知识点梳理
python工具使用:
sklearn: 数据挖掘,数据分析工具,内置logistic回归
matplotlib: 做图工具,可绘制等高线等
绘制散点图: plt.scatter(X[0, :], X[1, :], c=np.squeeze(Y), s=40, cmap=plt.cm.Spectral); s:绘制点大小 cmap:颜色集
绘制等高线: 先做网格,计算结果,绘图
x_min, x_max = X[0, :].min() - 1, X[0, :].max() + 1
y_min, y_max = X[1, :].min() - 1, X[1, :].max() + 1
h = 0.01
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h), np.arange(y_min, y_max, h))
Z = model(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
#xx是x轴值, yy是y轴值, Z是预测结果值, cmap表示采用什么颜色
plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, cmap=plt.cm.Spectral)
关键变量:
m: 训练样本数量
n_x:一个训练样本的输入数量,输入层大小
n_h:隐藏层大小
方括号上标[l]: 第l层
圆括号上标(i): 第i个样本
$$
X =
\left[
\begin{matrix}
\vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \vdots \\
x^{(1)} & x^{(2)} & \vdots & x^{(m)} \\
\vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \vdots \\
\end{matrix}
\right]_{(n\_x, m)}
$$
$$
W^{[1]} =
\left[
\begin{matrix}
\cdots & w^{[1] T}_1 & \cdots \\
\cdots & w^{[1] T}_2 & \cdots \\
\cdots & \cdots & \cdots \\
\cdots & w^{[1] T}_{n\_h} & \cdots \\
\end{matrix}
\right]_{(n\_h, n\_x)}
$$
$$
b^{[1]} =
\left[
\begin{matrix}
b^{[1]}_1 \\
b^{[1]}_2 \\
\vdots \\
b^{[1]}_{n\_h} \\
\end{matrix}
\right]_{(n\_h, 1)}
$$
$$
A^{[1]}=
\left[
\begin{matrix}
\vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \vdots \\
a^{[1](1)} & a^{[1](2)} & \vdots & a^{[1](m)} \\
\vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \vdots \\
\end{matrix}
\right]_{(n\_h, m)}
$$
$$
Z^{[1]}=
\left[
\begin{matrix}
\vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \vdots \\
z^{[1](1)} & z^{[1](2)} & \vdots & z^{[1](m)} \\
\vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \vdots \\
\end{matrix}
\right]_{(n\_h, m)}
$$
***
单隐层神经网络关键公式:
前向传播:
$$Z^{[1]}=W^{[1]}X+b^{[1]}$$
$$A^{[1]}=g^{[1]}(Z^{[1]})$$
$$Z^{[2]}=W^{[2]}A^{[1]}+b^{[2]}$$
$$A^{[2]}=g^{[2]}(Z^{[2]})$$
Z1 = np.dot(W1, X) + b1
A1 = np.tanh(Z1)
Z2 = np.dot(W2, A1) + b2
A2 = sigmoid(Z2)
反向传播
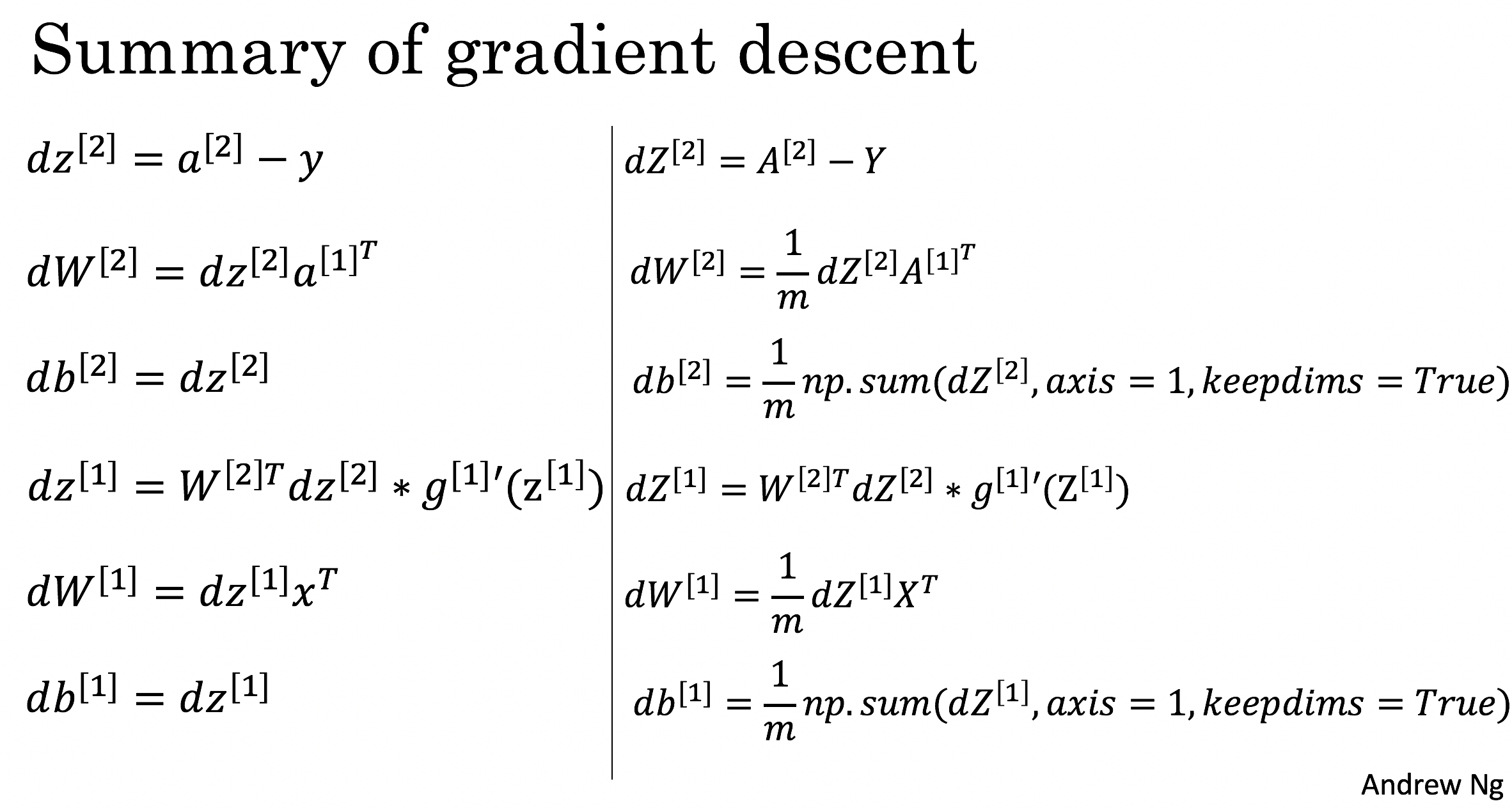
dZ2 = A2 - Y
dW2 = 1 / m * np.dot(dZ2, A1.T)
db2 = 1 / m * np.sum(dZ2, axis = 1, keepdims = True)
dZ1 = np.dot(W2.T, dZ2) * (1 - np.power(A1, 2))
dW1 = 1 / m * np.dot(dZ1, X.T)
db1 = 1 / m * np.sum(dZ1, axis = 1, keepdims = True)
cost计算
\[J = - \frac{1}{m} \sum\limits_{i = 0}^{m} \large{(} \small y^{(i)}\log\left(a^{[2] (i)}\right) + (1-y^{(i)})\log\left(1- a^{[2] (i)}\right) \large{)} \small
\]
logprobs = np.multiply(np.log(A2), Y) + np.multiply(np.log(1 - A2), 1 - Y)
cost = - 1 / m * np.sum(logprobs)
单隐层神经网络代码:
# Package imports
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import sklearn
import sklearn.datasets
import sklearn.linear_model
from planar_utils import plot_decision_boundary, sigmoid, load_planar_dataset, load_extra_datasets
%matplotlib inline
np.random.seed(1) # set a seed so that the results are consistent
def initialize_parameters(n_x, n_h, n_y):
np.random.seed(2) # we set up a seed so that your output matches ours although the initialization is random.
W1 = np.random.randn(n_h, n_x) * 0.01
b1 = np.zeros((n_h, 1))
W2 = np.random.randn(n_y, n_h)
b2 = np.zeros((n_y, 1))
assert (W1.shape == (n_h, n_x))
assert (b1.shape == (n_h, 1))
assert (W2.shape == (n_y, n_h))
assert (b2.shape == (n_y, 1))
parameters = {"W1": W1,
"b1": b1,
"W2": W2,
"b2": b2}
return parameters
def forward_propagation(X, parameters):
# Retrieve each parameter from the dictionary "parameters"
W1 = parameters["W1"]
b1 = parameters["b1"]
W2 = parameters["W2"]
b2 = parameters["b2"]
# Implement Forward Propagation to calculate A2 (probabilities)
Z1 = np.dot(W1, X) + b1
A1 = np.tanh(Z1)
Z2 = np.dot(W2, A1) + b2
A2 = sigmoid(Z2)
assert(A2.shape == (1, X.shape[1]))
cache = {"Z1": Z1,
"A1": A1,
"Z2": Z2,
"A2": A2}
return A2, cache
def compute_cost(A2, Y, parameters):
m = Y.shape[1] # number of example
# Compute the cross-entropy cost
logprobs = np.multiply(np.log(A2), Y) + np.multiply(np.log(1 - A2), 1 - Y)
cost = - 1 / m * np.sum(logprobs)
cost = np.squeeze(cost) # makes sure cost is the dimension we expect.
# E.g., turns [[17]] into 17
assert(isinstance(cost, float))
return cost
def backward_propagation(parameters, cache, X, Y):
m = X.shape[1]
# First, retrieve W1 and W2 from the dictionary "parameters".
W1 = parameters["W1"]
W2 = parameters["W2"]
# Retrieve also A1 and A2 from dictionary "cache".
A1 = cache["A1"]
A2 = cache["A2"]
# Backward propagation: calculate dW1, db1, dW2, db2.
dZ2 = A2 - Y
dW2 = 1 / m * np.dot(dZ2, A1.T)
db2 = 1 / m * np.sum(dZ2, axis = 1, keepdims = True)
dZ1 = np.dot(W2.T, dZ2) * (1 - np.power(A1, 2))
dW1 = 1 / m * np.dot(dZ1, X.T)
db1 = 1 / m * np.sum(dZ1, axis = 1, keepdims = True)
grads = {"dW1": dW1,
"db1": db1,
"dW2": dW2,
"db2": db2}
return grads
def update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate = 0.8):
# Retrieve each parameter from the dictionary "parameters"
W1 = parameters["W1"]
b1 = parameters["b1"]
W2 = parameters["W2"]
b2 = parameters["b2"]
# Retrieve each gradient from the dictionary "grads"
dW1 = grads["dW1"]
db1 = grads["db1"]
dW2 = grads["dW2"]
db2 = grads["db2"]
# Update rule for each parameter
W1 = W1 - learning_rate * dW1
b1 = b1 - learning_rate * db1
W2 = W2 - learning_rate * dW2
b2 = b2 - learning_rate * db2
parameters = {"W1": W1,
"b1": b1,
"W2": W2,
"b2": b2}
return parameters
def nn_model(X, Y, n_h, num_iterations = 10000, print_cost=False):
np.random.seed(3)
n_x = X.shape[0]
n_y = Y.shape[0]
# Initialize parameters, then retrieve W1, b1, W2, b2. Inputs: "n_x, n_h, n_y". Outputs = "W1, b1, W2, b2, parameters".
parameters = initialize_parameters(n_x, n_h, n_y)
W1 = parameters["W1"]
b1 = parameters["b1"]
W2 = parameters["W2"]
b2 = parameters["b2"]
# Loop (gradient descent)
for i in range(0, num_iterations):
# Forward propagation. Inputs: "X, parameters". Outputs: "A2, cache".
A2, cache = forward_propagation(X, parameters)
# Cost function. Inputs: "A2, Y, parameters". Outputs: "cost".
cost = compute_cost(A2, Y, parameters)
# Backpropagation. Inputs: "parameters, cache, X, Y". Outputs: "grads".
grads = backward_propagation(parameters, cache, X, Y)
# Gradient descent parameter update. Inputs: "parameters, grads". Outputs: "parameters".
parameters = update_parameters(parameters, grads)
# Print the cost every 1000 iterations
if print_cost and i % 1000 == 0:
print ("Cost after iteration %i: %f" %(i, cost))
return parameters
def predict(parameters, X):
# Computes probabilities using forward propagation, and classifies to 0/1 using 0.5 as the threshold.
A2, cache = forward_propagation(X, parameters)
predictions = A2 > 0.5
return predictions
X, Y = load_planar_dataset()
# Build a model with a n_h-dimensional hidden layer
parameters = nn_model(X, Y, n_h = 4, num_iterations = 10000, print_cost=True)
# Plot the decision boundary
plot_decision_boundary(lambda x: predict(parameters, x.T), X, np.squeeze(Y))
plt.title("Decision Boundary for hidden layer size " + str(4))
# planar_utils.py
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import sklearn
import sklearn.datasets
import sklearn.linear_model
def plot_decision_boundary(model, X, y):
# Set min and max values and give it some padding
x_min, x_max = X[0, :].min() - 1, X[0, :].max() + 1
y_min, y_max = X[1, :].min() - 1, X[1, :].max() + 1
h = 0.01
# Generate a grid of points with distance h between them
# 创造网格,以0.01为间隔划分整个区间
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h), np.arange(y_min, y_max, h))
# Predict the function value for the whole grid
# 计算每个网格点上的预测结果
Z = model(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
# 将预测结果变形为与网格形式一致
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
# Plot the contour and training examples
# xx是x轴值, yy是y轴值, Z是预测结果值, cmap表示采用什么颜色
plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, cmap=plt.cm.Spectral) #等位线
plt.ylabel('x2')
plt.xlabel('x1')
plt.scatter(X[0, :], X[1, :], c=y, cmap=plt.cm.Spectral)
def sigmoid(x):
"""
Compute the sigmoid of x
Arguments:
x -- A scalar or numpy array of any size.
Return:
s -- sigmoid(x)
"""
s = 1/(1+np.exp(-x))
return s
def load_planar_dataset():
np.random.seed(1)
m = 400 # number of examples
N = int(m/2) # number of points per class
D = 2 # dimensionality
X = np.zeros((m,D)) # data matrix where each row is a single example
Y = np.zeros((m,1), dtype='uint8') # labels vector (0 for red, 1 for blue)
a = 4 # maximum ray of the flower
for j in range(2):
ix = range(N*j,N*(j+1))
t = np.linspace(j*3.12,(j+1)*3.12,N) + np.random.randn(N)*0.2 # theta
r = a*np.sin(4*t) + np.random.randn(N)*0.2 # radius
X[ix] = np.c_[r*np.sin(t), r*np.cos(t)]
Y[ix] = j
X = X.T
Y = Y.T
return X, Y
def load_extra_datasets():
N = 200
noisy_circles = sklearn.datasets.make_circles(n_samples=N, factor=.5, noise=.3)
noisy_moons = sklearn.datasets.make_moons(n_samples=N, noise=.2)
blobs = sklearn.datasets.make_blobs(n_samples=N, random_state=5, n_features=2, centers=6)
gaussian_quantiles = sklearn.datasets.make_gaussian_quantiles(mean=None, cov=0.5, n_samples=N, n_features=2, n_classes=2, shuffle=True, random_state=None)
no_structure = np.random.rand(N, 2), np.random.rand(N, 2)
return noisy_circles, noisy_moons, blobs, gaussian_quantiles, no_structure




















 2219
2219











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








