1.二维数组螺旋打印
给定一个二维数组 array,请返回「螺旋遍历」该数组的结果。
螺旋遍历:从左上角开始,按照 向右、向下、向左、向上 的顺序 依次 提取元素,然后再进入内部一层重复相同的步骤,直到提取完所有元素。
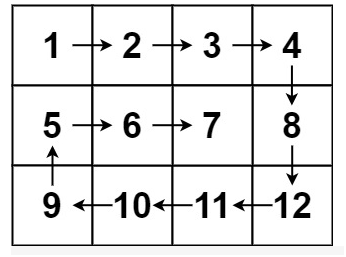
示例 1:
https://leetcode.cn/problems/shun-shi-zhen-da-yin-ju-zhen-lcof/comments/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/spiral-matrix/comments/
2.求数组中最大乘积
3.求数组中连续最大和
描述
一个数组有 N 个元素,求连续子数组的最大和。 例如:[-1,2,1],和最大的连续子数组为[2,1],其和为 3
4.和为 S 的连续正数序列
示例1
5.合并有序数组
两个有序数组合并成新的有序数组
示例 1:
6.数组排序
排序可以使用冒泡+插入+快速+希尔+归并+桶+基数等方式实现
最基础的四个算法:冒泡、选择、插入、快排中,快排的时间复杂度最小O(n*log2n),其他都是O(n2)
排序法 | 平均时间 | 最差情形 | 稳定度 | 额外空间 | 备注 |
冒泡 | O(n2) | O(n2) | 稳定 | O(1) | n小时较好 |
选择 | O(n2) | O(n2) | 不稳定 | O(1) | n小时较好 |
插入 | O(n2) | O(n2) | 稳定 | O(1) | 大部分已排序时较好 |
基数 | O(logRB) | O(logRB) | 稳定 | O(n) | B是真数(0-9), R是基数(个十百) |
Shell | O(nlogn) | O(ns) 1 | 不稳定 | O(1) | s是所选分组 |
快速 | O(nlogn) | O(n2) | 不稳定 | O(nlogn) | n大时较好 |
归并 | O(nlogn) | O(nlogn) | 稳定 | O(1) | n大时较好 |
堆 | O(nlogn) | O(nlogn) | 不稳定 | O(1) | n大时较好 |





















 729
729

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








