逻辑回归
- 垃圾邮件分类
- 测试肿瘤是良性还是恶性
- 预测某人的信用是否良好
Sigmoid/Logistic Function
θ和x是矩阵类型的,θ是参数矩阵,x是数据矩阵
 g(x)的取值范围是0—1,就可以分为两类,大于0.5为1类,小于0.5为另一类。
g(x)的取值范围是0—1,就可以分为两类,大于0.5为1类,小于0.5为另一类。

决策边界
中间这条线是值为零的等高线。

画一个圆,半径为1,这就是一个决策边界。

很复杂的决策边界。

逻辑回归的代价函数:
h(X)是样本值,y是标签值。
就是0,1两类代价函数的不同表达。

分段函数合并在一个表达式之中:
 要对θ进行求导:
要对θ进行求导:

求导过程:


逻辑回归一般来说是做二分类的问题的。
正确率、召回率,F1指标

举个例子:


 F1指标的真正的公式:
F1指标的真正的公式:

梯度下降法的逻辑回归
数据:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
from sklearn import preprocessing
#数据是否需要标准化
scale=False
#载入数据
data = np.genfromtxt("LR-testSet.csv",delimiter=',')
x_data = data[:,:-1]
y_data = data[:,-1]
def plot():
x0=[]
x1=[]
y0=[]
y1=[]
#切分不同类别的数据,一行一行的判别
for i in range(len(x_data)):
if y_data[i]==0:
x0.append(x_data[i,0])
y0.append(x_data[i,1])
else:
x1.append(x_data[i, 0])
y1.append(x_data[i, 1])
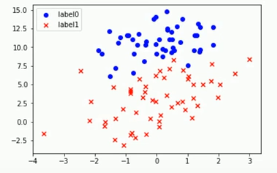
#画图(散点图)
scatter0 = plt.scatter(x0,y0,c='b',marker='o')#实心圆点
scatter1 = plt.scatter(x1, y1, c='r', marker='x')#画叉点
#画图例(上方说明)
plt.legend(handles=[scatter0,scatter1],labels=['label0','label1'],loc='best')
plot()#绘制二维图像
plt.show()#打印出来
#数据处理,添加偏置值
x_data = data[:,:-1]
y_data = data[:,-1,np.newaxis]
print(np.mat(x_data).shape)#(100,2)
print(np.mat(y_data).shape)#(100,1)
#给样本添加偏置值
X_data = np.concatenate((np.ones(100,1),x_data),axis=1)
print(X_data.shape)#(100,3)
def sigmoid(x) :
return 1.0/(1+np.exp(-x))
#ws权值矩阵θ,按位相乘
def cost(xMat,yMat,ws):
left = np.multiply(yMat,np.log(sigmoid(xMat*ws)))
right = np.multiply(1-yMat,np.log(1-sigmoid(xMat*ws)))
return np.sum(left+right)/-(len(xMat))
def gradAscent(xArr,yArr):
#是否要做数据标准化
if scale == True:
xArr = preprocessing.scale(xArr)
xMat = np.mat(xArr)
yMat = np.mat(yArr)
lr=0.001
epochs = 10000
costList=[]
#计算数据行列数
#把矩阵行列值得到,行代表数据个数,列代表权值个数
m,n = np.shape(xMat)#值为100和3
#初始化权值
ws = np.mat(np.ones((n,1)))
#在迭代过程中ws是在改变着的
for i in range(epochs+1):
#xMat和weights矩阵相乘
h=sigmoid(xMat*ws)
#计算误差,代价函数,得到三行一列的矩阵
ws_grad = xMat.T*(h-yMat)/m
ws = ws-lr*ws_grad
#每迭代50次保存一下cost值
if i % 50 == 0:
costList.append(cost(xMat,yMat,ws))
return ws,costList
#训练模型,得到权值和cost的变化
ws,costList = gradAscent(X_data,y_data)
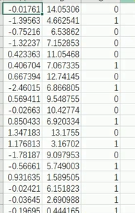
print(ws)
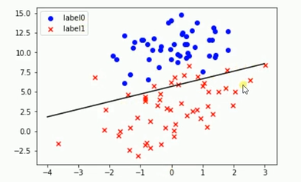
#决策边界 w[0]+w[1]x1+w[2]x2
if scale == False :
plot()
x_test = [[-4],[3]]
y_test = (-ws[0]-x_test*ws[1])/ws[2]
plt.plot(x_test,y_test,'k')
plt.show()
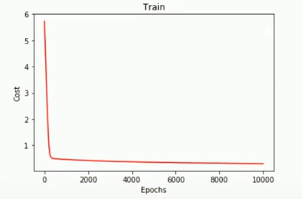
#画图loss值的变化
x = np.linspace(0,10000,201)
plt.plot(x,costList,c='r')
plt.title('Train')
plt.xlabel('Epochs')
plt.ylabel('Cost')
plt.show()
#预测
def predict(x_data,ws):
if scale == True:
x_data = preprocessing.scale(x_data)
xMat = np.mat(x_data)
ws = np.mat(ws)
return [1 if x>=0.5 else 0 for x in sigmoid(xMat*ws)]
predictions = predict(X_data,ws)
predict(classification_report(y_data,predictions))
打印出的ws的值

分界线:
loss值的变化:记录了201次
准确率、召回率
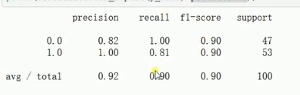
如果数据标准化设置为true的画,loss值变化会缓慢,得到的cost值比较高一点。
调用sklean的逻辑回归完成程序
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
from sklearn import preprocessing
from sklearn import linear_model
#数据是否需要标准化
scale=False
#载入数据
data = np.genfromtxt("LR-testSet.csv",delimiter=',')
x_data = data[:,:-1]
y_data = data[:,-1]
def plot():
x0=[]
x1=[]
y0=[]
y1=[]
#切分不同类别的数据,一行一行的判别
for i in range(len(x_data)):
if y_data[i]==0:
x0.append(x_data[i,0])
y0.append(x_data[i,1])
else:
x1.append(x_data[i, 0])
y1.append(x_data[i, 1])
#画图(散点图)
scatter0 = plt.scatter(x0,y0,c='b',marker='o')#实心圆点
scatter1 = plt.scatter(x1, y1, c='r', marker='x')#画叉点
#画图例(上方说明)
plt.legend(handles=[scatter0,scatter1],labels=['label0','label1'],loc='best')
plot()#绘制二维图像
plt.show()#打印出来
logistic = linear_model.LogisticRegression()
logistic.fit(x_data,y_data)
#决策边界 w[0]+w[1]x1+w[2]x2
if scale == False :
plot()
x_test = np.array([[-4],[3]])
#intercept偏置 coef是权值,模型参数,二维的,两个特征值,所以是两个参数
y_test = (-logistic.intercept_-x_test*logistic.coef_[0][0])/logistic.coef_[0][1]
plt.plot(x_test,y_test,'k')
plt.show()
predictions = logistic.predict(x_data)
print(classification_report(y_data,predictions))























 4402
4402











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








