部分转自:

递归
一棵树要么是空树,要么有两个指针,每个指针指向一棵树。树是一种递归结构,很多树的问题可以使用递归来处理。
0.相同的树
判断两个树是否相等
迭代(调用函数后左右与)
class Solution {
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(p==null && q==null){
return true;
}
if (q == null || p == null) return false;
if (p.val != q.val) return false;
return (isSameTree(p.left, q.left) && isSameTree(q.right, q.left));
}
}
递归(成对放入队列中)
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
Queue<TreeNode> queuep = new LinkedList<>();
queuep.add(p);
queuep.add(q);
while (!queuep.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode t1 = queuep.poll();
TreeNode t2 = queuep.poll();
if (t1 == null && t2 == null) {
continue;
}
if (t1 == null || t2 == null) {//结构不同
return false;
}
if (t1.val != t2.val) {
return false;
}
queuep.add(t1.left);
queuep.add(t2.left);
queuep.add(t1.right);
queuep.add(t2.right);
}
return true;
}
0.5 对称二叉树
给定一个二叉树,检查它是否是镜像对称的。
迭代
注意和上面的思路差不多,所以是有套路的
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(root);
q.add(root);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode t1 = q.poll();
TreeNode t2 = q.poll();
//一定要注意放入一个null值后队列也是有值的
if (t1 == null && t2 == null) continue;
if (t1 == null || t2 == null) return false;
if (t1.val != t2.val) return false;
q.add(t1.left);
q.add(t2.right);
q.add(t1.right);
q.add(t2.left);
}
return true;
}
递归(‘左右根’与 模板)
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
//太机智了,不用单独谈论null的情形
return isMirror(root, root);
}
private static isMirror helper(TreeNode h, TreeNode t){
if (t1 == null && t2 == null) return true;
if (t1 == null || t2 == null) return false;
//注意参数里面传的是哪些节点
return (t1.val == t2.val)
&& isMirror(t1.right, t2.left)
&& isMirror(t1.left, t2.right);
}
}
0.6 锯齿遍历树
z字形
103. 二叉树的锯齿形层次遍历
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> levels = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
if(root == null) return levels;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
int level = 0;
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
levels.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
int lens = queue.size();
for(int i = 0; i < lens; i++) {
TreeNode p = queue.poll();
if (level % 2 == 0) {
levels.get(level).add(p.val);
}
else {
levels.get(level).add(0, p.val);//倒序输入数值满足要求,始终将其新的值放在最前面
}
if(p.left != null) queue.add(p.left);
if(p.right != null) queue.add(p.right);
}
level++;
}
return levels;
}
}
1. 树的高度
104. Maximum Depth of Binary Tree (Easy)
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1;
}
1.2 前序和中序构造二叉树
1.2 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
要么在inorder建个map;要么搜索
class Solution {
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
if(preorder.length==0) return null;
int val = preorder[0], i=0;
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(val);
while(inorder[i]!=val) {
i++;
if(i > inorder.length){
return null;
}
}
node.left = buildTree(Arrays.copyOfRange(preorder,1,i+1),Arrays.copyOfRange(inorder,0,i));
node.right = buildTree(Arrays.copyOfRange(preorder,i+1,preorder.length),Arrays.copyOfRange(inorder,i+1,inorder.length));
return node;
}
}
中序和后序遍历重建树
与上题基本一致,只不过后序是左右根,最后一个一定是根。
从先序遍历还原二叉树
2. 平衡树
110. Balanced Binary Tree (Easy)
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
平衡树左右子树高度差都小于等于 1
//这个是自下而上
private boolean result = true;
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
maxDepth(root);
return result;
}
//缺点:需要遍历每个叶子节点才能结束
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int l = maxDepth(root.left);
int r = maxDepth(root.right);
if (Math.abs(l - r) > 1) result = false;
return 1 + Math.max(l, r);
}
力扣官方题解
//自上而下
很经典的一种模板:辅助函数与主函数之间求与
class Solution {
// Recursively obtain the height of a tree. An empty tree has -1 height
private int height(TreeNode root) {
// An empty tree has height -1
if (root == null) {
return -1;
}
return 1 + Math.max(height(root.left), height(root.right));
}
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
// An empty tree satisfies the definition of a balanced tree
if (root == null) {
return true;
}
// Check if subtrees have height within 1. If they do, check if the
// subtrees are balanced
return Math.abs(height(root.left) - height(root.right)) < 2
&& isBalanced(root.left)
&& isBalanced(root.right);
}
};
//自下而上,可以提前终止
// Utility class to store information from recursive calls
final class TreeInfo {
public final int height;
public final boolean balanced;
public TreeInfo(int height, boolean balanced) {
this.height = height;
this.balanced = balanced;
}
}
class Solution {
private TreeInfo isBalancedTreeHelper(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return new TreeInfo(-1, true);
}
TreeInfo left = isBalancedTreeHelper(root.left);
if (!left.balanced) {
return new TreeInfo(-1, false);
}
TreeInfo right = isBalancedTreeHelper(root.right);
if (!right.balanced) {
return new TreeInfo(-1, false);
}
if (Math.abs(left.height - right.height) < 2) {
return new TreeInfo(Math.max(left.height, right.height) + 1, true);
}
return new TreeInfo(-1, false);
}
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
return isBalancedTreeHelper(root).balanced;
}
};
2.8 最长路径
class Solution {
private int res = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
public int maxPathSum(TreeNode root) {
//思路遍历下,每个都找以左子树为端点的最长和以右子树为端点的最长值
helper(root);
return res;
}
private int helper(TreeNode root){
if(root==null) return 0;
//一定要注意这个,不要写错。有一个和0判断的值。
int le = Math.max(0, helper(root.left));
int ri = Math.max(0, helper(root.right));
res = Math.max(res, Math.max(Math.max, res));
return root.val + Math.max(0, Math.max(le, ri));
}
}
3. 两节点的最长路径
与节点的值是无关的。
Input:
1
/ \
2 3
/ \
4 5
Return 3, which is the length of the path [4,2,1,3] or [5,2,1,3].
private int max = 0;
public int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
depth(root);
return max;
}
private int depth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int leftDepth = depth(root.left);
int rightDepth = depth(root.right);
max = Math.max(max, leftDepth + rightDepth);
return Math.max(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1;
}
3.2 二叉树的最小深度
111. 二叉树的最小深度
// 应该这么做
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return 0;
// 当前节点的左节点为空, 右节点不为空,就不计算左边的!!
else if (root.left == null) return minDepth(root.right) + 1;
else if (root.right == null) return minDepth(root.left) + 1; // 处理情况:当前节点的右节点为空, 左节点不为空
else return Math.min(minDepth(root.left), minDepth(root.right)) + 1; // 处理情况:当前节点的左右节点全不为空或全为空
}
}
3.3 路径总和
112.路径总和
class Solution {
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if(root==null) return false;
if(root.left==null && root.right == null){
return sum==root.val;
}
return hasPathSum(root.left, sum - root.val) || hasPathSum(root.right, sum - root.val);
}
}
3.4 路径总和2
class Solution {
private List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
helper(root, sum);
return res;
}
private void helper(TreeNode root, int sum){
if(root==null) return;
temp.add(root.val);
if(root.left==null && root.right == null){
if(sum==root.val){
res.add(new ArrayList<>(temp));
}
temp.remove(temp.size() - 1);
return;
}
helper(root.left, sum - root.val);
helper(root.right, sum - root.val);
temp.remove(temp.size() - 1);
}
}
别人的,注意辅助函数的细微差别,这个是记录一个cursum,上一个是直接减sum
List<List<Integer>> res;
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
res = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null)
return res;
backTrack(root, sum, 0, new ArrayList<>());
return res;
}
private void backTrack(TreeNode x, int sum, int curSum, List<Integer> vals){
vals.add(x.val);
curSum += x.val;
if(x.left == null && x.right == null){
if(curSum == sum){
res.add(new ArrayList<>(vals));
}
vals.remove(vals.size() - 1);
return;
}
if(x.left != null)
backTrack(x.left, sum, curSum, vals);
if(x.right != null)
backTrack(x.right, sum, curSum, vals);
vals.remove(vals.size() - 1);
}
先序遍历,将前一个节点保存,右指针指向新的。此时需要用一个节点保存原节点的右指针
class Solution {
TreeNode pre = null;
public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return;
}
if(pre != null){
pre.right = root;
pre.left = null;
}
// 很巧妙,pre
pre = root;
TreeNode t = root.right;
flatten(root.left);
flatten(t);
}
}
后序遍历 ,将前一个节点保存,新节点的右指针指向前一个。
4. 翻转树
226. Invert Binary Tree (Easy)
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
TreeNode right = invertTree(root.right);
TreeNode left = invertTree(root.left);
root.left = right;
root.right = left;
return root;
}
5. 归并两棵树
617. Merge Two Binary Trees (Easy)
Input:
Tree 1 Tree 2
1 2
/ \ / \
3 2 1 3
/ \ \
5 4 7
Output:
3
/ \
4 5
/ \ \
5 4 7
public TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode t1, TreeNode t2) {
if (t1 == null && t2 == null) return null;
if (t1 == null) return t2;
if (t2 == null) return t1;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(t1.val + t2.val);
root.left = mergeTrees(t1.left, t2.left);
root.right = mergeTrees(t1.right, t2.right);
return root;
}
6. 判断路径和是否等于一个数
Leetcdoe : 112. Path Sum (Easy)
Given the below binary tree and sum = 22,
5
/ \
4 8
/ / \
11 13 4
/ \ \
7 2 1
return true, as there exist a root-to-leaf path 5->4->11->2 which sum is 22.
路径和定义为从 root 到 leaf 的所有节点的和。
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if (root == null) return false;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null && root.val == sum) return true;
return hasPathSum(root.left, sum - root.val) || hasPathSum(root.right, sum - root.val);
}
6.1 求根到叶子节点数字之和
class Solution {
int res = 0;
public int sumNumbers(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return 0;
helper(root, 0);
return res;
}
private void helper(TreeNode root, long cur){
if(root.left==null && root.right==null) {
res += cur + root.val;
return;
}
if(root.left!=null){
helper(root.left, (root.val + cur)*10);
}
if(root.right != null){
helper(root.right, (root.val + cur)*10);
}
}
}
别人的,辅助函数带返回值 ,返回判断也恰到好处
public int sumNumbers(TreeNode root) {
return helper(root, 0);
}
public int helper(TreeNode root, int i){
if (root == null) return 0;
int temp = i * 10 + root.val;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null)
return temp;
return helper(root.left, temp) + helper(root.right, temp);
}
7. 统计路径和等于一个数的路径数量
437. Path Sum III (Easy)
root = [10,5,-3,3,2,null,11,3,-2,null,1], sum = 8
10
/ \
5 -3
/ \ \
3 2 11
/ \ \
3 -2 1
Return 3. The paths that sum to 8 are:
1. 5 -> 3
2. 5 -> 2 -> 1
3. -3 -> 11
路径不一定以 root 开头,也不一定以 leaf 结尾,但是必须连续。
public int pathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int ret = pathSumStartWithRoot(root, sum) + pathSum(root.left, sum) + pathSum(root.right, sum);
return ret;
}
private int pathSumStartWithRoot(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int ret = 0;
if (root.val == sum) ret++;
ret += pathSumStartWithRoot(root.left, sum - root.val) + pathSumStartWithRoot(root.right, sum - root.val);
return ret;
}
8. 子树
572. Subtree of Another Tree (Easy)
Given tree s:
3
/ \
4 5
/ \
1 2
Given tree t:
4
/ \
1 2
Return true, because t has the same structure and node values with a subtree of s.
Given tree s:
3
/ \
4 5
/ \
1 2
/
0
Given tree t:
4
/ \
1 2
Return false.
public boolean isSubtree(TreeNode s, TreeNode t) {
if (s == null) return false;
return isSubtreeWithRoot(s, t) || isSubtree(s.left, t) || isSubtree(s.right, t);
}
private boolean isSubtreeWithRoot(TreeNode s, TreeNode t) {
if (t == null && s == null) return true;
if (t == null || s == null) return false;
if (t.val != s.val) return false;
return isSubtreeWithRoot(s.left, t.left) && isSubtreeWithRoot(s.right, t.right);
}
9. 树的对称
101. Symmetric Tree (Easy)
1
/ \
2 2
/ \ / \
3 4 4 3
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return true;
return isSymmetric(root.left, root.right);
}
private boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode t1, TreeNode t2) {
if (t1 == null && t2 == null) return true;
if (t1 == null || t2 == null) return false;
if (t1.val != t2.val) return false;
return isSymmetric(t1.left, t2.right) && isSymmetric(t1.right, t2.left);
}
10. 最小路径
111. Minimum Depth of Binary Tree (Easy)
树的根节点到叶子节点的最小路径长度
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int left = minDepth(root.left);
int right = minDepth(root.right);
if (left == 0 || right == 0) return left + right + 1;
return Math.min(left, right) + 1;
}
11. 统计左叶子节点的和
404. Sum of Left Leaves (Easy)
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
There are two left leaves in the binary tree, with values 9 and 15 respectively. Return 24.
public int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
if (isLeaf(root.left)) return root.left.val + sumOfLeftLeaves(root.right);
return sumOfLeftLeaves(root.left) + sumOfLeftLeaves(root.right);
}
private boolean isLeaf(TreeNode node){
if (node == null) return false;
return node.left == null && node.right == null;
}
12. 相同节点值的最大路径长度
687. Longest Univalue Path (Easy)
1
/ \
4 5
/ \ \
4 4 5
Output : 2
private int path = 0;
public int longestUnivaluePath(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root);
return path;
}
private int dfs(TreeNode root){
if (root == null) return 0;
int left = dfs(root.left);
int right = dfs(root.right);
int leftPath = root.left != null && root.left.val == root.val ? left + 1 : 0;
int rightPath = root.right != null && root.right.val == root.val ? right + 1 : 0;
path = Math.max(path, leftPath + rightPath);
return Math.max(leftPath, rightPath);
}
13. 间隔遍历
337. House Robber III (Medium)
3
/ \
2 3
\ \
3 1
Maximum amount of money the thief can rob = 3 + 3 + 1 = 7.
public int rob(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int val1 = root.val;
if (root.left != null) val1 += rob(root.left.left) + rob(root.left.right);
if (root.right != null) val1 += rob(root.right.left) + rob(root.right.right);
int val2 = rob(root.left) + rob(root.right);
return Math.max(val1, val2);
}
14. 找出二叉树中第二小的节点
671. Second Minimum Node In a Binary Tree (Easy)
Input:
2
/ \
2 5
/ \
5 7
Output: 5
一个节点要么具有 0 个或 2 个子节点,如果有子节点,那么根节点是最小的节点。
public int findSecondMinimumValue(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return -1;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return -1;
int leftVal = root.left.val;
int rightVal = root.right.val;
if (leftVal == root.val) leftVal = findSecondMinimumValue(root.left);
if (rightVal == root.val) rightVal = findSecondMinimumValue(root.right);
if (leftVal != -1 && rightVal != -1) return Math.min(leftVal, rightVal);
if (leftVal != -1) return leftVal;
return rightVal;
}
二叉树的最近公共祖先
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root == null || root == p || root==q) return root;
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
if(left == null && right==null){
return null;
}
if(left==null) return right;
if(right==null) return left;
//当两个均不为null时,说明两个节点散落在两个子树中。
return root;
}
}
层次遍历
使用 BFS 进行层次遍历。不需要使用两个队列来分别存储当前层的节点和下一层的节点,因为在开始遍历一层的节点时,当前队列中的节点数就是当前层的节点数,只要控制遍历这么多节点数,就能保证这次遍历的都是当前层的节点。
1. 一棵树每层节点的平均数
637. Average of Levels in Binary Tree (Easy)
public List<Double> averageOfLevels(TreeNode root) {
List<Double> ret = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return ret;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int cnt = queue.size();
double sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
sum += node.val;
if (node.left != null) queue.add(node.left);
if (node.right != null) queue.add(node.right);
}
ret.add(sum / cnt);
}
return ret;
}
2. 得到左下角的节点
513. Find Bottom Left Tree Value (Easy)
Input:
1
/ \
2 3
/ / \
4 5 6
/
7
Output:
7
public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
root = queue.poll();
if (root.right != null) queue.add(root.right);
if (root.left != null) queue.add(root.left);
}
return root.val;
}
3.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
利用了辅助前节点,再次注意,加入节点时判断是否时空的
class Solution {
public Node connect(Node root) {
//层次遍历
if(root == null) return root;
Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(root);
while(!q.isEmpty()){
Node temp = new Node(-1);
int len = q.size();
while(len-- > 0){
temp.next = q.poll();
temp = temp.next;
if(temp.left != null) q.add(temp.left);
if(temp.right != null) q.add(temp.right);
}
temp.next = null;
}
return root;
}
}
二叉树的右视图
bfs :将每次循环得到的每层的最后一个add上
class Solution {
public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return res;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if (node.left != null) {
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.offer(node.right);
}
if (i == size - 1) { //将当前层的最后一个节点放入结果列表
res.add(node.val);
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
dfs
用一个数记录深度,非常精妙
class Solution {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root, 0); // 从根节点开始访问,根节点深度是0
return res;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root, int depth) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
// 先访问 当前节点,再递归地访问 右子树 和 左子树。
if (depth == res.size()) { // 如果当前节点所在深度还没有出现在res里,说明在该深度下当前节点是第一个被访问的节点,因此将当前节点加入res中。
res.add(root.val);
}
depth++;
dfs(root.right, depth);
dfs(root.left, depth);
}
}
二叉树的序列化与反序列化
反序列化的时候 的
- 使用一个队列来存储父节点
- 遍历数组,添加为上一个父节点的左右孩子节点。放完右边的孩子节点的时候更新父节点。
public class Codec {
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
public String serialize(TreeNode root) {
//tree: [v1,v2,null,...]
//node: ,
//val: str(val)
//null: "null"
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder("[");
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList();
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode cur = queue.remove();
if(cur == null){
res.append("null,");
}else{
res.append(cur.val + ",");
queue.add(cur.left);
queue.add(cur.right);
}
}
res.setLength(res.length() - 1);
res.append("]");
return res.toString();
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
public TreeNode deserialize(String data) {
String[] nodes = data.substring(1, data.length()-1).split(",");
TreeNode root = getNode(nodes[0]);
Queue<TreeNode> parents = new LinkedList();
TreeNode parent = root;
boolean isLeft = true;
int i = 1;
while(i < nodes.length){
parent.left = getNode(nodes[i++]);
if(parent.left != null) parents.add(parent.left);
if(i < nodes.length){
parent.right = getNode(nodes[i++]);
if(parent.right != null) parents.add(parent.right);
parent = parents.poll();
}
}
return root;
}
private TreeNode getNode(String val){
if(val.equals("null")){
return null;
}
return new TreeNode(Integer.valueOf(val));
}
}
前中后序遍历
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ \
4 5 6
- 层次遍历顺序:[1 2 3 4 5 6]
- 前序遍历顺序:[1 2 4 5 3 6]
- 中序遍历顺序:[4 2 5 1 3 6]
- 后序遍历顺序:[4 5 2 6 3 1]
层次遍历使用 BFS 实现,利用的就是 BFS 一层一层遍历的特性;而前序、中序、后序遍历利用了 DFS 实现。
前序、中序、后序遍只是在对节点访问的顺序有一点不同,其它都相同。
① 前序
void dfs(TreeNode root) {
visit(root);
dfs(root.left);
dfs(root.right);
}
② 中序
void dfs(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root.left);
visit(root);
dfs(root.right);
}
③ 后序
void dfs(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root.left);
dfs(root.right);
visit(root);
}
1. 非递归实现二叉树的前序遍历
144. Binary Tree Preorder Traversal (Medium)
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> ret = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
if (node == null) continue;
ret.add(node.val);
stack.push(node.right); // 先右后左,保证左子树先遍历
stack.push(node.left);
}
return ret;
}
2. 非递归实现二叉树的后序遍历
145. Binary Tree Postorder Traversal (Medium)
前序遍历为 root -> left -> right,后序遍历为 left -> right -> root。可以修改前序遍历成为 root -> right -> left,那么这个顺序就和后序遍历正好相反。
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> ret = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
if (node == null) continue;
ret.add(node.val);
stack.push(node.left);
stack.push(node.right);
}
Collections.reverse(ret);
return ret;
}
3. 非递归实现二叉树的中序遍历
94. Binary Tree Inorder Traversal (Medium)
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> ret = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return ret;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (cur != null) {
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
ret.add(node.val);
cur = node.right;
}
return ret;
}
返回二叉搜索树的第k小的值
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
//中序遍历,找到第k个值
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
inorder(root, res);
return res.get(k-1);
}
private void inorder(TreeNode root, ArrayList<Integer> res) {
if(root == null) return;
inorder(root.left,res);
res.add(root.val);
inorder(root.right,res);
}
}
可以只使用一个值记录,并且进行剪枝
class Solution {
int n = 0;
int res = 0;
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
//中序遍历,找到第k个值
inorder(root, k);
return res;
}
private void inorder(TreeNode root, int k) {
if(root == null || n > k) return;
inorder(root.left,k);
n++;
if(n==k) res = root.val;
inorder(root.right,k);
}
}
迭代写法
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
//使用一个栈
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
int n = 0;
int res = 0;
tage:while(true){
while(root != null){
//把左边都压入栈
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stack.pop();
if(--k == 0) return root.val;
root = root.right;
}
}
}
这篇的遍历讲的非常好
https://www.jianshu.com/p/456af5480cee
二叉树的堂兄弟节点
- 使用两个map,一个存储节点和深度,另一个存储节点的父亲。
- 千万要注意,层数是从上向下数的,千万不能从叶子节点开始计算。
class Solution {
Map<Integer,TreeNode> panret = new HashMap<>();
Map<Integer,Integer> depth = new HashMap<>();
public boolean isCousins(TreeNode root, int x, int y) {
if(root == null) return false;
dfs(root, 0);
if(depth.get(x) == depth.get(y) && panret.get(x) != panret.get(y)){
return true;
}
return false;
}
private int dfs(TreeNode root, int d) {
if(root == null) return 0;
if(root.left != null);
int l = dfs(root.left, d + 1);
int r = dfs(root.right, d + 1);
if(root.left != null){
panret.put(root.left.val, root);
}
if(root.right != null){
panret.put(root.right.val, root);
}
depth.put(root.val, d);
return d + 1;
}
}
BST
二叉查找树(BST):根节点大于等于左子树所有节点,小于等于右子树所有节点。
二叉查找树中序遍历有序。
1. 修剪二叉查找树
669. Trim a Binary Search Tree (Easy)
Input:
3
/ \
0 4
\
2
/
1
L = 1
R = 3
Output:
3
/
2
/
1
题目描述:只保留值在 L ~ R 之间的节点
public TreeNode trimBST(TreeNode root, int L, int R) {
if (root == null) return null;
if (root.val > R) return trimBST(root.left, L, R);
if (root.val < L) return trimBST(root.right, L, R);
root.left = trimBST(root.left, L, R);
root.right = trimBST(root.right, L, R);
return root;
}
2. 寻找二叉查找树的第 k 个元素
230. Kth Smallest Element in a BST (Medium)
中序遍历解法:
private int cnt = 0;
private int val;
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
inOrder(root, k);
return val;
}
private void inOrder(TreeNode node, int k) {
if (node == null) return;
inOrder(node.left, k);
cnt++;
if (cnt == k) {
val = node.val;
return;
}
inOrder(node.right, k);
}
递归解法:
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
int leftCnt = count(root.left);
if (leftCnt == k - 1) return root.val;
if (leftCnt > k - 1) return kthSmallest(root.left, k);
return kthSmallest(root.right, k - leftCnt - 1);
}
private int count(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) return 0;
return 1 + count(node.left) + count(node.right);
}
3. 把二叉查找树每个节点的值都加上比它大的节点的值
Convert BST to Greater Tree (Easy)
Input: The root of a Binary Search Tree like this:
5
/ \
2 13
Output: The root of a Greater Tree like this:
18
/ \
20 13
先遍历右子树。
private int sum = 0;
public TreeNode convertBST(TreeNode root) {
traver(root);
return root;
}
private void traver(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) return;
traver(node.right);
sum += node.val;
node.val = sum;
traver(node.left);
}
4. 二叉查找树的最近公共祖先
235. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Search Tree (Easy)
_______6______
/ \
___2__ ___8__
/ \ / \
0 4 7 9
/ \
3 5
For example, the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of nodes 2 and 8 is 6. Another example is LCA of nodes 2 and 4 is 2, since a node can be a descendant of itself according to the LCA definition.
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (root.val > p.val && root.val > q.val) return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
if (root.val < p.val && root.val < q.val) return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
return root;
}
5. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
236. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree (Medium)
_______3______
/ \
___5__ ___1__
/ \ / \
6 2 0 8
/ \
7 4
For example, the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of nodes 5 and 1 is 3. Another example is LCA of nodes 5 and 4 is 5, since a node can be a descendant of itself according to the LCA definition.
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (root == null || root == p || root == q) return root;
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
return left == null ? right : right == null ? left : root;
}
6. 从有序数组中构造二叉查找树
108. Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree (Easy)
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
return toBST(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
private TreeNode toBST(int[] nums, int sIdx, int eIdx){
if (sIdx > eIdx) return null;
int mIdx = (sIdx + eIdx) / 2;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(nums[mIdx]);
root.left = toBST(nums, sIdx, mIdx - 1);
root.right = toBST(nums, mIdx + 1, eIdx);
return root;
}
7. 根据有序链表构造平衡的二叉查找树
109. Convert Sorted List to Binary Search Tree (Medium)
Given the sorted linked list: [-10,-3,0,5,9],
One possible answer is: [0,-3,9,-10,null,5], which represents the following height balanced BST:
0
/ \
-3 9
/ /
-10 5
public TreeNode sortedListToBST(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) return null;
if (head.next == null) return new TreeNode(head.val);
ListNode preMid = preMid(head);
ListNode mid = preMid.next;
preMid.next = null; // 断开链表
TreeNode t = new TreeNode(mid.val);
t.left = sortedListToBST(head);
t.right = sortedListToBST(mid.next);
return t;
}
private ListNode preMid(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head, fast = head.next;
ListNode pre = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
pre = slow;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return pre;
}
8. 在二叉查找树中寻找两个节点,使它们的和为一个给定值
653. Two Sum IV - Input is a BST (Easy)
Input:
5
/ \
3 6
/ \ \
2 4 7
Target = 9
Output: True
使用中序遍历得到有序数组之后,再利用双指针对数组进行查找。
应该注意到,这一题不能用分别在左右子树两部分来处理这种思想,因为两个待求的节点可能分别在左右子树中。
public boolean findTarget(TreeNode root, int k) {
List<Integer> nums = new ArrayList<>();
inOrder(root, nums);
int i = 0, j = nums.size() - 1;
while (i < j) {
int sum = nums.get(i) + nums.get(j);
if (sum == k) return true;
if (sum < k) i++;
else j--;
}
return false;
}
private void inOrder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> nums) {
if (root == null) return;
inOrder(root.left, nums);
nums.add(root.val);
inOrder(root.right, nums);
}
9. 在二叉查找树中查找两个节点之差的最小绝对值
530. Minimum Absolute Difference in BST (Easy)
Input:
1
\
3
/
2
Output:
1
利用二叉查找树的中序遍历为有序的性质,计算中序遍历中临近的两个节点之差的绝对值,取最小值。
private int minDiff = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
private TreeNode preNode = null;
public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {
inOrder(root);
return minDiff;
}
private void inOrder(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) return;
inOrder(node.left);
if (preNode != null) minDiff = Math.min(minDiff, node.val - preNode.val);
preNode = node;
inOrder(node.right);
}
10. 寻找二叉查找树中出现次数最多的值
501. Find Mode in Binary Search Tree (Easy)
1
\
2
/
2
return [2].
答案可能不止一个,也就是有多个值出现的次数一样多。
private int curCnt = 1;
private int maxCnt = 1;
private TreeNode preNode = null;
public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> maxCntNums = new ArrayList<>();
inOrder(root, maxCntNums);
int[] ret = new int[maxCntNums.size()];
int idx = 0;
for (int num : maxCntNums) {
ret[idx++] = num;
}
return ret;
}
private void inOrder(TreeNode node, List<Integer> nums) {
if (node == null) return;
inOrder(node.left, nums);
if (preNode != null) {
if (preNode.val == node.val) curCnt++;
else curCnt = 1;
}
if (curCnt > maxCnt) {
maxCnt = curCnt;
nums.clear();
nums.add(node.val);
} else if (curCnt == maxCnt) {
nums.add(node.val);
}
preNode = node;
inOrder(node.right, nums);
}
Trie
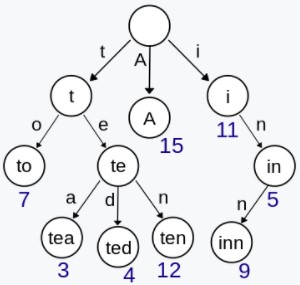
Trie,又称前缀树或字典树,用于判断字符串是否存在或者是否具有某种字符串前缀。
1. 实现一个 Trie
208. Implement Trie (Prefix Tree) (Medium)
class Trie {
private class Node {
Node[] childs = new Node[26];
boolean isLeaf;
}
private Node root = new Node();
public Trie() {
}
public void insert(String word) {
insert(word, root);
}
private void insert(String word, Node node) {
if (node == null) return;
if (word.length() == 0) {
node.isLeaf = true;
return;
}
int index = indexForChar(word.charAt(0));
if (node.childs[index] == null) {
node.childs[index] = new Node();
}
insert(word.substring(1), node.childs[index]);
}
public boolean search(String word) {
return search(word, root);
}
private boolean search(String word, Node node) {
if (node == null) return false;
if (word.length() == 0) return node.isLeaf;
int index = indexForChar(word.charAt(0));
return search(word.substring(1), node.childs[index]);
}
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
return startWith(prefix, root);
}
private boolean startWith(String prefix, Node node) {
if (node == null) return false;
if (prefix.length() == 0) return true;
int index = indexForChar(prefix.charAt(0));
return startWith(prefix.substring(1), node.childs[index]);
}
private int indexForChar(char c) {
return c - 'a';
}
}
2. 实现一个 Trie,用来求前缀和
677. Map Sum Pairs (Medium)
Input: insert("apple", 3), Output: Null
Input: sum("ap"), Output: 3
Input: insert("app", 2), Output: Null
Input: sum("ap"), Output: 5
class MapSum {
private class Node {
Node[] child = new Node[26];
int value;
}
private Node root = new Node();
public MapSum() {
}
public void insert(String key, int val) {
insert(key, root, val);
}
private void insert(String key, Node node, int val) {
if (node == null) return;
if (key.length() == 0) {
node.value = val;
return;
}
int index = indexForChar(key.charAt(0));
if (node.child[index] == null) {
node.child[index] = new Node();
}
insert(key.substring(1), node.child[index], val);
}
public int sum(String prefix) {
return sum(prefix, root);
}
private int sum(String prefix, Node node) {
if (node == null) return 0;
if (prefix.length() != 0) {
int index = indexForChar(prefix.charAt(0));
return sum(prefix.substring(1), node.child[index]);
}
int sum = node.value;
for (Node child : node.child) {
sum += sum(prefix, child);
}
return sum;
}
private int indexForChar(char c) {
return c - 'a';
}
}
树的变体:三角形
树的结构问题
大多会用上递归,因为树具有高度的自相似性
class Solution {
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return 0;
return countNodes(root.left) + countNodes(root.right) + 1;
}
}
路径问题
递归三要素:
- 返回值为void,res在参数中传递
- 终止:遇到叶子节点时终止并且将结果放入结果集res
- 当前层不利用上一层的结果。
还要注意:
暂时结果放在path中,在非叶子节点的每一层都会继续调用递归函数两次,两次中的path应相同,如果path使用了stringBuilder就不行,第一次调用的结果会影响第二次调用的
我开始图简单了, 下面的做法不对,会产生重复值,因为遇到null返回而不是遇到叶子节点返回就会将叶子节点
class Solution {
public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
helper(root, res, new String());
return res;
}
private void helper(TreeNode root, List<String> res, String path) {
if(root == null) {
res.add(path.substring(0, path.length()-2));
return;
}
path += root.val;
path += "->";
helper(root.left, res, path);
helper(root.right, res, path);
}
}
正确的结果应该是在叶子节点而不是null中添加到结果集。
class Solution {
public void construct_paths(TreeNode root, String path, LinkedList<String> paths) {
if (root != null) {
path += Integer.toString(root.val);
if ((root.left == null) && (root.right == null)) // 当前节点是叶子节点
paths.add(path); // 把路径加入到答案中
else {
path += "->"; // 当前节点不是叶子节点,继续递归遍历
construct_paths(root.left, path, paths);
construct_paths(root.right, path, paths);
}
}
}
public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
LinkedList<String> paths = new LinkedList();
construct_paths(root, "", paths);
return paths;
}
}
作者:LeetCode
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-paths/solution/er-cha-shu-de-suo-you-lu-jing-by-leetcode/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
二叉搜索树
二叉搜索树的公共祖先
235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
思路很简单但是容易想复杂了。
递归方法略
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
int pVal = p.val;
int qVal = q.val;
while(root != null){
int rVal = root.val;
if(rVal > pVal && rVal > qVal){
root = root.left;
}
else if(rVal < pVal && rVal < qVal){
root = root.right;
}
else {
return root;
}
}
return null;
}
}
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root == null || root == p || root==q) return root;
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
if(left == null && right==null){
return null;
}
if(left==null) return right; //说明下一级递归中的root不是null;
if(right==null) return left;
return root;
}
}
$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$图
二分图
如果可以用两种颜色对图中的节点进行着色,并且保证相邻的节点颜色不同,那么这个图就是二分图。
1. 判断是否为二分图
785. Is Graph Bipartite? (Medium)
Input: [[1,3], [0,2], [1,3], [0,2]]
Output: true
Explanation:
The graph looks like this:
0----1
| |
| |
3----2
We can divide the vertices into two groups: {0, 2} and {1, 3}.
Example 2:
Input: [[1,2,3], [0,2], [0,1,3], [0,2]]
Output: false
Explanation:
The graph looks like this:
0----1
| \ |
| \ |
3----2
We cannot find a way to divide the set of nodes into two independent subsets.
public boolean isBipartite(int[][] graph) {
int[] colors = new int[graph.length];
Arrays.fill(colors, -1);
for (int i = 0; i < graph.length; i++) { // 处理图不是连通的情况
if (colors[i] == -1 && !isBipartite(i, 0, colors, graph)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
private boolean isBipartite(int curNode, int curColor, int[] colors, int[][] graph) {
if (colors[curNode] != -1) {
return colors[curNode] == curColor;
}
colors[curNode] = curColor;
for (int nextNode : graph[curNode]) {
if (!isBipartite(nextNode, 1 - curColor, colors, graph)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
拓扑排序
常用于在具有先序关系的任务规划中。
1. 课程安排的合法性
207. Course Schedule (Medium)
2, [[1,0]]
return true
2, [[1,0],[0,1]]
return false
题目描述:一个课程可能会先修课程,判断给定的先修课程规定是否合法。
本题不需要使用拓扑排序,只需要检测有向图是否存在环即可。
public boolean canFinish(int numCourses, int[][] prerequisites) {
List<Integer>[] graphic = new List[numCourses];
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
graphic[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
for (int[] pre : prerequisites) {
graphic[pre[0]].add(pre[1]);
}
boolean[] globalMarked = new boolean[numCourses];
boolean[] localMarked = new boolean[numCourses];
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
if (hasCycle(globalMarked, localMarked, graphic, i)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
private boolean hasCycle(boolean[] globalMarked, boolean[] localMarked,
List<Integer>[] graphic, int curNode) {
if (localMarked[curNode]) {
return true;
}
if (globalMarked[curNode]) {
return false;
}
globalMarked[curNode] = true; //全局记录
localMarked[curNode] = true;
for (int nextNode : graphic[curNode]) {
if (hasCycle(globalMarked, localMarked, graphic, nextNode)) {
return true;
}
}
localMarked[curNode] = false;
return false;
}
更简洁的方法,使用拓扑排序
class Solution {
public boolean canFinish(int numCourses, int[][] prerequisites) {
List<List<Integer>> adj = new ArrayList<>();
int[] indegree = new int[numCourses];
Deque<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
adj.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
for (int i = 0; i < prerequisites.length; i++) {
adj.get(prerequisites[i][1]).add(prerequisites[i][0]);
indegree[prerequisites[i][0]]++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
if (indegree[i] == 0) q.add(i);
}
while(!q.isEmpty()){
//弹出这门课
int t = q.poll();
numCourses--;
for(Integer next: adj.get(t)){
if(--indegree[next] == 0) q.add(next);
}
}
return numCourses==0;
}
}
2. 课程安排的顺序
210. Course Schedule II (Medium)
4, [[1,0],[2,0],[3,1],[3,2]]
There are a total of 4 courses to take. To take course 3 you should have finished both courses 1 and 2. Both courses 1 and 2 should be taken after you finished course 0. So one correct course order is [0,1,2,3]. Another correct ordering is [0,2,1,3].
使用 DFS 来实现拓扑排序,使用一个栈存储后序遍历结果,这个栈的逆序结果就是拓扑排序结果。
证明:对于任何先序关系:v->w,后序遍历结果可以保证 w 先进入栈中,因此栈的逆序结果中 v 会在 w 之前。
class Solution {
public int[] findOrder(int numCourses, int[][] prerequisites) {
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> graph = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < prerequisites.length; i++) {
List<Integer> pre = graph.getOrDefault(prerequisites[i][0], new ArrayList<Integer>());
pre.add(prerequisites[i][1]);
graph.put(prerequisites[i][0], pre);
}
List<Integer> res = new LinkedList<>();
Set<Integer> tempMemo = new HashSet<>();
Set<Integer> visited = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
if(visited.contains(i)) continue;
if(!graph.containsKey(i)){
res.add(i);
visited.add(i);
continue;
}
if(!dfs(graph, res, tempMemo, visited, i)){
return new int[0];
}
}
int[] ans = new int[numCourses];
for (int j = 0; j < numCourses; j++) {
ans[j] = res.get(j);
}
return ans;
}
private boolean dfs(Map<Integer, List<Integer>> graph, List<Integer> res, Set<Integer> tempMemo, Set<Integer> visited, int i) {
if (tempMemo.contains(i)) return false;
if (visited.contains(i)) return true;
//已访问这个
tempMemo.add(i);
for(Integer pre : graph.getOrDefault(i, new ArrayList<>())){
if(!dfs(graph, res, tempMemo, visited, pre)){
return false;
}
}
res.add(i);
visited.add(i);
tempMemo.remove(i);
return true;
}
}
public int[] findOrder(int numCourses, int[][] prerequisites) {
List<Integer>[] graphic = new List[numCourses];
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
graphic[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
for (int[] pre : prerequisites) {
graphic[pre[0]].add(pre[1]);
}
Stack<Integer> postOrder = new Stack<>();
boolean[] globalMarked = new boolean[numCourses];
boolean[] localMarked = new boolean[numCourses];
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
if (hasCycle(globalMarked, localMarked, graphic, i, postOrder)) {
return new int[0];
}
}
int[] orders = new int[numCourses];
for (int i = numCourses - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
orders[i] = postOrder.pop();
}
return orders;
}
private boolean hasCycle(boolean[] globalMarked, boolean[] localMarked, List<Integer>[] graphic, int curNode, Stack<Integer> postOrder) {
if (localMarked[curNode]) {
return true;
}
if (globalMarked[curNode]) {
return false;
}
globalMarked[curNode] = true;
localMarked[curNode] = true;
for (int nextNode : graphic[curNode]) {
if (hasCycle(globalMarked, localMarked, graphic, nextNode, postOrder)) {
return true;
}
}
localMarked[curNode] = false;
postOrder.push(curNode);
return false;
}
并查集
并查集可以动态地连通两个点,并且可以非常快速地判断两个点是否连通。
1. 冗余连接
684. Redundant Connection (Medium)
Input: [[1,2], [1,3], [2,3]]
Output: [2,3]
Explanation: The given undirected graph will be like this:
1
/ \
2 - 3
题目描述:有一系列的边连成的图,找出一条边,移除它之后该图能够成为一棵树。
public int[] findRedundantConnection(int[][] edges) {
int N = edges.length;
UF uf = new UF(N);
for (int[] e : edges) {
int u = e[0], v = e[1];
if (uf.connect(u, v)) {
return e;
}
uf.union(u, v);
}
return new int[]{-1, -1};
}
private class UF {
private int[] id;
UF(int N) {
id = new int[N + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < id.length; i++) {
id[i] = i;
}
}
void union(int u, int v) {
int uID = find(u);
int vID = find(v);
if (uID == vID) {
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < id.length; i++) {
if (id[i] == uID) {
id[i] = vID;
}
}
}
int find(int p) {
return id[p];
}
boolean connect(int u, int v) {
return find(u) == find(v);
}
}






















 1287
1287

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








