
练习题1:如何根据二叉树的遍历结果重置二叉树:
对于先序遍历我们知道,最先出现的一般是根节点,而中序遍历一般将根节点出现在中间,后序遍历将跟节点出现在最后,我们可以根据根节点所在为止划分子树,然后重置二叉树


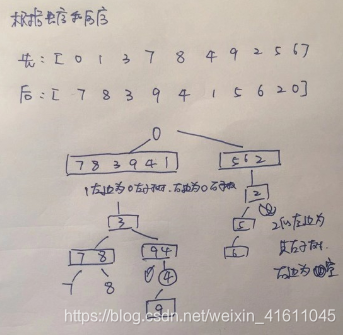
例题1:对于上述二叉树,请实现层次遍历、先序遍历、中序遍历和后序遍历
'''
二叉树的遍历
将以下二叉树分别用先序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历和层次遍历进行遍历
0
1 2
3 4 5 6
7 8 9
先序遍历:中左右
中序遍历:左中右
后序遍历:左右中
'''
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left=None
self.right=None
#生成二叉树
node_0=TreeNode(0)
node_1=TreeNode(1)
node_2=TreeNode(2)
node_3=TreeNode(3)
node_4=TreeNode(4)
node_5=TreeNode(5)
node_6=TreeNode(6)
node_7=TreeNode(7)
node_8=TreeNode(8)
node_9=TreeNode(9)
node_0.left=node_1
node_0.right=node_2
node_1.left=node_3
node_1.right=node_4
node_2.left=node_5
node_2.right=node_6
node_3.left=node_7
node_3.right=node_8
node_4.left=node_9
#前序遍历
def priosearch(head):
if head==None:
return
print(head.val,end=' ')
priosearch(head.left)
priosearch(head.right)
priosearch(node_0)
#0 1 3 7 8 4 9 2 5 6
#中序遍历
def midsearch(head):
if head==None:
return
midsearch(head.left)
print(head.val,end=' ')
midsearch(head.right)
midsearch(node_0)
#7 3 8 1 9 4 0 5 2 6
#后序遍历
def backsearch(head):
if head==None:
return
backsearch(head.left)
backsearch(head.right)
print(head.val,end=' ')
backsearch(node_0)
#层次遍历,利用队列的方式去遍历
def cengcisearch(head):
arr=[]
arr.append(head)
while arr:
c_root=arr.pop(0)
print(c_root.val,end=' ')
if c_root.left is not None:
arr.append(c_root.left)
if c_root.right is not None:
arr.append(c_root.right)
cengcisearch(node_0)
#0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
习题2:剑指offer32
按层打印二叉树,从上到下从左向右
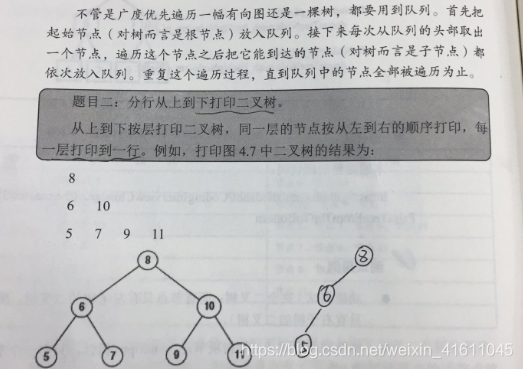
'''
从上至下层次打印二叉树
如:
8
6 10
5 7 9 11
'''
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
Node1=TreeNode(8)
Node2=TreeNode(6)
Node3=TreeNode(10)
Node4=TreeNode(5)
Node5=TreeNode(7)
Node6=TreeNode(9)
Node7=TreeNode(11)
Node1.left=Node2
Node1.right=Node3
Node2.left=Node4
Node2.right=Node5
Node3.left=Node6
Node3.right=Node7
head=Node1
def cenciprint(head):
if head is None:
return
list1=[] #当前节点要打印的元素
list2=[] #将节点弹出的下一层节点暂时存储的数组
list1.append(head)
while list1 or list2:
while list1:
c_root=list1.pop(0)
list2.append(c_root)
#此时list2已经将这一层节点全部存储了
while list2:
#将这一层的节点全部打印,并将当前节点的左右节点放入list1中
root=list2.pop(0)
print(root.val,end=' ')
if root.left is not None:
list1.append(root.left)
if root.right is not None:
list1.append(root.right)
print('\n')
cenciprint(Node1)
解析:使用两个list来实现,首先放入根节点,将根节点的所有子节点遍历并放入list2,从最开始的元素从list2依次弹出,每次打印这个元素,并将其加入list1,相当于在list1进行出栈并添加子树时,先将子树存储起来以防止不断出栈,这样list2中每次存储的都是每一层的所有元素,当两个list1、list2都为空时代表已经全部遍历结束。
习题3:之字形打印二叉树
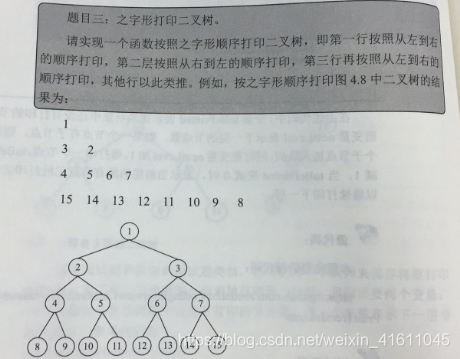
'''
之字形打印二叉树
1
2 3
4 5 6 7
8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
打印出来的结果:
1
3 2
4 5 6 7
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8
'''
##测试:来回打印
Node1=TreeNode(1)
Node2=TreeNode(2)
Node3=TreeNode(3)
Node4=TreeNode(4)
Node5=TreeNode(5)
Node6=TreeNode(6)
Node7=TreeNode(7)
Node8=TreeNode(8)
Node9=TreeNode(9)
Node10=TreeNode(10)
Node11=TreeNode(11)
Node12=TreeNode(12)
Node13=TreeNode(13)
Node14=TreeNode(14)
Node15=TreeNode(15)
Node16=TreeNode(16)
Node1.left=Node2
Node1.right=Node3
Node2.left=Node4
Node2.right=Node5
Node3.left=Node6
Node3.right=Node7
Node4.left=Node8
Node4.right=Node9
Node5.left=Node10
Node5.right=Node11
Node6.left=Node12
Node6.right=Node13
Node7.left=Node14
Node7.right=Node15
def zhizi_print(head,right_left_triger=False):
if head is None:
return
list1=[] #临时存储下一层节点的值,以队列的形式存储,后面进,前面出
list2=[] #存储当前节点要打印的值
list1.append(head)
while list1 or list2:
while list1:
c_root=list1.pop(0)
list2.append(c_root)
while list2:
if right_left_triger==True:#从右向左打印
root=list2.pop()
print(root.val,end=' ')
if root.right is not None:
list1.append(root.right)
if root.left is not None:
list1.append(root.left)
#此时list1中存储的元素也是从右往左的所以需要将list1颠倒
#list1=list1[::-1]
else: #从左向右打印
root=list2.pop(0)
print(root.val,end=' ')
if root.left is not None:
list1.append(root.left)
if root.right is not None:
list1.append(root.right)
#arr=[i.val for i in list1]
#print(arr)
if right_left_triger==True:
right_left_triger=False
list1=list1[::-1]
else:
right_left_triger=True
print('\n')
zhizi_print(Node1)
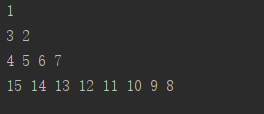
在上一道每行打印二叉树的基础上进行修改,从左到右和从右到左只需改变list2的弹出顺序,即一个弹出最前面的元素,一个弹出最右边的元素,每次循环完成后改变left的值,如果left时True改为False,如果是False改为True.
习题4:判断二叉树是否为满二叉树
首先完全二叉树树的定义是,加入一个二叉树有h层,除了h层外,其余h-1层均满二叉树状态,第h层所有的节点均从最左边开始生长。








 本文详细介绍了二叉树的遍历方法,包括先序、中序、后序及层次遍历,同时探讨了之字形打印和满二叉树判断等高级主题,为读者提供了深入理解二叉树结构的基础。
本文详细介绍了二叉树的遍历方法,包括先序、中序、后序及层次遍历,同时探讨了之字形打印和满二叉树判断等高级主题,为读者提供了深入理解二叉树结构的基础。
















 1098
1098

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








