写在前面
关于数据科学环境的建立,可以参考我的博客:
【深耕 Python】Data Science with Python 数据科学(1)环境搭建
往期数据科学博文:
【深耕 Python】Data Science with Python 数据科学(2)jupyter-lab和numpy数组
【深耕 Python】Data Science with Python 数据科学(3)Numpy 常量、函数和线性空间
【深耕 Python】Data Science with Python 数据科学(4)(书337页)练习题及解答
【深耕 Python】Data Science with Python 数据科学(5)Matplotlib可视化(1)
【深耕 Python】Data Science with Python 数据科学(6)Matplotlib可视化(2)
【深耕 Python】Data Science with Python 数据科学(7)书352页练习题
【深耕 Python】Data Science with Python 数据科学(8)pandas数据结构:Series和DataFrame
【深耕 Python】Data Science with Python 数据科学(9)书361页练习题
【深耕 Python】Data Science with Python 数据科学(10)pandas 数据处理(一)
【深耕 Python】Data Science with Python 数据科学(11)pandas 数据处理(二)
【深耕 Python】Data Science with Python 数据科学(12)pandas 数据处理(三)
代码说明: 由于实机运行的原因,可能省略了某些导入(import)语句。
本期完成书第377页的练习题,继续对诺奖得主laureates.csv文件进行分析。文件的下载、读取等预操作,见上期博文(第12期)。
Exercises(第2题非编程)
1. Confirm that Frederic Joliot-Curie, who shared the 1935 Nobel Prize for Chemistry with his wife Irene, appears in the laureates.csv dataset. Why did we miss him when we searched for “Curies” in Listing 11.15? Hint: Search for an entry with “firstname” equal to “Frederic” (making sure to include the proper accents).
Answer in Python:
import pandas as pd
nobel = pd.read_csv("laureates.csv")
print(nobel[(nobel["year"] == 1935) & (nobel["category"] == "chemistry")])
print(nobel[nobel["firstname"] == "Frédéric"])
Output:
Irene Joliot-Curie和Frederic Joliot 分享了1935年的诺贝尔化学奖。
id firstname surname ... name city country
190 193 Frédéric Joliot ... Institut du Radium Paris France
191 194 Irène Joliot-Curie ... Institut du Radium Paris France
[2 rows x 20 columns]
id firstname surname ... name city country
190 193 Frédéric Joliot ... Institut du Radium Paris France
461 463 Frédéric Passy ... NaN NaN NaN
568 573 Frédéric Mistral ... NaN NaN NaN
[3 rows x 20 columns]
Process finished with exit code 0
2. Verify that the Nobel Prize categories cited after Listing 11.16 are correct (e.g. that Frederick Sanger’s Nobel Prizes really were for Chemistry, etc.).
2022年前仅有的4位双料得主:
6 Marie Curie 2
66 John Bardeen 2
217 Linus Pauling 2
222 Frederick Sanger 2
dtype: int64
Answer (from Wikipedia):
(1). Marie Curie:
In December 1903 the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences awarded Pierre Curie, Marie Curie, and Henri Becquerel the Nobel Prize in Physics,[44] “in recognition of the extraordinary services they have rendered by their joint researches on the radiation phenomena discovered by Professor Henri Becquerel.”[23]
International recognition for her work had been growing to new heights, and the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences, overcoming opposition prompted by the Langevin scandal, honoured her a second time, with the 1911 Nobel Prize in Chemistry.[15] This award was “in recognition of her services to the advancement of chemistry by the discovery of the elements radium and polonium, by the isolation of radium and the study of the nature and compounds of this remarkable element.”[54]
(2). John Bardeen:
In 1956, John Bardeen shared the Nobel Prize in Physics with William Shockley of Semiconductor Laboratory of Beckman Instruments and Walter Brattain of Bell Telephone Laboratories “for their researches on semiconductors and their discovery of the transistor effect”.[33]
In 1972, Bardeen shared the Nobel Prize in Physics with Leon N Cooper of Brown University and John Robert Schrieffer of the University of Pennsylvania “for their jointly developed theory of superconductivity, usually called the BCS-theory”.[39] This was Bardeen’s second Nobel Prize in Physics. He became the first person to win two Nobel Prizes in the same field.[40]
(3). Linus Pauling:
1954 Nobel Prize in Chemistry.[32][190]
1962 Nobel Peace Prize.[32][190]
(4). Frederick Sanger:
Nobel Prize in Chemistry – 1958, 1980[20][30]
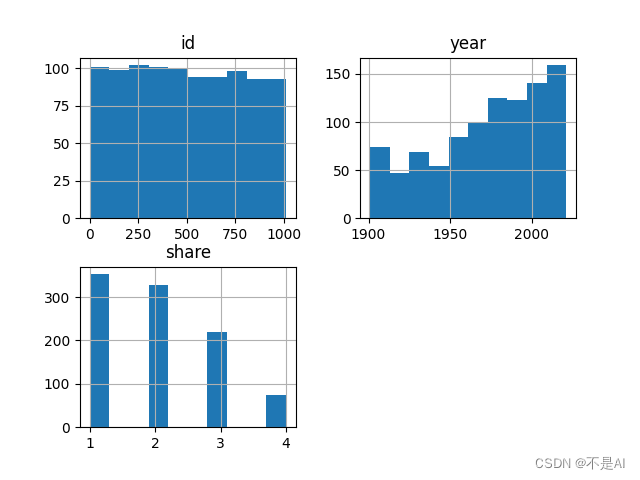
3. In Listing 11.17, what happens if you just call nobel.hist(), with no column specified?
Answer in Python:
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
nobel = pd.read_csv("laureates.csv")
nobel.hist()
plt.show()
Output Histograms:
根据id列、year列和share列进行绘图。
参考文献 Reference
《Learn Enough Python to be Dangerous——Software Development, Flask Web Apps, and Beginning Data Science with Python》, Michael Hartl, Boston, Pearson, 2023.

























 777
777

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










