题解:
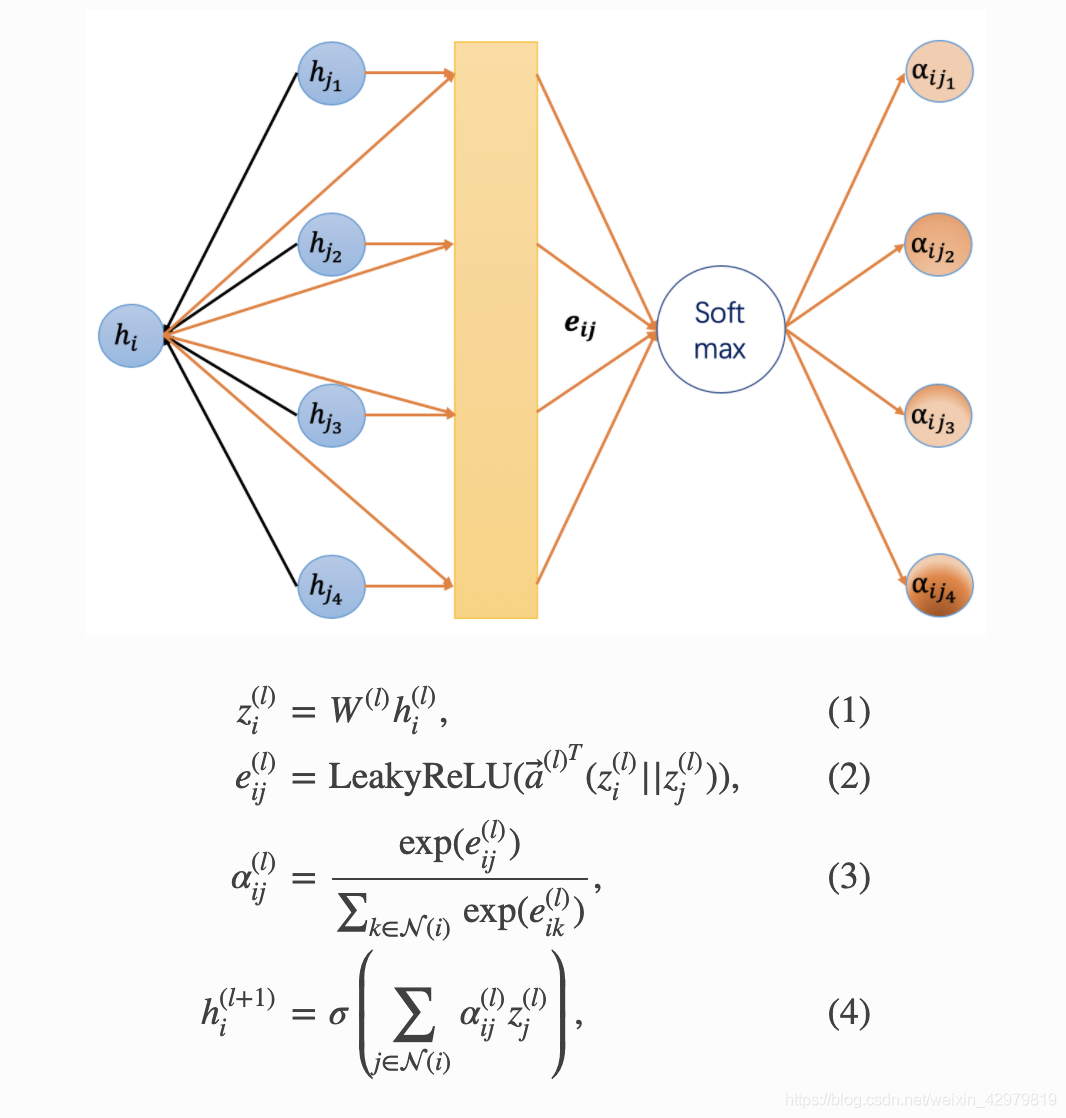
首先挂出核心公式和训练过程生成的aij注意系数
layer.py
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class GraphAttentionLayer(nn.Module):
"""
Simple GAT layer, similar to https://arxiv.org/abs/1710.10903
"""
def __init__(self, in_features, out_features, dropout, alpha, concat=True):
super(GraphAttentionLayer, self).__init__()
self.dropout = dropout #dropout 参数
self.in_features = in_features # 输入的特征
self.out_features = out_features # 输出特征
self.alpha = alpha
self.concat = concat
self.W = nn.Parameter(torch.empty(size=(in_features, out_features)))
'''
先torch.empty创建的是一个size 大小的 torch.Tensor类型 这个类型是不可训练的
然后使用Parameter命令对 原来的Parameter类型进行绑定并且转化为Parameter 类型
Parameter 是一个可训练的类型
'''
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.W.data, gain=1.414) # gain 是两种方法计算的中 a 和 std 计算的重要参数
'''
Xavier 是一种初始化的方式 pytroch 提供了uniform 和 normal 两种方式:
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(tensor, gain =1) 是均匀分布 (-a,a)
nn.init.xavier_normal_(tensor, gain=1) 正态分布~N ( 0 ,std )
https://blog.csdn.net/dss_dssssd/article/details/83959474 讲解博客地址
'''
self.a = nn.Parameter(torch.empty(size=(2*out_features, 1)))
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.a.data, gain=1.414)
'''
论文中有一个公式whi||whj
|| 是连接符号 通过这个连接,我们把两个1 X F 的矩阵变成了 一个 1 X 2F 的矩阵
然后论文中乘以了一个a 2F X 1 的矩阵 那么就得到了一个数
这个a就是论文中的那个a
而我们的得到的那个数就是我们的attention系数
'''
self.leakyrelu = nn.LeakyReLU(self.alpha)
'''
因为原式是 aij= softmax(sigmod(a (whi||whj)))
sigmod 是激活函数 这里用的是leaky ReLU 函数
'''
'''
forward 和 _prepare_attentional_mechanism_input 对应的论文 2.1环节
'''
def forward(self, h, adj): # 正向传播
Wh = torch.mm(h, self.W) # h.shape: (N, in_features), Wh.shape: (N, out_features)
# 这里是做一个乘法
a_input = self._prepare_attentional_mechanism_input(Wh)
e = self.leakyrelu(torch.matmul(a_input, self.a).squeeze(2))
zero_vec = -9e15*torch.ones_like(e)
attention = torch.where(adj > 0, e, zero_vec)
attention = F.softmax(attention, dim=1)
attention = F.dropout(attention, self.dropout, training=self.training)
h_prime = torch.matmul(attention, Wh)
if self.concat:
return F.elu(h_prime)
else:
return h_prime
def _prepare_attentional_mechanism_input(self, Wh):
N = Wh.size()[0] # number of nodes
'''
Wh size = [2708,8] 8 是标签数目
size()[0] size顾名思义是大小的意思 [] 的应用是在维度上
这里[0]代表的是在0维度
例如我们创建一个torch.rand([2, 1, 3, 3])
那么 size()[1] 就等于 1
'''
# 下面,创建了两个矩阵,它们在行中的嵌入顺序不同
# (e stands for embedding) e 是 embedding 的基础
# 这些是第一个矩阵的行 (Wh_repeated_in_chunks):
# e1, e1, ..., e1, e2, e2, ..., e2, ..., eN, eN, ..., eN
# '-------------' -> N times '-------------' -> N times '-------------' -> N times
#
# 这些是第二个矩阵的行 (Wh_repeated_alternating):
# e1, e2, ..., eN, e1, e2, ..., eN, ..., e1, e2, ..., eN
# '----------------------------------------------------' -> N times
#
Wh_repeated_in_chunks = Wh.repeat_interleave(N, dim=0)
'''
repeat_interleave(self: Tensor, repeats: _int, dim: Optional[_int]=None) 是复制函数
参数说明:
self: 传入 的数据为 tensor
repeats : 复制到几份
dim : 要复制的维度 可以设定为 0、1、2
Examples:
此处定义了一个4维tensor,要对第2个维度复制,由原来的1变为3,即将设定dim=1。
data1 = torch.rand([2, 1, 3, 3])
data2 = torch.repeat_interleave(data1, repeats=3, dim=1)
'''
Wh_repeated_alternating = Wh.repeat(N, 1)
'''
repeat 函数:
第一个参数是复制的份数
第二个参数是复制的维度是那个维度
Examples1:
data1 = np.array([[1,2,3],
[4,5,6]])
data1.repeat(2,0)
array([[1, 2, 3],
[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6],
[4, 5, 6]])
Examples2:
data1 = np.array([[1,2,3],
[4,5,6]])
data1.repeat(2,1)
array([[1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3],








 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章














 7236
7236











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








