这个案例先自己造了一个线性回归的轮子,然后对比python自带库进行对比,代码放出来,亲测可行:
# %load ../../standard_import.txt
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import axes3d
pd.set_option('display.notebook_repr_html', False)
pd.set_option('display.max_columns', None)
pd.set_option('display.max_rows', 150)
pd.set_option('display.max_seq_items', None)
# %config InlineBackend.figure_formats = {'pdf',}
import seaborn as sns
sns.set_context('notebook')
sns.set_style('white')
def warmUpExercise():
return(np.identity(5))
warmUpExercise()
data = np.loadtxt('linear_regression_data1.txt', delimiter=',')
X = np.c_[np.ones(data.shape[0]),data[:,0]]
y = np.c_[data[:,1]]
plt.scatter(X[:,1], y, s=30, c='r', marker='x', linewidths=1)
plt.xlim(4,24)
plt.xlabel('Population of City in 10,000s')
plt.ylabel('Profit in $10,000s');
plt.show()
# 计算损失函数
def computeCost(X, y, theta=[[0], [0]]):
m = y.size
J = 0
h = X.dot(theta)
J = 1.0 / (2 * m) * (np.sum(np.square(h - y)))
return J
s = computeCost(X,y)
print s
# 梯度下降
def gradientDescent(X, y, theta=[[0], [0]], alpha=0.01, num_iters=1500):
m = y.size
J_history = np.zeros(num_iters)
for iter in np.arange(num_iters):
h = X.dot(theta)
theta = theta - alpha * (1.0 / m) * (X.T.dot(h - y))
J_history[iter] = computeCost(X, y, theta)
return (theta, J_history)
# 画出每一次迭代和损失函数变化
theta , Cost_J = gradientDescent(X, y)
print('theta: ',theta.ravel())
plt.plot(Cost_J)
plt.ylabel('Cost J')
plt.xlabel('Iterations');
plt.show()
xx = np.arange(5,23)
yy = theta[0]+theta[1]*xx
# 画出我们自己写的线性回归梯度下降收敛的情况
plt.scatter(X[:,1], y, s=30, c='r', marker='x', linewidths=1)
plt.plot(xx,yy, label='Linear regression (Gradient descent)')
# 和Scikit-learn中的线性回归对比一下
regr = LinearRegression()
regr.fit(X[:,1].reshape(-1,1), y.ravel())
plt.plot(xx, regr.intercept_+regr.coef_*xx, label='Linear regression (Scikit-learn GLM)')
plt.xlim(4,24)
plt.xlabel('Population of City in 10,000s')
plt.ylabel('Profit in $10,000s')
plt.legend(loc=4);
plt.show()
# 预测一下人口为35000和70000的城市的结果
print(theta.T.dot([1, 3.5])*10000)
print(theta.T.dot([1, 7])*10000)
最终输出结果如下:
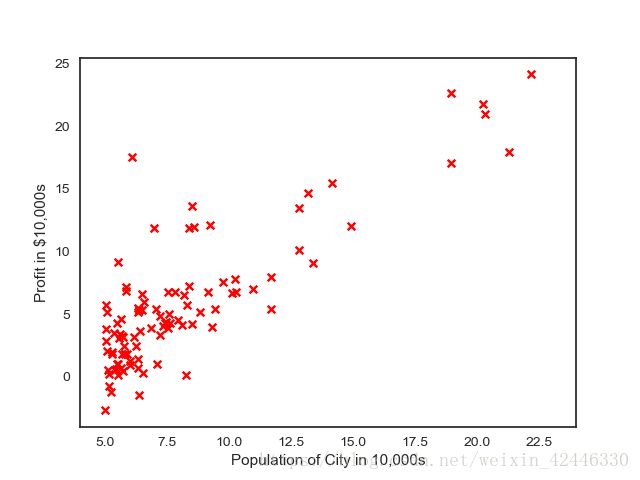
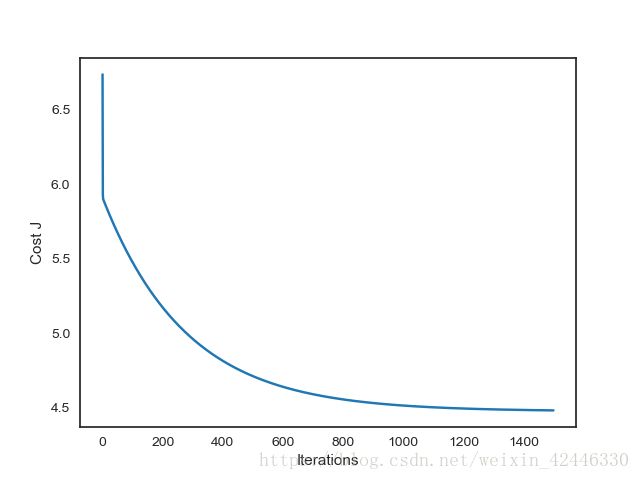
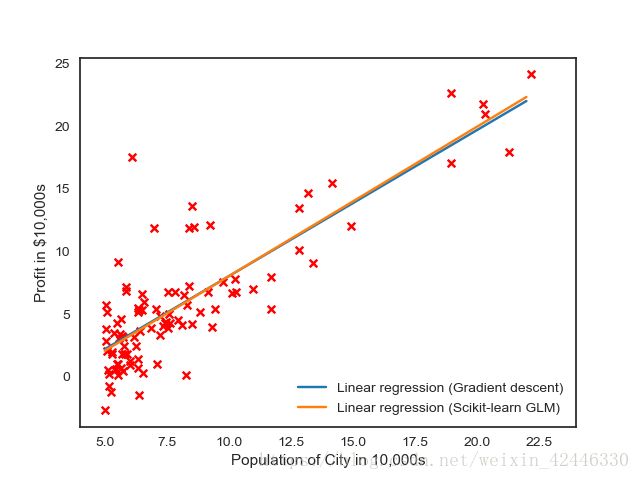
运行结果:
32.072733877455676
('theta: ', array([-3.63029144, 1.16636235]))
[4519.7678677]
[45342.45012945]




















 1493
1493











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








