第一种
- 此时将待测试的图片分类放置于test的子文件下,文件夹的名称就是labels中的名称,如图:
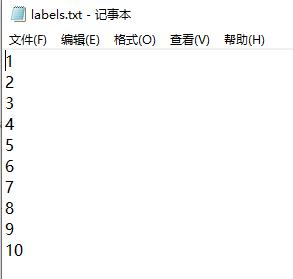
labels.txt文件截图:
# coding=utf-8
from __future__ import division
import os
import caffe
import numpy as np
import datetime
import time
import cv2
root = 'D:/caffe-master/' #修改成你的Caffe项目路径
deploy = 'D:/caffe-master/zzfl/deploy.prototxt' # 修改成你的deploy.prototxt文件路径
#Different models correspond to different deploy.prototxt
caffe_model = 'D:/caffe-master/zzfl/fenlei__iter_40000.caffemodel.h5' # 修改成你的caffemodel文件的路径
#Replace trim or original model
mean_file = 'D:/caffe-master/zzfl/mean.npy' #由mean.binaryproto文件生成的mean.npy文件
labels_filename = 'D:/caffe-master/zzfl/labels.txt' #标签文件
dir = 'D:/caffe-master/zzfl/test/' # 待测试图片所在文件夹
for class_name in os.listdir(dir): #读取文件夹中每一类
#for index,name in enumerate(classes):
class_path = dir+class_name+"/"
for filename in os.listdir(class_path):
img_path = class_path + filename
image = cv2.imread(img_path)
caffe.set_mode_gpu()
filelist = []
filenames = os.listdir(dir)
for fn in filenames:
fullfilename = os.path.join(dir, fn)
filelist.append(fullfilename)
net = caffe.Net(deploy, caffe_model, caffe.TEST)
transformer = caffe.io.Transformer({'data': net.blobs['data'].data.shape})
transformer.set_transpose('data', (2, 0, 1))
transformer.set_mean('data', np.load(mean_file).mean(1).mean(1))
transformer.set_raw_scale('data', 255)
transformer.set_channel_swap('data', (2, 1, 0))
#f=open(root + 'examples/facetestquestions/plant_test.txt','r')
#lines=f.readlines()
#f.close()
#def time_1():
# begin = datetime.datetime.now()
# sum = 0
# for i in xrange(10000000):
# sum = sum + i
# end = datetime.datetime.now()
# return end - begin
#sts=[]
#for line in lines:
# for st in line.split():
# sts.append(st)
#print(sts)
#for st in sts:
# print(st[0:-1])
j = 0
x = 0
num = 0
i = 0
startall = time.time()
#for i in range(0, len(filelist)):
# start = time.time()
# img = filelist[i]
for class_name in os.listdir(dir):
#for index,name in enumerate(classes):
class_path = dir+class_name+"/"
for filename in os.listdir(class_path):
start = time.time()
img_path = class_path + filename
print filename
im = caffe.io.load_image(img_path)
net.blobs['data'].data[...] = transformer.preprocess('data', im)
out = net.forward()
labels = np.loadtxt(labels_filename, str, delimiter='/t')
prob = net.blobs['prob'].data[0].flatten()
index1 = prob.argsort()[-1]
index2 = prob.argsort()[-2]
index3 = prob.argsort()[-3]
index4 = prob.argsort()[-4]
#sts = []
#for line in lines:
# for st in line.split():
# sts.append(st)
#stc = sts[i]
#i = i + 1
#num = len(sts)
#stri = 'noplant'
#if labels[index1] == stri:
# x = x + 1
if class_name == labels[index1]:
j = j + 1
print labels[index1], '--', prob[index1]
print labels[index2], '--', prob[index2]
#print labels[index3], '--', prob[index3]
#print labels[index4], '--', prob[index4]
end = time.time()
print str(end - start)
endall = time.time()
number = 200
print 'TP=', j
print 'FN=', number - j
print 'TPR=', j/number
print 'The average processing time is:', (endall - startall)/len(filelist)
第二种
#coding=utf-8
import sys
caffe_root='D:/caffe-master/' #修改成你的Caffe项目路径
sys.path.append(caffe_root+'python')
import caffe
caffe.set_mode_gpu() #设置为GPU运行
import numpy as np
# from pylab import *
# 修改成你的deploy.prototxt文件路径
model_def = 'D:/caffe-master/zzfl/deploy.prototxt'
model_weights = 'D:/caffe-master/zzfl/fenlei__iter_40000.caffemodel.h5' # 修改成你的caffemodel文件的路径
net = caffe.Net(model_def, # defines the structure of the model
model_weights, # contains the trained weights
caffe.TEST) # use test mode (e.g., don't perform dropout)
#这是一个由mean.binaryproto文件生成mean.npy文件的函数
def convert_mean(binMean,npyMean):
blob = caffe.proto.caffe_pb2.BlobProto()
bin_mean = open(binMean, 'rb' ).read()
blob.ParseFromString(bin_mean)
arr = np.array( caffe.io.blobproto_to_array(blob) )
npy_mean = arr[0]
np.save(npyMean, npy_mean )
binMean='D:/caffe-master/zzfl/fenlei_train_mean.binaryproto' #修改成你的mean.binaryproto文件的路径
npyMean='D:/caffe-master/zzfl/mean.npy' #你想把生成的mean.npy文件放在哪个路径下
convert_mean(binMean,npyMean)
transformer = caffe.io.Transformer({'data': net.blobs['data'].data.shape})
transformer.set_transpose('data', (2,0,1)) # 通道变换,例如从(530,800,3) 变成 (3,530,800)
mu=np.load(npyMean)
# mu=mu.mean(1).mean(1)
transformer.set_mean('data', mu) #如果你在训练模型的时候没有对输入做mean操作,那么这边也不需要
transformer.set_raw_scale('data', 255) # rescale from [0, 1] to [0, 255]
transformer.set_channel_swap('data', (2, 1, 0)) # swap channels from RGB to BGR
with open('D:/caffe-master/zzfl/test.txt') as image_list: # 修改成你要测试的txt文件的路径,这个txt文件的内容一般是:每行表示图像的路径,然后空格,然后是标签,也就是说每行都是两列
with open('D:/caffe-master/zzfl/jieguo.txt','w') as result: # 如果你想把预测的结果写到一个txt文件中,那么把这个路径修改成你想保存这个txt文件的路径
count_right=0
count_all=0
while 1:
list_name=image_list.readline()
if list_name == '': #如果txt文件都读完了则跳出循环
break
image_type=list_name[0:-3].split('.')[-1]
if image_type == 'gif': #这里我对gif个数的图像直接跳过
continue
image = caffe.io.load_image('D:/caffe-master/zzfl/'+list_name)
# 这里要添加你的图像所在的路径,根据你的list_name灵活调整,总之就是图像路径
#imshow(image)
transformed_image = transformer.preprocess('data', image)
# 用转换后的图像代替net.blob中的data
net.blobs['data'].data[...] = transformed_image
net.blobs['data'].reshape(1, 3, 224, 224)
### perform classification
output = net.forward()
# 读取预测结果和真实label
output_prob = net.blobs['prob'].data[0]
true_label = int(list_name[-2:-1])
# 如果预测结果和真实label一样,则count_right+1
if(output_prob.argmax()==true_label):
count_right=count_right+1
count_all=count_all+1
# 保存预测结果,这个可选
result.writelines(list_name[0:-1]+' '+str(output_prob.argmax())+'\n')
#可以每预测完100个样本就打印一些,这样好知道预测的进度,尤其是要预测几万或更多样本的时候,否则你还以为代码卡死了
if(count_all%100==0):
print count_all
# 打印总的预测结果
print 'Accuracy: '+ str(float(count_right)/float(count_all))
print 'count_all: ' + str(count_all)
print 'count_right: ' + str(count_right)
print 'count_wrong: ' + str(count_all-count_right)























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








