生产者-消费者模型实现
生产者-消费者是多线程必谈的一个话题,本文利用synchronized、lock以及BlockingQueue分被实现生产者消费者模型。
使用synchronized
public class ProducerAndConsumer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
shareData sd = new shareData();
new Thread(()->{ //生产者线程
for (int i = 0; i <3 ; i++) {
try {
sd.produce();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"A").start();
new Thread(()->{ //消费者线程
for(int i=0;i<3;++i){
try {
sd.consume();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"B").start();
}
}
class shareData{ //使用synchronized
private volatile int number = 0;
public synchronized void produce() throws InterruptedException {
while (number != 0){
this.wait();
}
number ++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"生产了一个,当前为"+ number);
Thread.sleep(1000);
this.notify();
}
public synchronized void consume() throws InterruptedException {
while (number == 0){
this.wait();
}
number --;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"消费了一个,当前为"+ number);
Thread.sleep(1000);
this.notify();
}
}
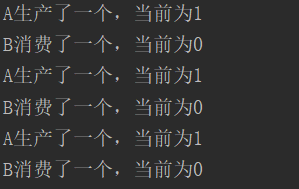
运行结果
使用lock
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class PandC {
public static void main(String[] args) {
data d = new data();
new Thread(()->{ //生产者线程
for(int i=0;i<3;++i){
d.incre();
}
},"A").start();
new Thread(()->{ //消费者线程
for(int i=0;i<3;++i){
d.decre();
}
},"B").start();
}
}
class data{ //使用Lock
private volatile int number = 0;
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Condition condition = lock.newCondition(); //线程之间通知
public void incre(){
lock.lock();
try {
while(number != 0){
condition.await(); //有则等待
}
number ++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "生产了一个,当前为" + number);
Thread.sleep(1000);
condition.signal(); //生产后通知消费者线程
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void decre(){
lock.lock();
try {
while(number == 0){
condition.await(); //无则等待
}
number --;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "消费了一个,当前为" + number);
Thread.sleep(1000);
condition.signal(); //消费后通知生产者线程
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
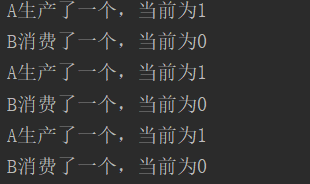
运行结果
使用BlockingQueue
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
public class ProAndCon {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
BlockingQueue<Integer> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(2);
Thread putThread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("put thread start");
try {
for (int i = 0; i <4 ; i++) {
queue.put(i);
System.out.println("put element: " + i);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("put thread end");
}
});
Thread takeThread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("take thread start");
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
//queue.take();
System.out.println("take from putThread: " + queue.take());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("take thread end");
}
});
putThread.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
takeThread.start();
}
}
运行结果























 1459
1459











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








