首先阅读apps/readme.md
## Built-In Applications
NuttX also supports applications that can be started using a name string. In
this case, application entry points with their requirements are gathered
together in two files:
- `builtin/builtin_proto.h` – Entry points, prototype function
- `builtin/builtin_list.h` – Application specific information and requirements
The build occurs in several phases as different build targets are executed: (1)
context, (2) depend, and (3) default (all). Application information is collected
during the make context build phase.
To execute an application function:
`exec_builtin()` is defined in the `apps/include/builtin/builtin.h`.
## NuttShell (NSH) Built-In Commands
One use of builtin applications is to provide a way of invoking your custom
application through the NuttShell (NSH) command line. NSH will support a
seamless method invoking the applications, when the following option is enabled
in the NuttX configuration file:
```conf
CONFIG_NSH_BUILTIN_APPS=y
```
Applications registered in the `apps/builtin/builtin_list.h` file will then be
accessible from the NSH command line. If you type `help` at the NSH prompt, you
will see a list of the registered commands.根据readme文件中的描述,查找关键文件builtin_list.h和builtin_proto.h
apps/builtin/Makefile文件中,找到builtin_list.h和builtin_proto.h的生成规则。
builtin_list.h: registry$(DELIM).updated
ifeq ($(BDATLIST),)
$(call DELFILE, builtin_list.h)
$(Q) touch builtin_list.h
else
$(call CATFILE, builtin_list.h, $(BDATLIST))
endif
builtin_proto.h: registry$(DELIM).updated
ifeq ($(PDATLIST),)
$(call DELFILE, builtin_proto.h)
$(Q) touch builtin_proto.h
else
$(call CATFILE, builtin_proto.h, $(PDATLIST))
endif
从Makfile上和实际文件内容能够看出,
builtin_list.h整合了registry目录下的bdat文件内容
builtin_proto.h整合了registry目录下的pdat文件内容

那么,这些bdat和pdat文件又是怎么来的?在apps/Make.defs中定义了REGISTER函数
define REGISTER
$(Q) echo Register: $1
$(Q) echo { \"$1\", $2, $3, $4 }, > "$(BUILTIN_REGISTRY)$(DELIM)$1.bdat"
$(Q) if [ ! -z $4 ]; then \
echo "int $4(int argc, char *argv[]);" > "$(BUILTIN_REGISTRY)$(DELIM)$1.pdat"; \
fi;
$(Q) touch "$(BUILTIN_REGISTRY)$(DELIM).updated"
endef apps/Application.mk中进行了调用
$(call REGISTER,$(firstword $(APPLIST)),$(firstword $(PRIORITY)),$(firstword $(STACKSIZE)),$(if $(BUILD_MODULE),,$(firstword $(APPLIST))_main))
APPLIST:继承自PROGNAME,也就是apps/examples/demo/Makefile中的
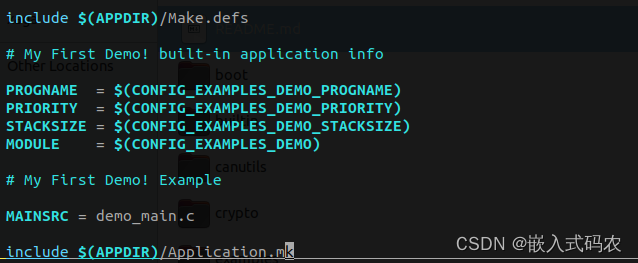
来自于apps/examples/demo/Kconfig中的配置项,REGISTER函数的其他几项形参,也是如此。
config EXAMPLES_DEMO_PROGNAME
string "Program name"
default "demo"
---help---
This is the name of the program that will be used when the NSH ELF
program is installed.
至此,builtin_list.h和builtin_proto.h的来历已经弄清楚了。apps/builtin/builtin_list.c中定义了一个关键的结构体数组g_builtins,结构体的定义在nuttx/include/nuttx/lib/builtin.h中。
struct builtin_s
{
const char *name; /* Invocation name and as seen under /sbin/ */ sbin下显示的名字
int priority; /* Use: SCHED_PRIORITY_DEFAULT */,task优先级
int stacksize; /* Desired stack size */ task栈大小
main_t main; /* Entry point: main(int argc, char *argv[]) */ 线程入口函数指针
};
#include "builtin_proto.h"
const struct builtin_s g_builtins[] =
{
# include "builtin_list.h"
{ NULL, 0, 0, 0 }
};
const int g_builtin_count = sizeof(g_builtins) / sizeof(g_builtins[0]);
展开后:
int demo_main(int argc, char *argv[]);
int nsh_main(int argc, char *argv[]);
int sh_main(int argc, char *argv[]);
int gpio_main(int argc, char *argv[]);
int hello_main(int argc, char *argv[]);
const struct builtin_s g_builtins[] =
{
{ "demo", 100, 2048, demo_main },
{ "sh", 100, 2048, sh_main },
{ "hello", 100, 2048, hello_main },
{ "nsh", 100, 2048, nsh_main },
{ "gpio", 100, 2048, gpio_main },
{ NULL, 0, 0, 0 }
};编译完成后,nuttx在nsh中进行人机交互,下面是app启动的流程。
apps/nshlib/nsh_parse.c中的nsh_parse-->
apps/nshlib/nsh_parse.c中的nsh_parse_cmdparm和nsh_parse_command--->
apps/nshlib/nsh_parse.c中的nsh_execute--->
apps/nshlib/nsh_builtin.c中nsh_builtin函数---->apps/builtin/exec_builtin.c中的exec_builtin,
int exec_builtin(FAR const char *appname, FAR char * const *argv,
FAR const char *redirfile, int oflags)
{
FAR const struct builtin_s *builtin;
posix_spawnattr_t attr;
posix_spawn_file_actions_t file_actions;
struct sched_param param;
pid_t pid;
int index;
int ret;
/* Verify that an application with this name exists */
index = builtin_isavail(appname);
if (index < 0)
{
ret = ENOENT;
goto errout_with_errno;
}
/* Get information about the builtin */
builtin = builtin_for_index(index);
if (builtin == NULL)
{
ret = ENOENT;
goto errout_with_errno;
}
/* Initialize attributes for task_spawn(). */
ret = posix_spawnattr_init(&attr);
if (ret != 0)
{
goto errout_with_errno;
}
ret = posix_spawn_file_actions_init(&file_actions);
if (ret != 0)
{
goto errout_with_attrs;
}
/* Set the correct task size and priority */
param.sched_priority = builtin->priority;
ret = posix_spawnattr_setschedparam(&attr, ¶m);
if (ret != 0)
{
goto errout_with_actions;
}
ret = task_spawnattr_setstacksize(&attr, builtin->stacksize);
if (ret != 0)
{
goto errout_with_actions;
}
/* If robin robin scheduling is enabled, then set the scheduling policy
* of the new task to SCHED_RR before it has a chance to run.
*/
#if CONFIG_RR_INTERVAL > 0
ret = posix_spawnattr_setschedpolicy(&attr, SCHED_RR);
if (ret != 0)
{
goto errout_with_actions;
}
ret = posix_spawnattr_setflags(&attr,
POSIX_SPAWN_SETSCHEDPARAM |
POSIX_SPAWN_SETSCHEDULER);
if (ret != 0)
{
goto errout_with_actions;
}
#else
ret = posix_spawnattr_setflags(&attr, POSIX_SPAWN_SETSCHEDPARAM);
if (ret != 0)
{
goto errout_with_actions;
}
#endif
/* Is output being redirected? */
if (redirfile)
{
/* Set up to close open redirfile and set to stdout (1) */
ret = posix_spawn_file_actions_addopen(&file_actions, 1,
redirfile, oflags, 0644);
if (ret != 0)
{
serr("ERROR: posix_spawn_file_actions_addopen failed: %d\n", ret);
goto errout_with_actions;
}
}
#ifdef CONFIG_LIBC_EXECFUNCS
/* Load and execute the application. */
ret = posix_spawn(&pid, builtin->name, &file_actions, &attr, argv, NULL);
if (ret != 0 && builtin->main != NULL)
#endif
{
/* Start the built-in */
pid = task_spawn(builtin->name, builtin->main, &file_actions,
&attr, (argv) ? &argv[1] : (FAR char * const *)NULL,
(FAR char * const *)NULL);
ret = pid < 0 ? -pid : 0;
}
if (ret != 0)
{
serr("ERROR: task_spawn failed: %d\n", ret);
goto errout_with_actions;
}
/* Free attributes and file actions. Ignoring return values in the case
* of an error.
*/
/* Return the task ID of the new task if the task was successfully
* started. Otherwise, ret will be ERROR (and the errno value will
* be set appropriately).
*/
posix_spawn_file_actions_destroy(&file_actions);
posix_spawnattr_destroy(&attr);
return pid;
errout_with_actions:
posix_spawn_file_actions_destroy(&file_actions);
errout_with_attrs:
posix_spawnattr_destroy(&attr);
errout_with_errno:
errno = ret;
return ERROR;
}
最终通过下面的接口实现了任务的创建,虽然每个任务有自己的栈,但是由于内存,在没有MMU的情况下,如果同一个app启动了多个实例,app中使用的全局变量、静态变量等存放在bss段、data段的数据,多个实例将共享该变量,都可以进行修改,所以需要特别注意。

























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








