注意:单击此处https://urlify.cn/NV3Erq下载完整的示例代码,或通过Binder在浏览器中运行此示例
此示例显示了在二维模式下的数据集上层次聚类(hierarchical clustering)的不同链接方法的特征。 主要观察到的有:- 单链接的速度很快,并且可以在非球形数据上表现良好,但是在存在噪声的情况下,效果表现较差。
- 平均链接和完全链接在分离干净的球状上表现良好,但在其他方面却有不同的结果。
- Ward是处理有噪声数据的最有效方法。
print(__doc__)import timeimport warningsimport numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom sklearn import cluster, datasetsfrom sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScalerfrom itertools import cycle, islicenp.random.seed(0)n_samples = 1500noisy_circles = datasets.make_circles(n_samples=n_samples, factor=.5, noise=.05)noisy_moons = datasets.make_moons(n_samples=n_samples, noise=.05)blobs = datasets.make_blobs(n_samples=n_samples, random_state=8)no_structure = np.random.rand(n_samples, 2), None# 各向异性(Anisotropicly)分布的数据random_state = 170X, y = datasets.make_blobs(n_samples=n_samples, random_state=random_state)transformation = [[0.6, -0.6], [-0.4, 0.8]]X_aniso = np.dot(X, transformation)aniso = (X_aniso, y)# 具有变化的斑点(blobs)varied = datasets.make_blobs(n_samples=n_samples, cluster_std=[1.0, 2.5, 0.5], random_state=random_state)# 设置聚类参数plt.figure(figsize=(9 * 1.3 + 2, 14.5))plt.subplots_adjust(left=.02, right=.98, bottom=.001, top=.96, wspace=.05, hspace=.01)plot_num = 1default_base = {'n_neighbors': 10, 'n_clusters': 3}datasets = [ (noisy_circles, {'n_clusters': 2}), (noisy_moons, {'n_clusters': 2}), (varied, {'n_neighbors': 2}), (aniso, {'n_neighbors': 2}), (blobs, {}), (no_structure, {})]for i_dataset, (dataset, algo_params) in enumerate(datasets): # 使用数据集特定的值更新参数 params = default_base.copy() params.update(algo_params) X, y = dataset # 标准化数据集,以便更轻松地选择参数 X = StandardScaler().fit_transform(X) # ============ # 创建聚类对象 # ============ ward = cluster.AgglomerativeClustering( n_clusters=params['n_clusters'], linkage='ward') complete = cluster.AgglomerativeClustering( n_clusters=params['n_clusters'], linkage='complete') average = cluster.AgglomerativeClustering( n_clusters=params['n_clusters'], linkage='average') single = cluster.AgglomerativeClustering( n_clusters=params['n_clusters'], linkage='single') clustering_algorithms = ( ('Single Linkage', single), ('Average Linkage', average), ('Complete Linkage', complete), ('Ward Linkage', ward), ) for name, algorithm in clustering_algorithms: t0 = time.time() # 捕获与kneighbors_graph有关的警告 with warnings.catch_warnings(): warnings.filterwarnings( "ignore", message="the number of connected components of the " + "connectivity matrix is [0-9]{1,2}" + " > 1. Completing it to avoid stopping the tree early.", category=UserWarning) algorithm.fit(X) t1 = time.time() if hasattr(algorithm, 'labels_'): y_pred = algorithm.labels_.astype(np.int) else: y_pred = algorithm.predict(X) plt.subplot(len(datasets), len(clustering_algorithms), plot_num) if i_dataset == 0: plt.title(name, size=18) colors = np.array(list(islice(cycle(['#377eb8', '#ff7f00', '#4daf4a', '#f781bf', '#a65628', '#984ea3', '#999999', '#e41a1c', '#dede00']), int(max(y_pred) + 1)))) plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], s=10, color=colors[y_pred]) plt.xlim(-2.5, 2.5) plt.ylim(-2.5, 2.5) plt.xticks(()) plt.yticks(()) plt.text(.99, .01, ('%.2fs' % (t1 - t0)).lstrip('0'), transform=plt.gca().transAxes, size=15, horizontalalignment='right') plot_num += 1plt.show()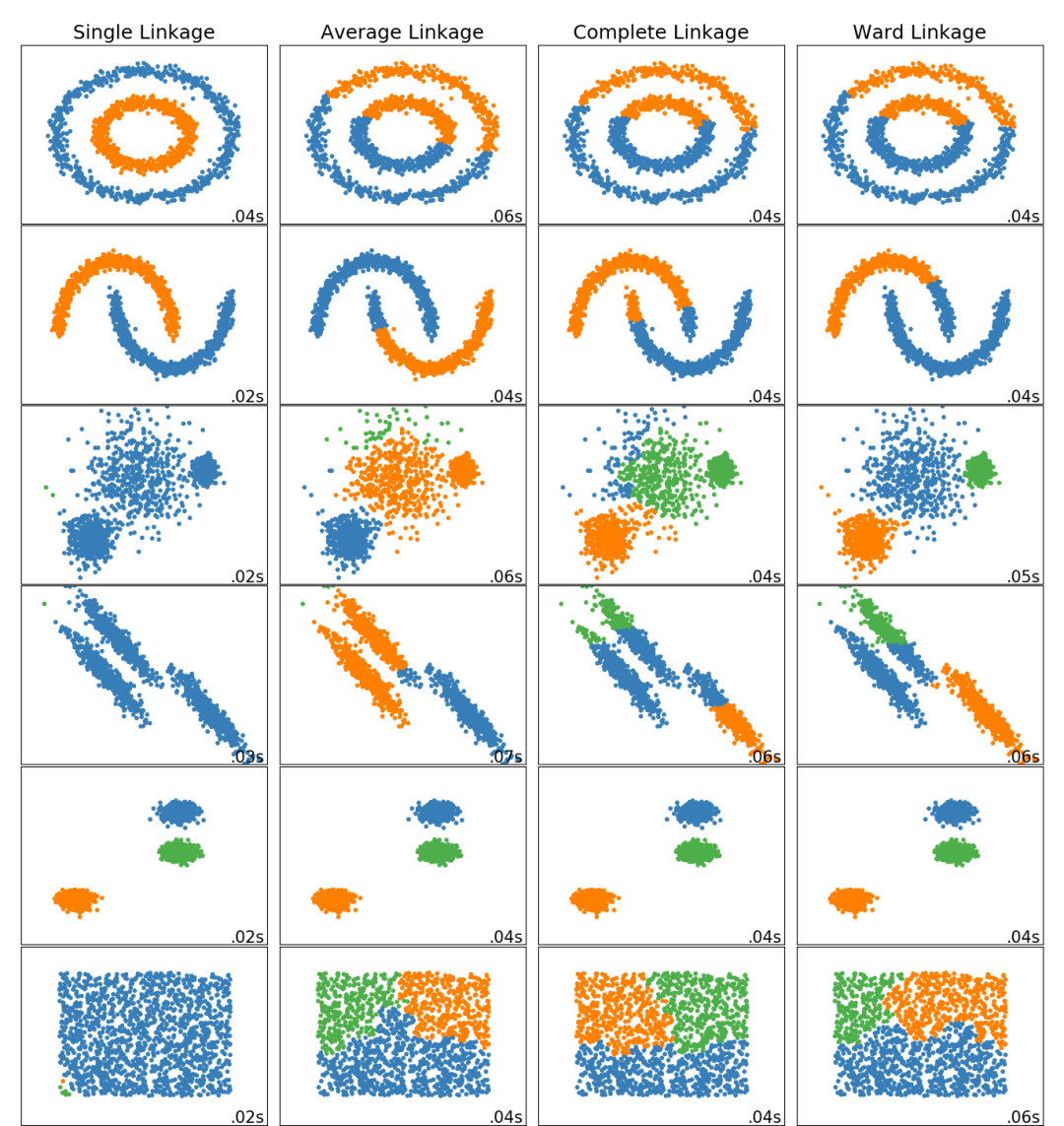

下载Python源代码: plot_linkage_comparison.py
下载Jupyter notebook源代码: plot_linkage_comparison.ipynb
由Sphinx-Gallery生成的画廊
文壹由“伴编辑器”提供技术支持
☆☆☆为方便大家查阅,小编已将scikit-learn学习路线专栏 文章统一整理到公众号底部菜单栏,同步更新中,关注公众号,点击左下方“系列文章”,如图:
欢迎大家和我一起沿着scikit-learn文档这条路线,一起巩固机器学习算法基础。(添加微信:mthler,备注:sklearn学习,一起进【sklearn机器学习进步群】开启打怪升级的学习之旅。)





















 6799
6799

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








