文章中所有代码均来自Mask-RCNN_Benchmark,讲述其底层实现细节,框架为Pytorch1.0,用于更深入的理解其思想,当然,这相当于是我的阅读笔记,所以有些地方会讲述的不是那么详细,如果有疑惑,建议评论区讨论或者自己读源码!
https://github.com/facebookresearch/maskrcnn-benchmarkgithub.comRPN Loss的构建
由于RPN的分类属于二分类的问题,二分类的CrossEntropy loss就相当于BCE loss,所以这个项目在复现时直接使用了BCE loss,边框回归使用的还是Smooth L1 损失!
def 到此,RPN的整个结果以及其匹配过程就结束了,接下来需要将训练好的proposal喂给ROI Head,然后进行分类和回归!
ROI Head
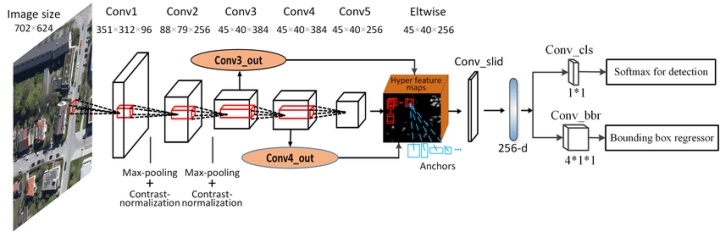
在原版的Faster RCNN中,其Head结构如下:
经过RPN网络得到的一系列Region Proposals经过ROI Pooling后得到了固定尺寸,论文中为7x7的特征图,然后经过全连接层,用于分类和回归。
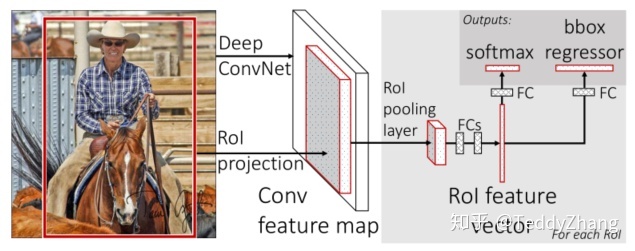
但在Mask RCNN中,作者对Faster RCNN做了些调整,而Mask RCNN Benchmark复现也是按照后来的Mask RCNN来进行的!网络结构如下(默认使用的为左图):
- 首先使用ROI Align应用到backbone的Conv4的输出,得到14x14的特征图(Mask RCNN中为了提高Mask的精度,使用ROI Align来代替ROI Pooling)
- 再经过Conv5得到7x7的特征图,并进行average pooling,然后直接送入分类和回归两个检测分支,这与原版的Faster RCNN也有区别
疑惑:虽然大致的结构是相同的,但实际复现的代码与其论文上的结构还是有些出入的!
代码如下:
class ResNet50Conv5ROIFeatureExtractor(nn.Module): # 提取特征
def __init__(self, config, in_channels):
super(ResNet50Conv5ROIFeatureExtractor, self).__init__()
resolution = config.MODEL.ROI_BOX_HEAD.POOLER_RESOLUTION
scales = config.MODEL.ROI_BOX_HEAD.POOLER_SCALES
sampling_ratio = config.MODEL.ROI_BOX_HEAD.POOLER_SAMPLING_RATIO
pooler = Pooler(
output_size=(resolution, resolution), # 这里默认的Box_pooling也是14,与论文不同
scales=scales,
sampling_ratio=sampling_ratio,
)
stage = resnet.StageSpec(index=4, block_count=3, return_features=False)
# 构建ResNet最后一个卷积层 Conv5
head = resnet.ResNetHead(
block_module=config.MODEL.RESNETS.TRANS_FUNC,
stages=(stage,),
num_groups=config.MODEL.RESNETS.NUM_GROUPS,
width_per_group=config.MODEL.RESNETS.WIDTH_PER_GROUP,
stride_in_1x1=config.MODEL.RESNETS.STRIDE_IN_1X1,
stride_init=None,
res2_out_channels=config.MODEL.RESNETS.RES2_OUT_CHANNELS,
dilation=config.MODEL.RESNETS.RES5_DILATION
)
self.pooler = pooler
self.head = head
self.out_channels = head.out_channels
def forward(self, x, proposals):
x = self.pooler(x, proposals)
x = self.head(x)
return x
# Box检测分支
class FastRCNNPredictor(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config, in_channels):
super(FastRCNNPredictor, self).__init__()
assert in_channels is not None
num_inputs = in_channels
num_classes = config.MODEL.ROI_BOX_HEAD.NUM_CLASSES
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.cls_score = nn.Linear(num_inputs, num_classes)
num_bbox_reg_classes = 2 if config.MODEL.CLS_AGNOSTIC_BBOX_REG else num_classes
self.bbox_pred = nn.Linear(num_inputs, num_bbox_reg_classes * 4)
nn.init.normal_(self.cls_score.weight, mean=0, std=0.01)
nn.init.constant_(self.cls_score.bias, 0)
nn.init.normal_(self.bbox_pred.weight, mean=0, std=0.001)
nn.init.constant_(self.bbox_pred.bias, 0)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
cls_logit = self.cls_score(x) # 首先进行平均池化,然后送入两个全连接层的分支
bbox_pred = self.bbox_pred(x)
return cls_logit, bbox_pred至此,ROI Head构建完毕,在项目中,其ROI Align和ROI Pooling操作都使用C++代码进行编写,从而加快了处理速度!具体ROI Align和ROI Pooling的差距我们回头再说!
构建Faster RCNN Loss
当我们得到了对应的预测值和真实值后,我们需要计算两者之间的loss,分成分类loss和边框回归loss, 对于分类loss我们使用的是交叉熵损失,而对于边框回归,我们使用的是Smooth L1 loss,其计算形式如下:
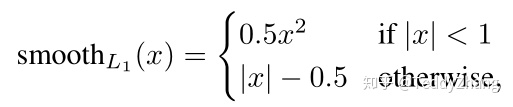
def __call__(self, class_logits, box_regression):
"""
Computes the loss for Faster R-CNN.
This requires that the subsample method has been called beforehand.
Arguments:
class_logits (list[Tensor])
box_regression (list[Tensor])
Returns:
classification_loss (Tensor)
box_loss (Tensor)
"""
class_logits = cat(class_logits, dim=0)
box_regression = cat(box_regression, dim=0)
device = class_logits.device
if not hasattr(self, "_proposals"):
raise RuntimeError("subsample needs to be called before")
proposals = self._proposals
labels = cat([proposal.get_field("labels") for proposal in proposals], dim=0)
regression_targets = cat(
[proposal.get_field("regression_targets") for proposal in proposals], dim=0
)
classification_loss = F.cross_entropy(class_logits, labels)
# get indices that correspond to the regression targets for
# the corresponding ground truth labels, to be used with
# advanced indexing
sampled_pos_inds_subset = torch.nonzero(labels > 0).squeeze(1)
labels_pos = labels[sampled_pos_inds_subset]
if self.cls_agnostic_bbox_reg:
map_inds = torch.tensor([4, 5, 6, 7], device=device)
else:
map_inds = 4 * labels_pos[:, None] + torch.tensor(
[0, 1, 2, 3], device=device)
box_loss = smooth_l1_loss(
box_regression[sampled_pos_inds_subset[:, None], map_inds],
regression_targets[sampled_pos_inds_subset],
size_average=False,
beta=1,
)
box_loss = box_loss / labels.numel()
return classification_loss, box_loss





















 821
821

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








