{
return "prot:"+port+",contextPath:"+contextPath+",site:"+site+",site:"+site+",academy:"+academy;
}
}
执行 Application , 访问浏览器查看数据
1.2.4.4.3 警告解决
在 SchoolInfo 类中使用了 ConfigurationProperties 注解,IDEA 会出现一个警告,不影响程序的执行
点击 open documentnation 跳转到网页,在网页中提示需要加一个依赖,我们将这个依赖拷贝,粘贴到 pom.xml 文件中
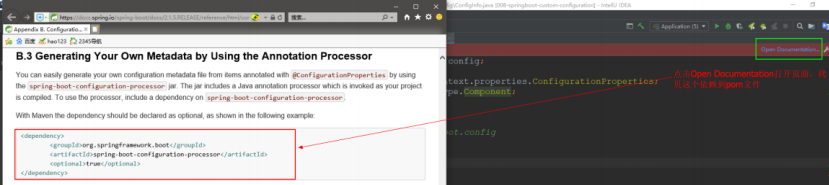
<!--解决使用@ConfigurationProperties 注解出现警告问题-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
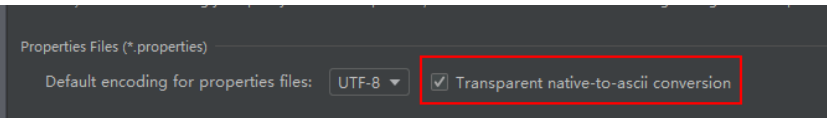
1.2.4.4.4 中文乱码
如果在 SpringBoot 核心配置文件中有中文信息,会出现乱码:
◼ 一般在配置文件中,不建议出现中文(注释除外)
◼ 如果有,可以先转化为 ASCII 码
1.2.5 Spring Boot 中使用 JSP
1.2.5.1 在 pom.xml 文件中配置以下依赖项
<dependencies>
<!--处理jsp依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-embed-jasper</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
1.2.5.2 在 pom.xml 的 build 标签中要配置以下信息
SpringBoot 要求 jsp 文件必须编译到指定的 META-INF/resources 目录下才能访问,否则访问不到。其实官方已经更建议使用模板技术(后面会讲模板技术)
<!--指定jsp编译后的存放目录-->
<resources>
<resource>
<!--jsp原来的目录-->
<directory>src/main/webapp</directory>
<!--指定编译后的存放目录-->
<targetPath>META-INF/resources</targetPath>
<!--指定处理的目录和文件-->
<includes>
<include>**/*.*</include>
</includes>
</resource>
</resources>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
1.2.5.3 在 application.properties 文件配置 Spring MVC 的视图展示为
jsp,这里相当于 Spring MVC 的配置
spring.mvc.view.prefix=/
spring.mvc.view.suffix=.jsp
1.2.5.4 在 com.bjpowernode.springboot.controller 包 下 创 建JspController 类,并编写代码
@Controller
public class JspController {
/*public String doJsp(HttpServletRequest request){
request.setAttribute("data","SpringBoot使用Jsp");
//视图的逻辑名称
return "index";
}*/
/**
* ModelAndView:
* @param model
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/myjsp")
public String doJsp(Model model){
//把数据放入到request作用域
model.addAttribute("data","SpringBoot使用Jsp");
//request.setAttribute("data","SpringBoot使用Jsp");
//视图的逻辑名称
return "index";
}
}
1.2.5.5 在 src/main 下创建一个 webapp 目录,然后在该目录下新建index.jsp 页面
如果在webapp目录下右键,没有创建jsp的选项,可以在Project Structure中指定webapp
为 Web Resource Directory

1.2.5.6 在 jsp 中获取 Controller 传递过来的数据
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>jsp文件</title>
</head>
<body>
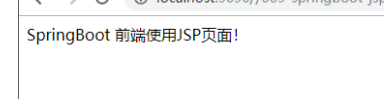
<h3>使用jsp,显示Controller中的数据 ${data}</h3>
</body>
</html>
1.2.5.7 重新运行 Application,通过浏览器访问测试
1.2.6 Spring Boot 中使用 ApplicationContext
在 main 方法中 SpringApplication.run()方法获取返回的 Spring 容器对象,再获取业务 bean进行调用.
本质上是通过SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args); 返回值获取容器。
1.创建一个接口 UserService 和他的实现类
public interface UserService {
void sayHello(String name);
}
2.创建启动类, main 方法中创建ConfigurableApplicationContext对象获取容器对象
@SpringBootApplication
public class Ch10SpringbootContainerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext ctx= SpringApplication.run(Ch10SpringbootContainerApplication.class, args);
UserService userService = ctx.getBean("userService", UserService.class);
userService.sayHello("李四");
}
}
1.2.7 CommandLineRunner 接口
开发中可能会有这样的情景。需要在容器启动后执行一些内容。比如读取配置文件,数据库连接之类的。SpringBoot 给我们提供了两个接口来帮助我们实现这种需求。这两个接口分别为 CommandLineRunner 和 ApplicationRunner。他们的执行时机为容器启动完成的时候。
public interface HelloService {
String sayHello(String name);
}
@Service("helloService")
public class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService {
@Override
public String sayHello(String name) {
return "你好:"+name;
}
}
@SpringBootApplication
public class Ch11SpringbootCommandlinerunnerApplication implements CommandLineRunner {
@Resource
private HelloServiceImpl helloService;
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("准备创建容器对象");
//创建容器对象
ConfigurableApplicationContext ctx = SpringApplication.run(Ch11SpringbootCommandlinerunnerApplication.class, args);
System.out.println("容器对象创建之后");
}
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
String str = helloService.sayHello("lisi");
System.out.println("调用容器中的对象="+str);
//可做自定义的操作,比如读取文件, 数据库等等
System.out.println("在容器对象创建好,执行的方法");
}
}
注意:@SpringBootApplication 启动类必须放在项目的根目录与所有包平级,一般在main方法内部通过执行
main方法启动类位于项目根目录的原因
@ComponentScan注解有个特性:如果不指定需要扫描的包或者需要注册的类,则默认是扫描该使用@ComponentScan注解的类所在的包以及子包,所以将使用了@SpringBootApplication注解的包含main方法的启动类放在项目根目录,则会扫描项目的所有包。
除了@ComponentScan注解之外,@EnableAutoConfiguration注解也是扫描使用了这个注解的类所在的包及其子包,故放在项目根目录,则可以扫描项目所有的包,对所有的类(具体为使用Spring容器管理的)进行检测,从而决定是否需要自动创建功能组件类的bean对象到spring的IOC容器中。
1.3 第三章 Spring Boot 和 web 组件
1.3.1 SpringBoot 中拦截器
1.3.1.1SpringMVC 使用拦截器
SpringMVC 使用拦截器
1)自定义拦截器类,实现 HandlerInterceptor 接口
2)注册拦截器类
//拦截器类:拦截用户的请求。
public class MyInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
System.out.println("111111-拦截器的MyInterceptor的preHandle()");
return false;
}
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response,
Object handler, ModelAndView mv) throws Exception {
System.out.println("111111-拦截器的MyInterceptor的postHandle()");
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
System.out.println("111111-拦截器的MyInterceptor的afterCompletion()");
}
}
<!--声明拦截器: 拦截器可以有0或多个
在框架中保存多个拦截器是ArrayList,
按照声明的先后顺序放入到ArrayList
-->
<mvc:interceptors>
<!--声明第一个拦截器-->
<mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:mapping path="/**"/>
<!--声明拦截器对象-->
<bean class="com.link.handler.MyInterceptor" />
</mvc:interceptor>
<!--声明第二个拦截器-->
<mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:mapping path="/**"/>
<bean class="com.link.handler.MyInterceptor2" />
</mvc:interceptor>
</mvc:interceptors>
1.3.1.2Spring Boot 使用拦截器
1. 创建类实现 HandlerInterceptor 接口
public class LoginInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response,
Object handler) throws Exception {
System.out.println("执行了LoginInterceptor的preHandle");
return true;
}
}
2. 注册拦截器对象
@Configuration
public class MyAppConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
//添加拦截器对象, 注入到容器中
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
//创建拦截器对象
HandlerInterceptor interceptor = new LoginInterceptor();
//指定拦截的请求uri地址
String path []= {"/user/**"};
//指定不拦截的地址
String excludePath [] = {"/user/login"};
registry.addInterceptor(interceptor)
.addPathPatterns(path)
.excludePathPatterns(excludePath);
}
}
3. 创建测试使用的 Controller
@Controller
public class BootController {
@RequestMapping("/user/account")
@ResponseBody
public String userAccount(){
return "访问user/account地址";
}
@RequestMapping("/user/login")
@ResponseBody
public String userLogin(){
return "访问user/login地址";
}
}
4. 主启动类
5. 启动主类, 运行浏览器
访问 user/account , user/login 观察拦截的输出语句

1.3.2 Spring Boot 中使用 Servlet
ServletRegistrationBean 用来做在 servlet 3.0+容器中注册 servlet 的功能,但更具有SpringBean 友好性。
1.创建 Servlet
//创建Servlet类
public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet{
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(req, resp);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//使用HttpServletResponse输出数据,应答结果
resp.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out = resp.getWriter();
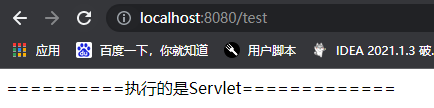
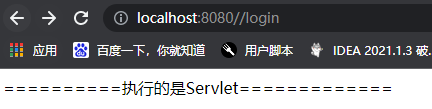
out.println("==========执行的是Servlet=============");
out.flush();
out.close();
}
}
2.注册 Servlet
@Configuration
public class WebApplictionConfig{
//定义方法, 注册Servlet对象
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean servletRegistrationBean()
{
//第一种初始化方式
ServletRegistrationBean bean = new ServletRegistrationBean(new MyServlet(),"/login","/test");
//第二种初始化方式
// ServletRegistrationBean bean = new ServletRegistrationBean();
// bean.setServlet(new MyServlet());
// bean.addUrlMappings("/login","/test");
return bean;
}
}
3.主启动类
4.启动主类,在浏览器中访问 loginServlet
1.3.3 Spring Boot 中使用 Filter
FilterRegistrationBean 用来注册 Filter 对象
实现步骤:
1.创建 Filter 对象
public class MyFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
System.out.println("执行了MyFilter,doFilter ");
filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest,servletResponse);
}
}
2.注册 Filter
@Configuration
public class WebApplicationConfig {
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean filterRegistrationBean(){
FilterRegistrationBean bean=new FilterRegistrationBean();
bean.setFilter(new MyFilter());
bean.addUrlPatterns("/user/*");
return bean;
}
}
3.创建 Controller
@Controller
public class CustomFilterController {
@RequestMapping("/user/account")
@ResponseBody
public String userAccount(){
return "user/account";
}
@RequestMapping("/query")
@ResponseBody
public String queryAccount(){
return "/query";
}
}
4.启动应用, 在浏览器访问 user/account, /query 查看浏览器运行结果
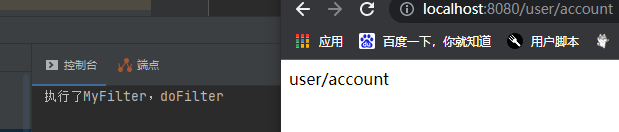
/query 则不会经过过滤器
1.3.4 字符集过滤器的应用
实现步骤:
1.创建 Servlet,输出中文数据
public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(req, resp);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
resp.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter out = resp.getWriter();
out.println("===在Servlet输出中文,默认编码ISO-8859-1===");
out.flush();
out.close();
}
}
2)注册 Servlet 和 Filter
@Configuration
public class WebSystemConfig{
//注册servlet
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean servletRegistrationBean(){
ServletRegistrationBean bean=new ServletRegistrationBean(new MyServlet(),"/myservlet");
return bean;
}
//注册filter
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean filterRegistrationBean(){
FilterRegistrationBean bean = new FilterRegistrationBean();
//使用框架中的过滤器类
CharacterEncodingFilter filter=new CharacterEncodingFilter();
//指定使用的编码方式
filter.setEncoding("utf-8");
//指定request response都使用encoding中的值
filter.setForceEncoding(true);
bean.setFilter(filter);
//指定 过滤的url地址
bean.addUrlPatterns("/*");
return bean;
}
}
3.在 application.properties , 禁用 Spring Boot 中默认启用的过滤器
server.servlet.encoding.enabled=false
4.启动主类,运行浏览器
1.3.5 在 application.properties 文件中设置过滤器
Spring Boot 项目默认启用了 CharacterEncodingFilter, 设置他的属性就可以
#设置 spring boot 中 CharacterEncodingFitler 的属性值
server.servlet.encoding.enabled=true
server.servlet.encoding.charset=utf-8
#强制 request, response 使用 charset 他的值 utf-8
server.servlet.encoding.force=true
1.3.6过滤器和拦截器的整合

1.创建拦截器 ,注意需要使用@Component 或者在注册拦截器import拦截器的包 最好都加上
@Component
public class LoginInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response,
Object handler) throws Exception {
System.out.println("执行了LoginInterceptor的preHandle");
return true;
}
}
2.注册拦截器
@Configuration
public class MyAppConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
//添加拦截器对象, 注入到容器中
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
//创建拦截器对象
HandlerInterceptor interceptor = new LoginInterceptor();
//指定拦截的请求uri地址
String path []= {"/user/**"};
//指定不拦截的地址
String excludePath [] = {"/user/login"};
registry.addInterceptor(interceptor)
.addPathPatterns(path)
.excludePathPatterns(excludePath);
}
}
3.注册过滤器 需要@Import(MyAppConfig.class) 需要import其他javaconfig
@Configuration
@Import(MyAppConfig.class)
public class WebSystemConfig{
//注册servlet
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean servletRegistrationBean(){
ServletRegistrationBean bean=new ServletRegistrationBean(new MyServlet(),"/myservlet");
return bean;
}
//注册filter
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean filterRegistrationBean(){
FilterRegistrationBean bean = new FilterRegistrationBean();
//使用框架中的过滤器类
CharacterEncodingFilter filter=new CharacterEncodingFilter();
//指定使用的编码方式
filter.setEncoding("utf-8");
//指定request response都使用encoding中的值
filter.setForceEncoding(true);
bean.setFilter(filter);
//指定 过滤的url地址
//bean.addUrlPatterns("/*");
bean.addUrlPatterns("/user");
return bean;
}
}
1.4 第四章 ORM 操作 MySQL
讲解 MyBatis 框架,读写 MySQL 数据。通过 SpringBoot +MyBatis 实现对数据库学生表的查询操作。
创建数据库:数据库 springdb,指定数据库字符编码为 utf-8
CREATE TABLE `student` (
`id` INT(10) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` VARCHAR(256) DEFAULT NULL,
`age` INT(10) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
INSERT INTO student(`name`,`age`)
VALUES("小红",23),("小白",24),("张三",28),("李四",34)
1.4.1 创建 Spring Boot 项目
pom.xml
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.2.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
加入 resources 插件
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
</resource>
</resources>
配置数据源:application.properties
server.port=9001
server.servlet.context-path=/orm
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springdb?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=123456
创建数实体 bean, dao 接口,mapper 文件

实体类
public class Student {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
创建 Dao 接口
/**
* @Mapper: 找到接口和他的 xml 文件
* 位置:在接口的上面
*/
@Mapper
public interface StudentMapper {
Student selectStudentById(@Param("stuid") Integer id);
}
mapper 文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.link.dao.StudentMapper">
<select id="selectStudentById" resultType="com.link.domain.Student">
select id name age from student where id=#{stuid}
</select>
</mapper>
service 接口
public interface StudentService {
Student queryStudent(Integer id);
}
service 接口实现类
public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService {
@Resource
private StudentMapper studentDao;
@Override
public Student queryStudent(Integer id) {
Student student = studentDao.selectStudentById(id);
return student;
}
}
controller 类
@Controller
public class StudentController {
@Resource
private StudentService studentService;
@RequestMapping("/query")
@ResponseBody
public String queryStudent(Integer id)
{
Student student=studentService.queryStudent(id);
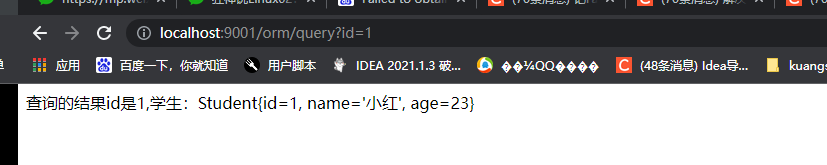
return "查询的结果id是"+id+",学生:"+student.toString();
}
}
启动 Application 类, 浏览器访问 http://localhost:9090/myboot/query
发现无法连接数据库
报错:
Failed to obtain JDBC Connection; nested exception is java.sql.SQLNonTransientConnectionException:
是mysql-connecter-java版本太高,自己安装的mysql数据库版本低的问题,把mysql的jar包降低到适合自己mysql数据库的版本就好了
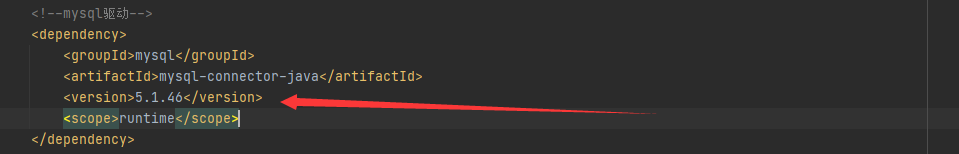
降低mysql-connector-java这个jar包的版本号,重新启动项目就可以正常访问了。
1.4.2 @MapperScan
在 Dao 接口上面加入@Mapper,需要在每个接口都加入注解。当 Dao 接口多的时候不方便。
可以使用如下的方式解决。
主类上添加注解包扫描:@MapperScan(“com.link.dao”)
/**
* @MapperScan: 扫描所有的 mybatis 的 dao 接口
* 位置:在主类的上面
* 属性:basePackages:指定 dao 接口的所在的包名。
* dao 接口和 mapper 文件依然在同一目录
*/
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.link.dao")
public class MyBatisApplication2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MyBatisApplication2.class,args);
}
}
1.4.3 mapper 文件和 java 代码分开管理
这种方式比较推荐,mapper 文件放在 resources 目录下, java 代码放在 src/main/java。
在 resources 创建自定义目录,例如 mapper, 存放 xml 文件
在 application.properties 配置文件中指定映射文件的位置,这个配置只有接口和映射文件不在同一个包的情况下,才需要指定。
#指定 mybatis 的配置, 相当于 mybatis 主配置文件的作用
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mapper/*.xml
mybatis.configuration.log-impl=org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl

1.4.4 事务支持
Spring Boot 使用事务非常简单,底层依然采用的是 Spring 本身提供的事务管理
在入口类中使用注解 @EnableTransactionManagement 开启事务支持
在访问数据库的 Service 方法上添加注解 @Transactional 即可
通过 SpringBoot +MyBatis 实现对数据库学生表的更新操作,在 service 层的方法中构建异常,查看事务是否生效。
@Service
public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService {
@Resource
private StudentMapper studentMapper;
/**
* @Transactional: 表示方法的有事务支持
* 默认:使用库的隔离级别, REQUIRED 传播行为; 超时时间 -1
* 抛出运行时异常,回滚事务
*/
@Override
@Transactional
public int addStudent(Student student) {
System.out.println("业务方法addStudent");
int rows = studentMapper.insert(student);
System.out.println("执行SQL语句");
//抛出运行时异常,目的是回滚事物
//int num = 5/0;
return rows;
}
}
在 Application 主类上,@EnableTransactionManagement 开启事务支持
@EnableTransactionManagement 可选,但是@Service 必须添加事务才生效
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableTransactionManagement
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.link.dao")
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}





















 1253
1253











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








