- DARTS: Differentiable Architecture Search, ICLR 2019.
- https://arxiv.org/pdf/1806.09055
背景
神经网络结构搜索(NAS)的原理是给定一个称为搜索空间的候选神经网络子结构集合,用某种策略从中搜索出最优的全局神经网络结构。神经网络结构的优劣即性能用某些指标如精度、速度来度量,称为性能评估。其结构可以用下图来衡量:
在每次结构搜索的迭代过程中,算法从搜索空间中选一个子结构,在训练集上训练该子网络,并在验证集上评估效果,接着通过搜索策略循环优化并找到最优的网络结构。
搜索空间定义了网络解的集合,搜索策略定义了以何种方法去寻找最优解,性能评估定义了怎样的网络结构是最优的。
传统的NAS方法大多基于强化学习(RL)或者遗传算法作为搜索的策略,基于离散的搜索空键进行黑箱优化,往往耗时巨大。
可微结构搜索
本文提出了全新的可微结构搜索算法(Differentiable Architecture Search),将搜索空间连续化处理,便于用梯度下降等连续优化算法求解最优网络结构。
该算法提出了一个新的参数 α \alpha α 用于表征网络结构,即该向量代表了最终网络各子结构之间的连接方式。连续结构的单次迭代分两部分:
- 在训练集中搜寻最优的结构参数 α \alpha α,并生成对应网络;
- 在验证集中应用该网络训练常规参数 w w w,并评估效果。
最后由结构参数 α \alpha α 生成离散结构作为最终的神经网络。
Cell
DARTS中的基本结构是Cell,整个网络主体由若干Cell连接而成。Cell分为两种,Normal cell和Reduction Cell。每个同类型Cell的结构相同且共享权重,其内部由若干节点(node)组成,每个节点可以看作一个表示(representation)或者特征图(feature map)。Cell由2个输入节点,一个输出和若干中间节点组成。中间节点与前序节点(包括之前的中间节点以及2个输入节点)的连接关系可以表示为:
x ( j ) = ∑ i < j o ( i , j ) ( x ( i ) ) x^{(j)} = \sum_{i \lt j} o^{(i,j)}(x^{(i)}) x(j)=i<j∑o(i,j)(x(i))
其中 o ( i , j ) o^{(i,j)} o(i,j) 代表某种连接关系,在CNN中,有如下备选:
# genotypes.py
PRIMITIVES = ['none', 'max_pool_3x3', 'avg_pool_3x3', 'skip_connect', 'sep_conv_3x3',
'sep_conv_5x5', 'dil_conv_3x3', 'dil_conv_5x5']
这些操作的集合构成了操作空间 O O O,上述公式具体在搜索过程和测试过程中有所不同。
2个输入节点分别与前2个Cell的输出相连,中间节点与前序节点相连,所有中间节点在通道维度上的concat构成了输出节点。
搜索过程 train & validation
连续网络
对于搜索过程,中间节点与单个前序节点的连接关系可以表示为:
o ‾ ( i , j ) ( x ) = ∑ o ∈ O s o f t m a x ( α o ( i , j ) ) ⋅ o ( x ) = ∑ w e i g h t ( i , j ) ⋅ o ( x ) \begin{aligned} \overline{o}^{(i,j)}(x) &= \sum_{o\in{O}} softmax(\alpha_o^{(i,j)}) \cdot o(x) \\ &= \sum weight^{(i,j)} \cdot o(x) \end{aligned} o(i,j)(x)=o∈O∑softmax(αo(i,j))⋅o(x)=∑weight(i,j)⋅o(x)
由所有在操作集中的操作加权形成mixed operation(每种操作都有一个结果,将结果加权),其中的权重由某两节点间的结构参数 α o ( i , j ) \alpha_o^{(i,j)} αo(i,j) 的 s o f t m a x softmax softmax 生成。
每个中间节点都与其前序节点都有mixed operation的连接关系,故若一个Cell有4个中间节点,就存在 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 = 14 2+3+4+5=14 2+3+4+5=14 个mixed operation。
α \alpha α 可由二维数组表示,行索引代表Cell中的第几个mixed operation连接,列索引代表操作种类。
测试过程 test
离散网络
对于测试过程,结构参数 α \alpha α 已经得到,需要由此确定具体的连接方式,而不是像搜索过程中用mixed operation。
中间节点与前序节点的连接关系由如下方式确定:
x ( j ) = ∑ k < t o p k m a x k ( w e i g h t ( i , j ) ) ⋅ o n o n − z e r o ( i , j ) ( x ( i ) ) x^{(j)} = \sum_{k \lt topk}max_k(weight^{(i,j)}) \cdot o_{non-zero}^{(i,j)}(x^{(i)}) x(j)=k<topk∑maxk(weight(i,j))⋅onon−zero(i,j)(x(i))
即先由 s o f t m a x ( α o ( i , j ) ) softmax(\alpha_o^{(i,j)}) softmax(αo(i,j)) 生成 w e i g h t ( i , j ) weight^{(i,j)} weight(i,j) 向量,每个 w e i g h t ( i , j ) weight^{(i,j)} weight(i,j) 都取最大的一个值并对应相关的非零操作,这样对于第 j j j 个中间节点就得到了 2 + j 2+j 2+j 个最大值,对应它的所有前序节点的某个操作,最后再取 t o p k topk topk 个作为最终的连接关系。
t o p k = { 1 , RNN 2 , CNN topk = \begin{cases} 1, &\text{RNN} \\ 2, &\text{CNN} \end{cases} topk={1,2,RNNCNN
这样就得到了离散的最优网络结构,重新训练得到常规参数后即可用于在测试集上检验效果。
单个Cell的搜索与构建网络过程可由下图表示:
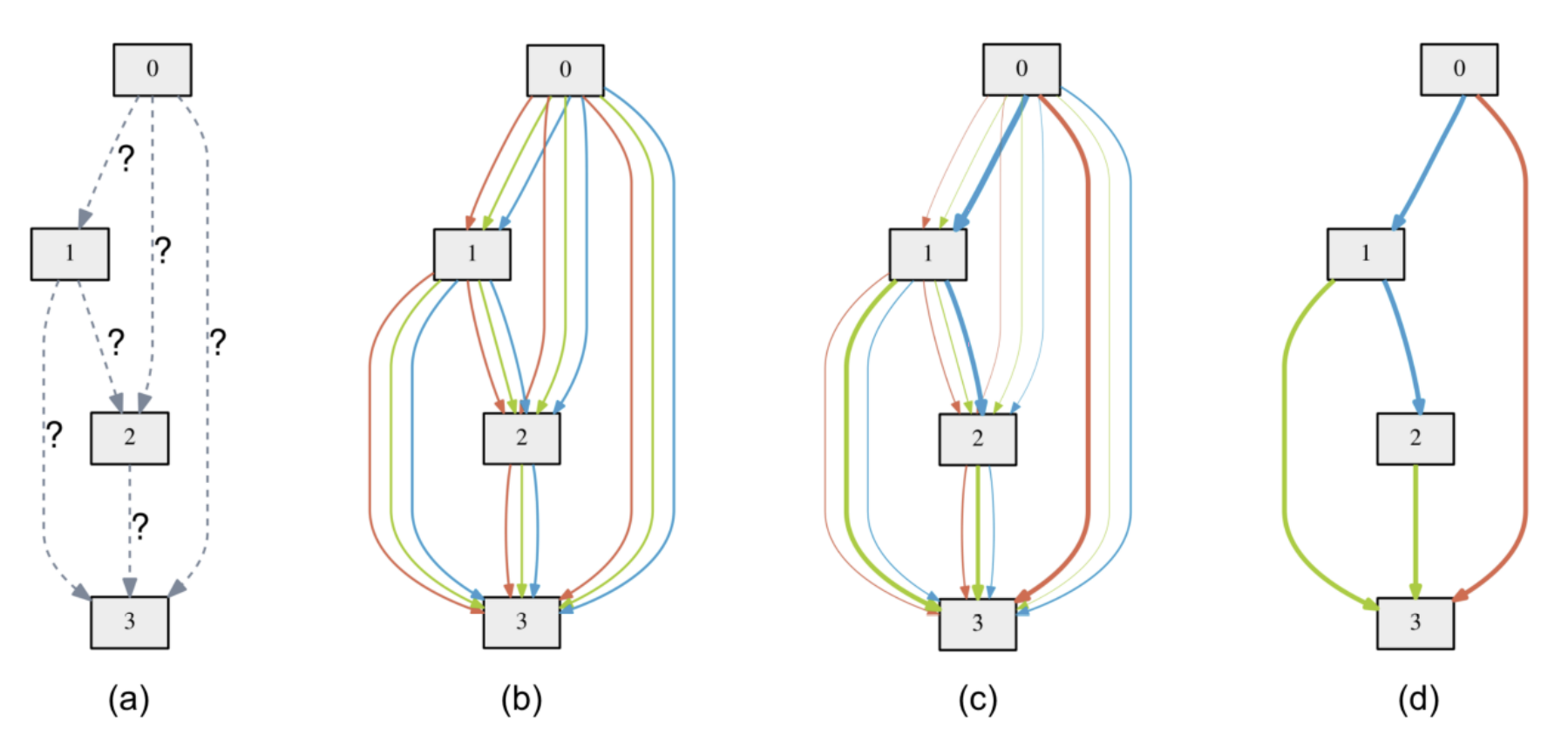
- [a] 初始化各边的结构参数 α \alpha α
- [b] 搜索过程的mixed operation
- [c] 搜索过程的循环双参数优化
- [d] 确定最终离散最优网络结构
离散结构的 Normal Cell 与 Reduction Cell (CNN)


Reduction Cell只出现在整个网络深度为1/3和2/3的位置,与输入节点连接的操作都是stride 2。
双参数优化算法
在DARTS中,因为在常规网络参数 w w w 的基础上引入了新的结构参数 α \alpha α,且结构参数在训练过程中由 s o f t m a x softmax softmax 进行的连续松弛化处理(Continuous Relaxation),两个参数都可以用基于梯度下降的算法进行优化,故这是一个连续性的双参数优化问题:
{ min α L v a l ( w ∗ ( α ) , α ) ( 1 ) s . t . w ∗ ( α ) = arg min w L t r a i n ( w , α ) ( 2 ) \begin{cases} \min_{\alpha} L_{val}(w^*(\alpha), \alpha) &(1) \\ s.t. ~~ w^*(\alpha) = \argmin_{w} L_{train}(w, \alpha) &(2) \end{cases} ⎩⎨⎧minαLval(w∗(α),α)s.t. w∗(α)=wargminLtrain(w,α)(1)(2)
优化目标是在验证集上的 l o s s loss loss 最小,也就是在当前 α \alpha α 所对应的连续性网络中先用常规方法优化 w w w,然后基于此再去优化 α \alpha α 使得 L v a l L_{val} Lval 最小。
整个优化过程分为了在训练集和在验证集上两个部分分别进行,一次循环作为一个epoch。
其中(2)式在较深的网络中耗时较长,且如果跑上几十个batch太费时间,故作者提出了一种近似的方式可以大大减少计算量。(2)式可以近似为:
w ∗ ( α ) = arg min w L t r a i n ( w , α ) ≈ w − ξ ∇ w L t r a i n ( w , α ) ( 3 ) \begin{aligned} w^*(\alpha) &= \argmin_{w} L_{train}(w, \alpha) \\ & \approx w - \xi\nabla_w L_{train}(w, \alpha) \end{aligned} ~~~~~ (3) w∗(α)=wargminLtrain(w,α)≈w−ξ∇wLtrain(w,α) (3)
即只在训练集上反向传递一次 w w w 的梯度并更新作为近似最优。(1)的优化也为反向传递一次:
∇ α L v a l ( w − ξ ∇ w L t r a i n ( w , α ) , α ) ( 4 ) \nabla_{\alpha}L_{val}(w - \xi\nabla_w L_{train}(w, \alpha), \alpha) ~~(4) ∇αLval(w−ξ∇wLtrain(w,α),α) (4)
P.S. 代码中的(4)式叫unrolled,同时也提供了常规方法直接计算 ∇ α L v a l ( w ∗ ( α ) , α ) \nabla_{\alpha} L_{val}(w^*(\alpha), \alpha) ∇αLval(w∗(α),α).
整个搜索+验证过程可以表示为:

对于(4)式的计算,可以简化为:
∇ α L v a l ( w − ξ ∇ w L t r a i n ( w , α ) , α ) = ∇ α L v a l ( w ′ ( α ) , α ) = ∇ α L v a l ( w ′ , α ) ⋅ 1 + ∇ α w ′ ( α ) ⋅ ∇ w ′ L v a l ( w ′ , α ) = ∇ α L v a l ( w ′ , α ) − ξ ∇ α , w 2 L t r a i n ( w , α ) ⋅ ∇ w ′ L v a l ( w ′ , α ) \begin{aligned} & \nabla_{\alpha}L_{val}(w - \xi\nabla_w L_{train}(w, \alpha), \alpha) \\ = & \nabla_{\alpha}L_{val}(w'(\alpha), \alpha) \\ = & \nabla_{\alpha}L_{val}(w', \alpha) \cdot 1 + \nabla_{\alpha}w'(\alpha) \cdot \nabla_{w'}L_{val}(w', \alpha) \\ = & \nabla_{\alpha}L_{val}(w', \alpha) -\xi \nabla_{\alpha, w}^2 L_{train}(w, \alpha) \cdot \nabla_{w'}L_{val}(w', \alpha) \\ \end{aligned} ===∇αLval(w−ξ∇wLtrain(w,α),α)∇αLval(w′(α),α)∇αLval(w′,α)⋅1+∇αw′(α)⋅∇w′Lval(w′,α)∇αLval(w′,α)−ξ∇α,w2Ltrain(w,α)⋅∇w′Lval(w′,α)
由泰勒展开:
f ( w ± ε W ) = f ( w ) ± f ′ ( w ) 1 ! ε W ± . . . f(w\pm\varepsilon W) = f(w) \pm \frac{f'(w)}{1!}\varepsilon W \pm ... f(w±εW)=f(w)±1!f′(w)εW±...
可以得到:
f ′ ( w ) ⋅ W ≈ f ( w + ε W ) − f ( w − ε W ) 2 ε f'(w) \cdot W \approx \frac{f(w + \varepsilon W) - f(w - \varepsilon W)}{2\varepsilon} f′(w)⋅W≈2εf(w+εW)−f(w−εW)
令 W = ∇ w ′ L v a l ( w ′ , α ) W = \nabla_{w'}L_{val}(w', \alpha) W=∇w′Lval(w′,α), f ( α ) = ∇ w L t r a i n ( w , α ) f(\alpha) = \nabla_wL_{train}(w, \alpha) f(α)=∇wLtrain(w,α),并令 w ± = w ± ε ∇ w ′ L v a l ( w ′ , α ) w^{\pm} = w \pm \varepsilon\nabla_{w'}L_{val}(w', \alpha) w±=w±ε∇w′Lval(w′,α)
则(4)式可以进一步化简为:
∇ α L v a l ( w ′ , α ) − ξ ∇ w L t r a i n ( w + , α ) − ∇ w L t r a i n ( w − , α ) 2 ε ( 5 ) \nabla_{\alpha}L_{val}(w', \alpha) - \xi \frac{\nabla_wL_{train}(w^+ , \alpha) - \nabla_wL_{train}(w^- , \alpha)}{2\varepsilon} ~~~ (5) ∇αLval(w′,α)−ξ2ε∇wLtrain(w+,α)−∇wLtrain(w−,α) (5)
由(3)式和(5)式分别对 w w w 和 α \alpha α 进行梯度下降优化,可以大大减少计算量。
代码解析
- https://github.com/quark0/darts
- Python >= 3.5.5, PyTorch == 0.3.1, torchvision == 0.2.0
一些定义
genotypes.py
# operation set in CNN.
PRIMITIVES = ['none', 'max_pool_3x3', 'avg_pool_3x3', 'skip_connect', 'sep_conv_3x3',
'sep_conv_5x5', 'dil_conv_3x3', 'dil_conv_5x5']
# building a model from Genotype.
Genotype = namedtuple('Genotype', 'normal normal_concat reduce reduce_concat')
# each geno consists of ('op_name', index of source node).
DARTS_V2 = Genotype(normal=[('sep_conv_3x3', 0), ('sep_conv_3x3', 1), ('sep_conv_3x3', 0), ('sep_conv_3x3', 1), ('sep_conv_3x3', 1), ('skip_connect', 0), ('skip_connect', 0), ('dil_conv_3x3', 2)], normal_concat=[2, 3, 4, 5], reduce=[('max_pool_3x3', 0), ('max_pool_3x3', 1), ('skip_connect', 2), ('max_pool_3x3', 1), ('max_pool_3x3', 0), ('skip_connect', 2), ('skip_connect', 2), ('max_pool_3x3', 1)], reduce_concat=[2, 3, 4, 5])
operations.py
# for BN, learnable parameters are disabled if affine is true.
# set padding to keep resolution.
OPS = {
'none' : lambda C, stride, affine: Zero(stride),
'avg_pool_3x3' : lambda C, stride, affine: nn.AvgPool2d(3, stride=stride, padding=1, count_include_pad=False),
'max_pool_3x3' : lambda C, stride, affine: nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=stride, padding=1),
'skip_connect' : lambda C, stride, affine: Identity() if stride == 1 else FactorizedReduce(C, C, affine=affine),
'sep_conv_3x3' : lambda C, stride, affine: SepConv(C, C, 3, stride, 1, affine=affine),
'sep_conv_5x5' : lambda C, stride, affine: SepConv(C, C, 5, stride, 2, affine=affine),
'sep_conv_7x7' : lambda C, stride, affine: SepConv(C, C, 7, stride, 3, affine=affine),
'dil_conv_3x3' : lambda C, stride, affine: DilConv(C, C, 3, stride, 2, 2, affine=affine),
'dil_conv_5x5' : lambda C, stride, affine: DilConv(C, C, 5, stride, 4, 2, affine=affine),
'conv_7x1_1x7' : lambda C, stride, affine: nn.Sequential(
nn.ReLU(inplace=False),
nn.Conv2d(C, C, (1,7), stride=(1, stride), padding=(0, 3), bias=False),
nn.Conv2d(C, C, (7,1), stride=(stride, 1), padding=(3, 0), bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(C, affine=affine)
),
}
# for skip_connect in reduction cell.
class FactorizedReduce(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, C_in, C_out, affine=True):
super(FactorizedReduce, self).__init__()
assert C_out % 2 == 0
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=False)
self.conv_1 = nn.Conv2d(C_in, C_out // 2, 1, stride=2, padding=0, bias=False)
self.conv_2 = nn.Conv2d(C_in, C_out // 2, 1, stride=2, padding=0, bias=False)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(C_out, affine=affine)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.relu(x)
out = torch.cat([self.conv_1(x), self.conv_2(x[:,:,1:,1:])], dim=1)
out = self.bn(out)
return out
class SepConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, C_in, C_out, kernel_size, stride, padding, affine=True):
super(SepConv, self).__init__()
self.op = nn.Sequential(
nn.ReLU(inplace=False),
# depthwise conv.
nn.Conv2d(C_in, C_in, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride, padding=padding, groups=C_in, bias=False),
# pointwise conv.
nn.Conv2d(C_in, C_in, kernel_size=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(C_in, affine=affine),
nn.ReLU(inplace=False),
# depthwise conv.
nn.Conv2d(C_in, C_in, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=1, padding=padding, groups=C_in, bias=False),
# pointwise conv.
nn.Conv2d(C_in, C_out, kernel_size=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(C_out, affine=affine),
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.op(x)
class DilConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, C_in, C_out, kernel_size, stride, padding, dilation, affine=True):
super(DilConv, self).__init__()
self.op = nn.Sequential(
nn.ReLU(inplace=False),
# depthwise conv.
nn.Conv2d(C_in, C_in, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride, padding=padding, dilation=dilation, groups=C_in, bias=False),
# pointwise conv.
nn.Conv2d(C_in, C_out, kernel_size=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(C_out, affine=affine),
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.op(x)
搜索过程中更新 α \alpha α 的方法
architect.py
# Architect.step() to update alpha.
class Architect(object):
def __init__(self, model, args):
self.network_momentum = args.momentum
self.network_weight_decay = args.weight_decay
self.model = model
# optimizer for α.
self.optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(self.model.arch_parameters(),
lr=args.arch_learning_rate, betas=(0.5, 0.999), weight_decay=args.arch_weight_decay)
# backward of w to compute w' = w - ξ*▽wLtrain(w, α), and construct a model using w'.
# equal to network_optimizer.step(), but we can't change w to w'.
def _compute_unrolled_model(self, input, target, eta, network_optimizer):
loss = self.model._loss(input, target)
# flatten w to 1D.
theta = _concat(self.model.parameters()).data
try:
moment = _concat(network_optimizer.state[v]['momentum_buffer'] for v in self.model.parameters()).mul_(self.network_momentum)
except:
moment = torch.zeros_like(theta)
dtheta = _concat(torch.autograd.grad(loss, self.model.parameters())).data + self.network_weight_decay*theta
# return the model with the same α and updated w'.
unrolled_model = self._construct_model_from_theta(theta.sub(eta, moment+dtheta))
return unrolled_model
def step(self, input_train, target_train, input_valid, target_valid, eta, network_optimizer, unrolled):
self.optimizer.zero_grad()
if unrolled:
# bilevel optimization. (another way to compute the gradient of α).
self._backward_step_unrolled(input_train, target_train, input_valid, target_valid, eta, network_optimizer)
else:
# traditional optimization.
self._backward_step(input_valid, target_valid)
# update α.
self.optimizer.step()
def _backward_step(self, input_valid, target_valid):
# compute ▽αLval(w, α) directly.
loss = self.model._loss(input_valid, target_valid)
loss.backward()
def _backward_step_unrolled(self, input_train, target_train, input_valid, target_valid, eta, network_optimizer):
# the network_optimizer contains both w and α.
unrolled_model = self._compute_unrolled_model(input_train, target_train, eta, network_optimizer)
# compute Lval.
unrolled_loss = unrolled_model._loss(input_valid, target_valid)
unrolled_loss.backward()
# compute ▽αLval(w', α).
dalpha = [v.grad for v in unrolled_model.arch_parameters()]
# compute ▽w'Lval(w', α).
vector = [v.grad.data for v in unrolled_model.parameters()]
# compute (▽αLtrain(w+, α) - ▽αLtrain(w-, α)) / (2 * epsilon).
implicit_grads = self._hessian_vector_product(vector, input_train, target_train)
# compute ▽αLval(w', α)-eta*(▽αLtrain(w+, α)-▽αLtrain(w-, α))/(2*epsilon).
for g, ig in zip(dalpha, implicit_grads):
g.data.sub_(eta, ig.data)
# update α's gradient.
for v, g in zip(self.model.arch_parameters(), dalpha):
if v.grad is None:
v.grad = Variable(g.data)
else:
v.grad.data.copy_(g.data)
def _construct_model_from_theta(self, theta):
...
return model_new.cuda()
def _hessian_vector_product(self, vector, input, target, r=1e-2):
...
return "implicit_grads"
连续结构的搜索过程
model_search.py
class MixedOp(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, C, stride):
super(MixedOp, self).__init__()
self._ops = nn.ModuleList()
for primitive in PRIMITIVES:
# learnable parameters of BN are banned during searching.
op = OPS[primitive](C, stride, affine=False)
if 'pool' in primitive:
op = nn.Sequential(op, nn.BatchNorm2d(C, affine=False))
self._ops.append(op)
def forward(self, x, weights):
# add each output of operation using weights(softmax of alfa).
return sum(w * op(x) for w, op in zip(weights, self._ops))
class Cell(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, steps, multiplier, C_prev_prev, C_prev, C, reduction, reduction_prev):
super(Cell, self).__init__()
# Is this a reduction cell?
self.reduction = reduction
# first input node, connect the output of C_[k-2].
if reduction_prev:
self.preprocess0 = FactorizedReduce(C_prev_prev, C, affine=False)
else:
self.preprocess0 = ReLUConvBN(C_prev_prev, C, 1, 1, 0, affine=False)
# second input node, connect the output of C_[k-1].
self.preprocess1 = ReLUConvBN(C_prev, C, 1, 1, 0, affine=False)
# the number of intermediate nodes.
self._steps = steps
# the muliplier of cell's output.
self._multiplier = multiplier
# the stack of all ops within a cell.
self._ops = nn.ModuleList()
self._bns = nn.ModuleList()
# traverse the intermediate nodes.
for i in range(self._steps):
# The inputs of each intermediate node consist of the outputs of all previous nodes
# including 2 input nodes. (e.g. 3rd intermediate node has 4 ops as its input)
for j in range(2+i):
stride = 2 if reduction and j < 2 else 1
op = MixedOp(C, stride)
# len: 2 + 3 + 4 + ...
self._ops.append(op)
def forward(self, s0, s1, weights):
# 2 input nodes.
s0 = self.preprocess0(s0)
s1 = self.preprocess1(s1)
# nodes.
states = [s0, s1]
# offset indicates the location of intermediate nodes. (e.g. range [offset]->[offset+2] is for 2nd intermediate node)
offset = 0
for i in range(self._steps):
# The output of current intermediate node consists of the sum of op(previous_node).
# j indicates a certain op source node, h is the current intermediate node.
s = sum(self._ops[offset+j](h, weights[offset+j]) for j, h in enumerate(states))
offset += len(states)
states.append(s)
# expand the channel of cell's output to multiplier*C.
return torch.cat(states[-self._multiplier:], dim=1)
class Network(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, C, num_classes, layers, criterion, steps=4, multiplier=4, stem_multiplier=3):
super(Network, self).__init__()
# initial number of channels.
self._C = C
self._num_classes = num_classes
self._layers = layers
self._criterion = criterion
self._steps = steps
self._multiplier = multiplier
C_curr = stem_multiplier*C
# stem module before the cell. [C -> stem_multiplier*C]
self.stem = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, C_curr, 3, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(C_curr)
)
# input nodes for 1st cell: stem, stem; for 2nd cell: stem, 1st cell.
# C_pre is the number of channels of the previous cell's output.
# C_curr is the number of channels inside the current cell.
C_prev_prev, C_prev, C_curr = C_curr, C_curr, C
self.cells = nn.ModuleList()
reduction_prev = False
for i in range(layers):
# reduction cells appear in the 1/3 and 2/3 of the total depth.
if i in [layers//3, 2*layers//3]:
# double the number of channels inside cells. (e.g. C, C, ..., 2*C, 2*C, ..., 4*C, 4*C, ...)
C_curr *= 2
reduction = True
else:
reduction = False
cell = Cell(steps, multiplier, C_prev_prev, C_prev, C_curr, reduction, reduction_prev)
reduction_prev = reduction
self.cells += [cell]
C_prev_prev, C_prev = C_prev, multiplier*C_curr
self.global_pooling = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.classifier = nn.Linear(C_prev, num_classes)
self._initialize_alphas()
# copy the model with the same alphas.
def new(self):
model_new = Network(self._C, self._num_classes, self._layers, self._criterion).cuda()
for x, y in zip(model_new.arch_parameters(), self.arch_parameters()):
x.data.copy_(y.data)
return model_new
def forward(self, input):
s0 = s1 = self.stem(input)
for i, cell in enumerate(self.cells):
if cell.reduction:
weights = F.softmax(self.alphas_reduce, dim=-1)
else:
weights = F.softmax(self.alphas_normal, dim=-1)
# apply the foward pass of cell.
s0, s1 = s1, cell(s0, s1, weights)
# [batch_size, C, H, W] -> [batch_size, C, 1, 1]
out = self.global_pooling(s1)
# flatten to [batch_size, C].
logits = self.classifier(out.view(out.size(0),-1))
return logits
def _loss(self, input, target):
logits = self(input)
return self._criterion(logits, target)
def _initialize_alphas(self):
k = sum(1 for i in range(self._steps) for n in range(2+i))
num_ops = len(PRIMITIVES)
# the shape of alphas: [k, num_ops].
self.alphas_normal = Variable(1e-3*torch.randn(k, num_ops).cuda(), requires_grad=True)
self.alphas_reduce = Variable(1e-3*torch.randn(k, num_ops).cuda(), requires_grad=True)
self._arch_parameters = [
self.alphas_normal,
self.alphas_reduce,
]
def arch_parameters(self):
return self._arch_parameters
# discrete architecure, top-2 strongest ops.
def genotype(self):
def _parse(weights):
# size of gene: number of intermediate nodes x 2.
gene = []
n = 2
start = 0
for i in range(self._steps):
end = start + n
# range[start:end] is the index of an intermediate mode.
W = weights[start:end].copy()
# take out the strongest op within each connection, then take out the top-2 op, return its index of source node.
edges = sorted(range(i + 2), key=lambda x: -max(W[x][k] for k in range(len(W[x])) if k != PRIMITIVES.index('none')))[:2]
# j indicates the top-2 strongest source nodes.
for j in edges:
k_best = None
for k in range(len(W[j])):
if k != PRIMITIVES.index('none'):
if k_best is None or W[j][k] > W[j][k_best]:
k_best = k
# k_best is the index of strongest op within the top-2 nodes.
gene.append((PRIMITIVES[k_best], j))
start = end
n += 1
return gene
# equal to dim=1, softmax the row vector.
gene_normal = _parse(F.softmax(self.alphas_normal, dim=-1).data.cpu().numpy())
gene_reduce = _parse(F.softmax(self.alphas_reduce, dim=-1).data.cpu().numpy())
concat = range(2+self._steps-self._multiplier, self._steps+2)
genotype = Genotype(
normal=gene_normal, normal_concat=concat,
reduce=gene_reduce, reduce_concat=concat
)
return genotype
train_search.py
def main():
...
# starting searching for α.
for epoch in range(args.epochs):
...
# training.
train_acc, train_obj = train(train_queue, valid_queue, model, architect, criterion, optimizer, lr)
logging.info('train_acc %f', train_acc)
# validation (forward pass only).
valid_acc, valid_obj = infer(valid_queue, model, criterion)
logging.info('valid_acc %f', valid_acc)
# save model.
utils.save(model, os.path.join(args.save, 'weights.pt'))
def train(train_queue, valid_queue, model, architect, criterion, optimizer, lr):
objs = utils.AvgrageMeter()
top1 = utils.AvgrageMeter()
top5 = utils.AvgrageMeter()
for step, (input, target) in enumerate(train_queue):
model.train()
n = input.size(0)
input = Variable(input, requires_grad=False).cuda()
target = Variable(target, requires_grad=False).cuda(async=True)
# get a random minibatch from the search queue with replacement.
input_search, target_search = next(iter(valid_queue))
input_search = Variable(input_search, requires_grad=False).cuda()
target_search = Variable(target_search, requires_grad=False).cuda(async=True)
# update α.
architect.step(input, target, input_search, target_search, lr, optimizer, unrolled=args.unrolled)
optimizer.zero_grad()
logits = model(input)
loss = criterion(logits, target)
loss.backward()
nn.utils.clip_grad_norm(model.parameters(), args.grad_clip)
# update w.
optimizer.step()
prec1, prec5 = utils.accuracy(logits, target, topk=(1, 5))
objs.update(loss.data[0], n)
top1.update(prec1.data[0], n)
top5.update(prec5.data[0], n)
if step % args.report_freq == 0:
logging.info('train %03d %e %f %f', step, objs.avg, top1.avg, top5.avg)
return top1.avg, objs.avg
def infer(valid_queue, model, criterion):
...
model.eval()
for step, (input, target) in enumerate(valid_queue):
...
if step % args.report_freq == 0:
logging.info('valid %03d %e %f %f', step, objs.avg, top1.avg, top5.avg)
return top1.avg, objs.avg
由genotype生成离散结构
model.py
class Cell(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, genotype, C_prev_prev, C_prev, C, reduction, reduction_prev):
super(Cell, self).__init__()
print(C_prev_prev, C_prev, C)
if reduction_prev:
self.preprocess0 = FactorizedReduce(C_prev_prev, C)
else:
self.preprocess0 = ReLUConvBN(C_prev_prev, C, 1, 1, 0)
self.preprocess1 = ReLUConvBN(C_prev, C, 1, 1, 0)
# indices[index_of_intermediate_nodes:...+1]: index of top-2 source nodes.
if reduction:
op_names, indices = zip(*genotype.reduce)
concat = genotype.reduce_concat
else:
op_names, indices = zip(*genotype.normal)
concat = genotype.normal_concat
self._compile(C, op_names, indices, concat, reduction)
# size of op_names, indices: 2 x num of intermediate nodes.
def _compile(self, C, op_names, indices, concat, reduction):
assert len(op_names) == len(indices)
self._steps = len(op_names) // 2
# index of nodes need to be concatened for output.
self._concat = concat
self.multiplier = len(concat)
self._ops = nn.ModuleList()
for name, index in zip(op_names, indices):
stride = 2 if reduction and index < 2 else 1
op = OPS[name](C, stride, True)
self._ops += [op]
self._indices = indices
def forward(self, s0, s1, drop_prob):
s0 = self.preprocess0(s0)
s1 = self.preprocess1(s1)
states = [s0, s1]
for i in range(self._steps):
h1 = states[self._indices[2*i]]
h2 = states[self._indices[2*i+1]]
op1 = self._ops[2*i]
op2 = self._ops[2*i+1]
h1 = op1(h1)
h2 = op2(h2)
if self.training and drop_prob > 0.:
if not isinstance(op1, Identity):
h1 = drop_path(h1, drop_prob)
if not isinstance(op2, Identity):
h2 = drop_path(h2, drop_prob)
s = h1 + h2
states += [s]
return torch.cat([states[i] for i in self._concat], dim=1)
class Network(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, C, num_classes, layers, auxiliary, genotype):
...
def forward(self, input):
...
train.py
def main():
...
for epoch in range(args.epochs):
...
# training.
train_acc, train_obj = train(train_queue, model, criterion, optimizer)
logging.info('train_acc %f', train_acc)
# validation (forward pass only).
valid_acc, valid_obj = infer(valid_queue, model, criterion)
logging.info('valid_acc %f', valid_acc)
# save model.
utils.save(model, os.path.join(args.save, 'weights.pt'))







 DARTS是一种神经网络结构搜索方法,通过将结构搜索空间连续化处理,利用梯度下降算法高效搜索最优网络结构。该方法引入了混合运算,采用双参数优化策略,能够在较少计算资源下快速收敛。
DARTS是一种神经网络结构搜索方法,通过将结构搜索空间连续化处理,利用梯度下降算法高效搜索最优网络结构。该方法引入了混合运算,采用双参数优化策略,能够在较少计算资源下快速收敛。
















 727
727

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








